To evaluate the effect of anti-TNF treatments on bone mineral density (BMD), bone remodelling markers (BRM) and receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand (RANKL) and osteoprotegerin (OPG) in patients with chronic inflammatory joint diseases.
MethodsA longitudinal prospective study was performed under clinical practice conditions on 31 patients diagnosed of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthropathy and ankylosing spondylitis who had received treatment with anti-TNF alpha drugs for one year. BMD, OPG and RANKL soluble form (sRANKL) were studied at the onset and end of the study. During the study (0, 3, 6, 9 and 12 month), disease activity (SDAI, BASDAI and CRP), functional capacity (HAQ, BASFI), BRM and vitamin D were studied.
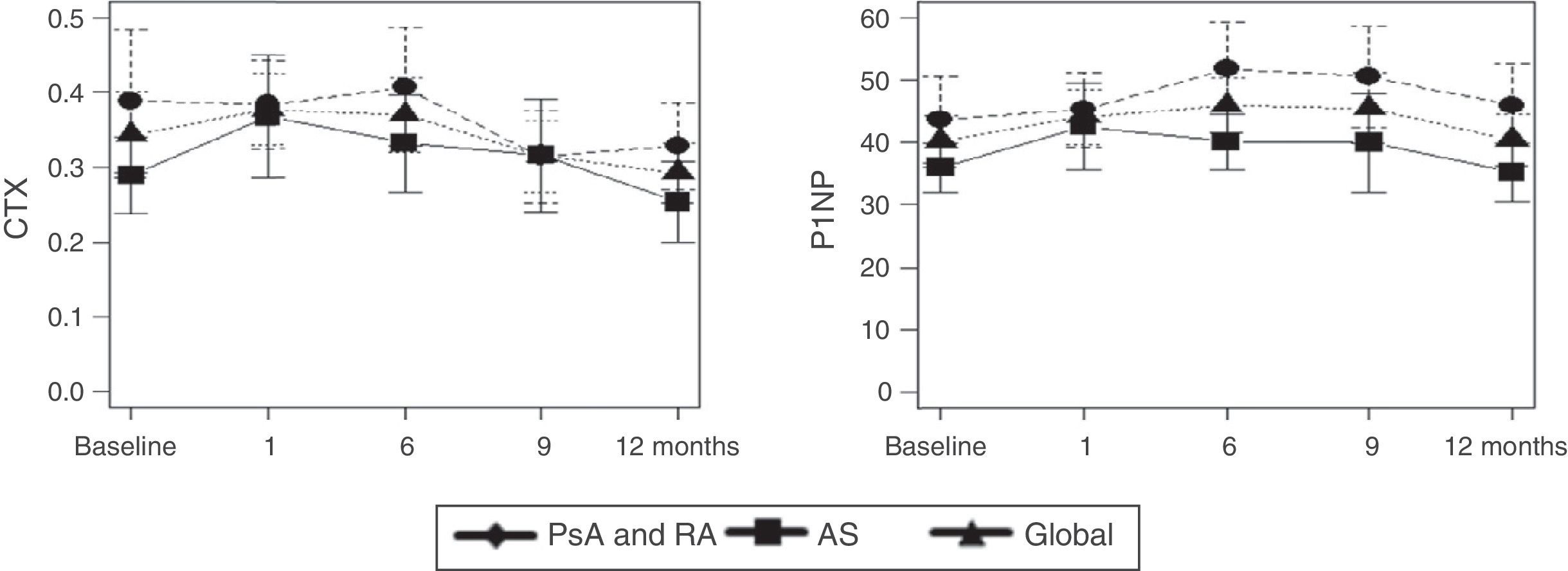
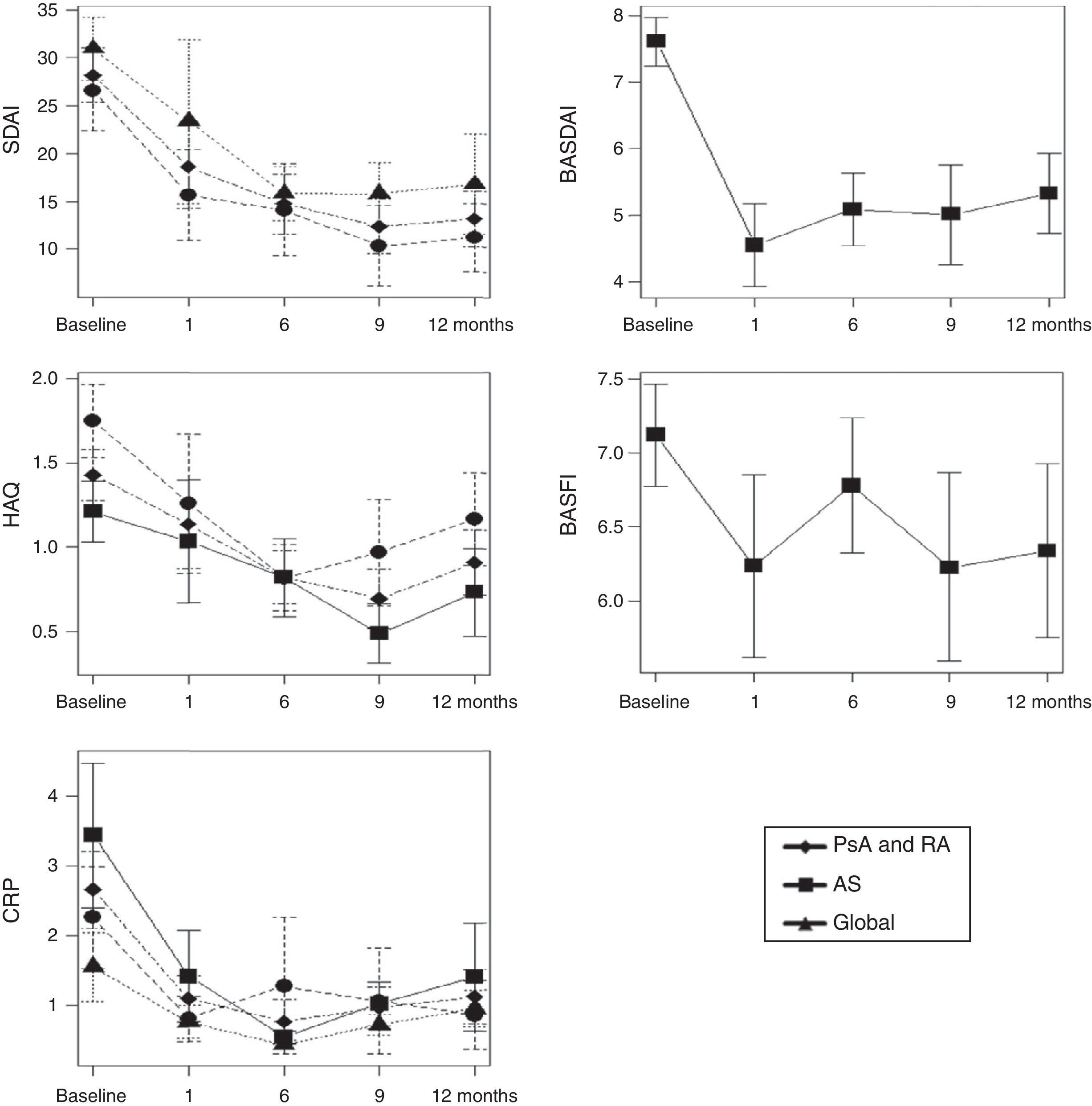
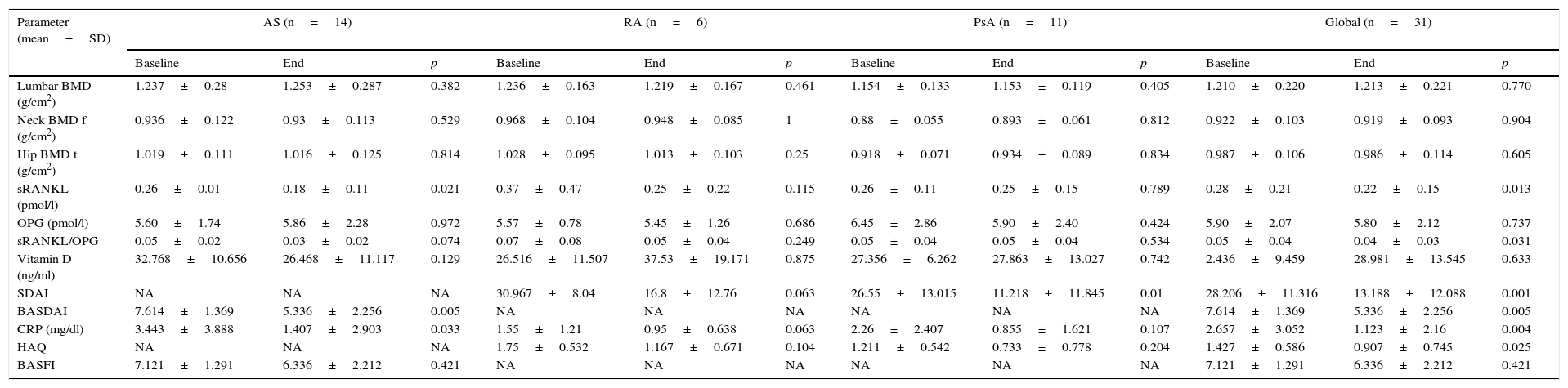
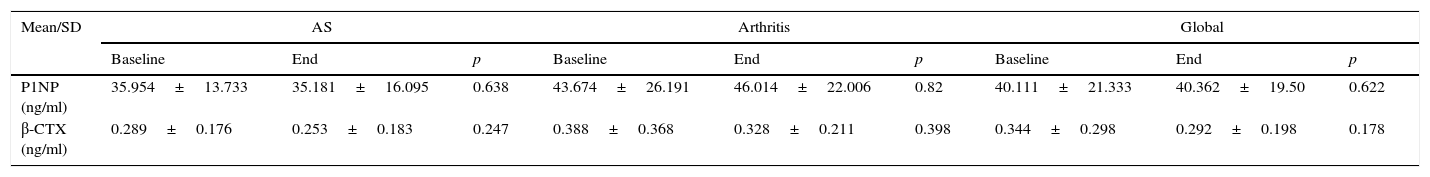
ResultsBMD was not modified after one year of treatment. The patients who took corticosteroids had a mean bone mass loss of 3% in the lumbar spine (±1.6, p=.02). In regards to the BRM, did