To describe the prevalence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in type 1 diabetes (T1DM) and to compare it with that observed in type 2 diabetes (T2DM) and normal population in Spain.
Patients and methodsCross-sectional study (18–70 years-old). Information on CVD was available from a nurse-administered questionnaire (Di@bet.es Study, NORMAL=3430, T2DM=312) and from a physician reporting form (T1DM=1382). Differences in the crude and adjusted prevalence of coronary heart (CHD), cerebrovascular (CNSD), peripheral vascular (PVD) and overall CV (CVD) disease were investigated between T1DM vs. NORMAL, and T1DM vs. T2DM groups.
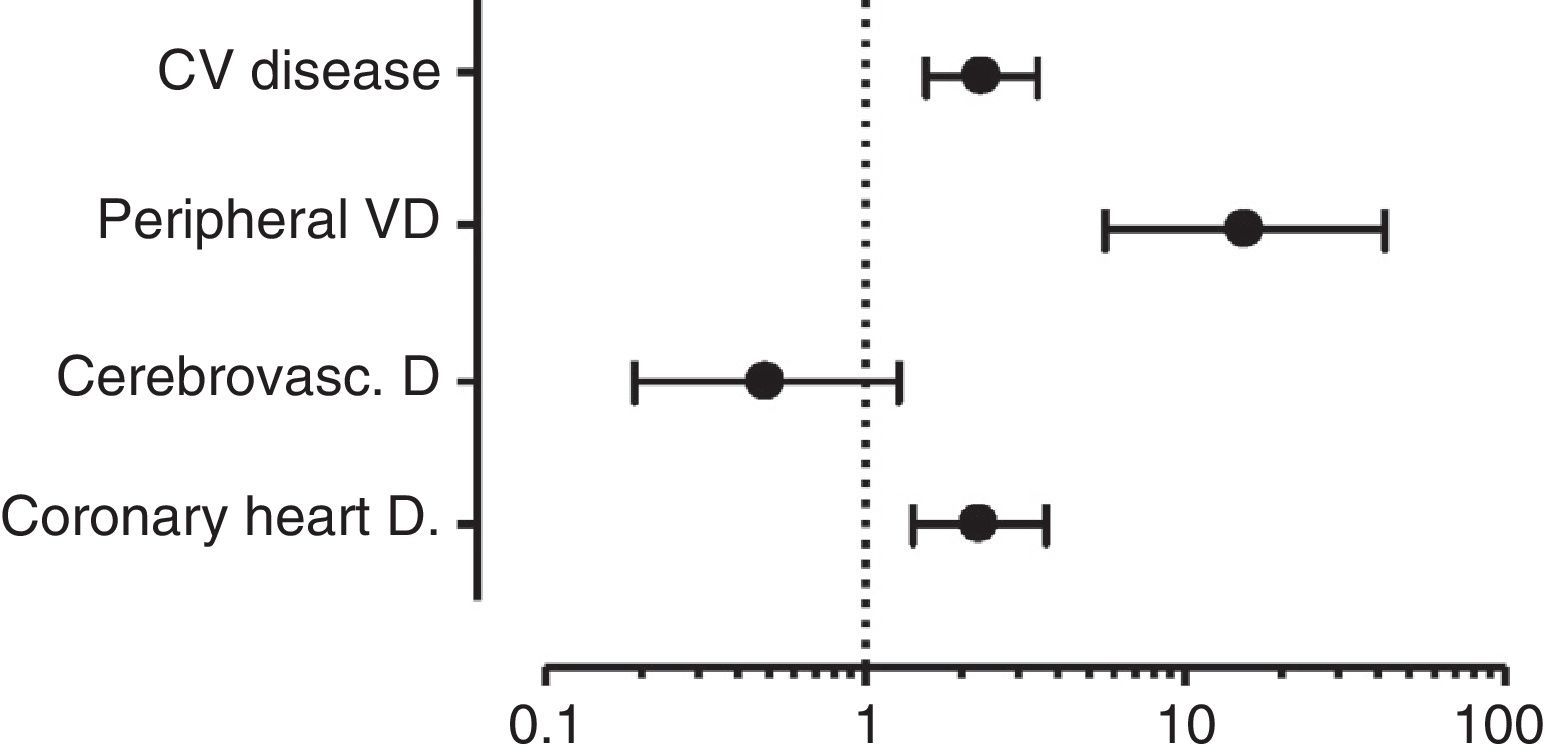
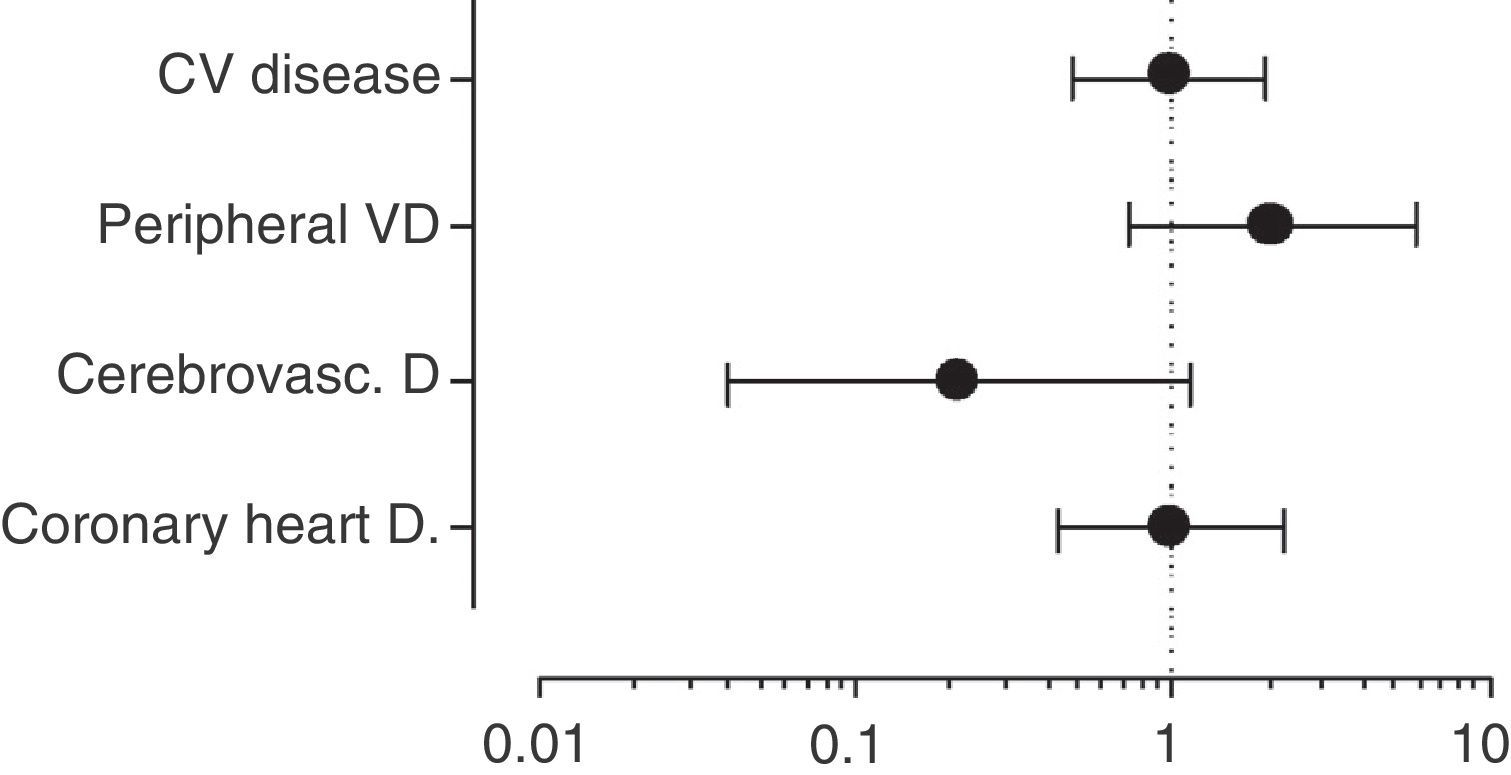
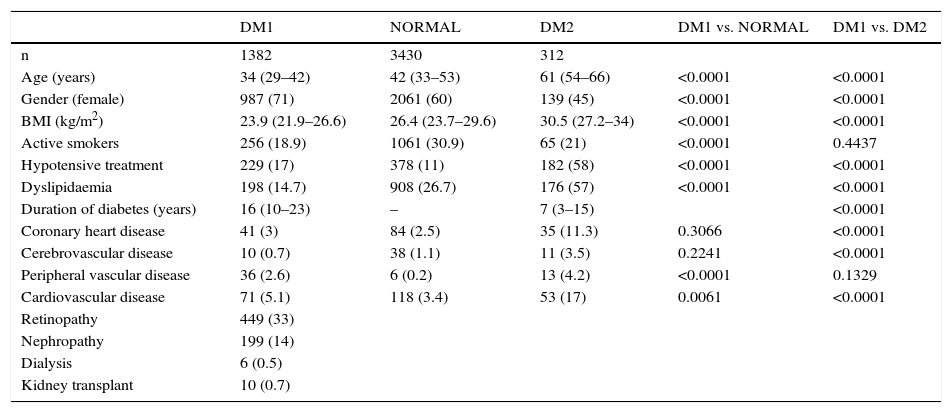
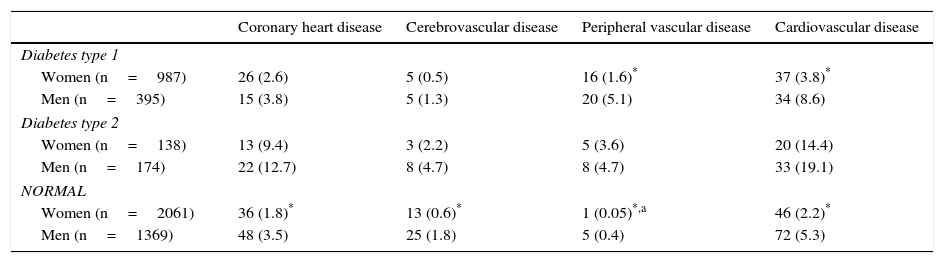
ResultsWe found differences in age, body mass index, proportion of women, dyslipemia and antihypertensive medication between T1DM vs. NORMAL and T1DM vs. T2DM (all p<.001). Smoking prevalence was not different between T1DM vs. T2DM and it was lower in T1DM compared to NORMAL (p<.0001). The percentage of CHD, CNSD, PVD, and overall CVD in T1DM vs. NORMAL was 3.0 vs. 2.5 (p=.31), 0.70 vs. 1.10 (p=.22), 2.61 vs. 0.20 (p<.0001), and 