Dyslipidaemia is a common comorbidity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Patients and methodsFifty-one patients were included. Variables associated with the disease and the drugs used were recorded. Atherogenic risk was calculated. Chi square was used for categorical variables. ANOVA was performed and a logistic regression model to determine the association of the variables with the presence of dyslipidaemia.
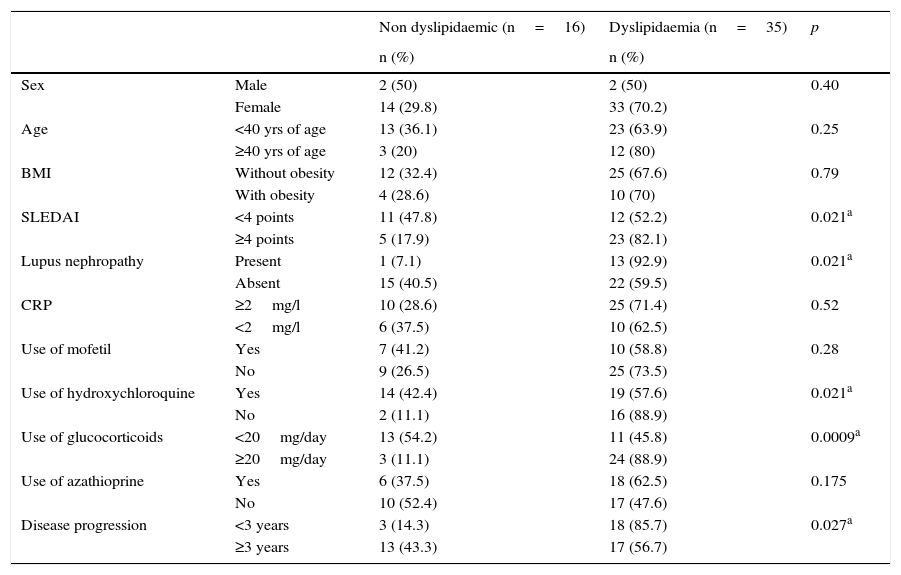
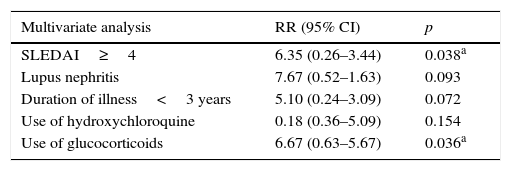
ResultsA percentage of 68.6 had dyslipidaemia. A significant difference between the presence of dyslipidaemia and activity index measured by SLEDAI was found, the presence of lupus nephritis, use of prednisone ≥20mg/day, evolution of the disease <3 years. Significance between the absence of dyslipidaemia and use of hydroxychloroquine was found. SLEDAI ≥4 and the use of prednisone ≥20mg/day were independently associated with the presence of dyslipidaemia. The average of Castelli rate was 5.02, the Kannel index was 2.97 and triglyceride/HDL-C ratio was 5.24.
ConclusionsPatients with systemic lupus erythematosus have a high prevalence of dyslipidaemia and a high atherogenic rate, which increases cardiovascular risk significantly.
La dislipidemia es una comorbilidad frecuente en los pacientes con lupus eritematoso sistémico.
Pacientes y métodosSe incluyeron 51 pacientes. Se registraron variables asociadas a la enfermedad y los fármacos empleados. Se calculó el riesgo aterogénico. Se empleó la prueba de Chi cuadrado para las variables categóricas. Se realizó ANOVA y un modelo de regresión logística para determinar la asociación de las variables con la presencia de dislipidemia.
ResultadosEl 68,6% presentó dislipidemia. Se encontró diferencia significativa entre la presencia de dislipidemia y el índice de actividad medido por SLEDAI, la presencia de nefropatía lúpica, el uso de prednisona≥20mg/día, la evolución de la enfermedad<3 años y entre la ausencia de dislipidemia y el empleo de hidroxicloroquina. SLEDAI≥4 y el uso de prednisona≥20mg/día se asociaron independientemente con la presencia de dislipidemia. La media del índice de Castelli fue de 5,02, la del de Kannel fue de 2,97 y la de triglicéridos/c-HDL fue de 5,24.
ConclusionesLos pacientes con lupus eritematoso sistémico presentan una gran prevalencia de dislipidemia y un alto índice aterogénico, lo cual aumenta el riesgo cardiovascular.