not experience significant changes over the course of the study. Disease activity, both SDAI (p=.002) and BASDAI (p=.002), decreased. OPG was maintained without changes during the year of treatment while both the sRANKL (0.28±0.22, p=.013) and sRANKL/OPG ratio significantly decreased (0.04±0.03, p=.031).
ConclusionThe patients being treated with anti-TNF did not present with a significant loss of DMO during the study (one year), at the same time experiencing an improvement in disease activity. This protection has been clearer in the responding patients.
Evaluar el efecto de los tratamientos anti-TNF sobre la densidad mineral ósea (DMO), los marcadores de remodelado óseo (MRO) y la ratio receptor activator for nuclear factor κB ligand (RANKL, «ligando del receptor activador del factor nuclear κB»)/osteoprotegerina (OPG) en los pacientes con enfermedades inflamatorias articulares crónicas.
MétodosEstudio longitudinal prospectivo en condiciones de práctica clínica sobre 31 pacientes diagnosticados de artritis reumatoide, artropatía psoriásica y espondilitis anquilosante que estuvieron durante un año en tratamiento con fármacos anti-TNF alfa. Al inicio y al final del estudio se evaluaron la DMO, la OPG y la forma soluble de RANKL (sRANKL), y durante el estudio (0, 3, 6, 9 y 12 meses), la actividad de la enfermedad (SDAI, BASDAI y PCR), la capacidad funcional (HAQ, BASFI), los MRO y la vitamina D.
ResultadosLa DMO no se modificó después de un año de tratamiento. Los pacientes que consumieron corticoides tuvieron una pérdida media de masa ósea del 3% en el raquis lumbar (±1,6, p=0,02). En cuanto a los MRO, no experimentaron cambios significativos a lo largo del estudio. Disminuyó la actividad de la enfermedad, tanto SDAI (p=0,002) como BASDAI (p=0,002). La OPG se mantuvo sin cambios durante el año de tratamiento, mientras que disminuyeron significativamente tanto el sRANKL (0,28±0,22, p=0,013) como la ratio sRANKL/OPG (0,04±0,03, p=0,031).
ConclusiónLos pacientes en tratamiento con anti-TNF no presentaron una pérdida de DMO significativa durante el seguimiento (un año), a la vez que experimentaron una mejora de la actividad de la enfermedad. Estos resultados han sido más evidentes en los pacientes respondedores.