5.1 vs. 3.44 (p<.01), respectively. The prevalence in T2DM (vs. T1DM) was 11.3 (p<.0001), 3.5 (p<.0001), 4.2 (p=.13), and 17% (p<.0001), respectively. Multiple logistic regression adjusted models showed a higher prevalence of CHD (odds ratio [OR] 2.27, 95% confidence interval [95% CI] 1.41–3.67), PVD (OR 15.35, 95% CI 5.61–42.04), and overall CVD (OR 2.32, 95% CI 1.55–3.46), but not for CNSD (OR 0.49, 95% CI 0.19–1.27) in T1DM compared to NORMAL. No differences were found between T1DM and T2DM.
ConclusionsWe found a higher prevalence of CVD in a Mediterranean population of T1DM individuals compared with non-diabetic subjects. This prevalence was similar to that observed in T2DM.
Describir la prevalencia de enfermedad cardiovascular (ECV) en la diabetes mellitus tipo 1 (DM1) y compararla con la observada en personas con diabetes tipo 2 (DM2) o sin ella, en España.
Pacientes y métodoEstudio transversal en sujetos de edad comprendida entre 18-70 años. La prevalencia de ECV se obtuvo mediante un cuestionario dirigido por una enfermera (Estudio Di@bet.es, NORMAL=3.430, DM2=312) o un registro cumplimentado por médicos (DM1=1.382). Se evaluaron las diferencias no ajustadas y ajustadas de enfermedad coronaria (EC), cerebrovascular (ECEV), vascular periférica (EVP), y ECV global de DM1 frente a NORMAL y DM1 frente a DM2.
ResultadosHubo diferencias en edad, índice de masa corporal, porcentaje de mujeres, dislipidemia y tratamiento hipotensor entre DM1 frente a NORMAL y DM1 frente a DM2 (todos p<0,001). El tabaquismo fue similar entre DM1 y DM2, y menor en DM1 frente a NORMAL (p<0,0001). El porcentaje de EC, ECEV, EVP y ECV global en DM1 frente a NORMAL fue de 3,0 frente a 2,5 (p=0,31), 0,70 frente a 1,10 (p=0,22), 2,61 frente a 0,20 (p<0,0001) y 5,10 frente a 3,44 (p<0,01), respectivamente. El porcentaje en DM2 (frente a DM1) fue de 11,3 (p<0,0001), 3,5 (p<0,0001), 4,2 (p=0,13) y 17% (p<0,0001), respectivamente. La regresión logística múltiple ajustada mostró una mayor prevalencia de EC (odds ratio [OR] 2,27, intervalo de confianza del 95% [IC 95%] 1,41–3,67), EVP (OR 15,35, IC 95% 5,61–42,04), y ECV global (OR 2,32, IC 95% 1,55–3,46), pero no de ECEV (OR 0,49, IC 95% 0,19–1,27) en DM1 frente a NORMAL. No encontramos diferencias entre DM1 y DM2.
ConclusionesLos pacientes con DM1 de un área mediterránea presentan mayor prevalencia de ECV que una población control, y similar prevalencia que pacientes con DM2 tras ajustar por factores de confusión.