Implantable cardiac defibrillator (ICD) has been established as a therapy for malignant ventricular arrhythmias in patients at high risk of suffering them.
Some studies suggest a possible relationship between the development of cancer and some prosthetic materials. Likewise, some investigations describe a higher incidence of cancer in patients with an ICD that suggest a potential relationship.
MethodsRetrospective cohort study of patients that underwent implantation of an ICD in the Complejo Hospitalario de Navarra between 2000 and 2016. The follow-up finished in June 2018.
Sociodemographic, comorbidities and oncological data was analysed. Cancer incidence rates were estimated and compared with the general population data and with data of a cohort of patients with reduced LVEF heart failure. Risk of cancer models were adjusted by competitive risk models.
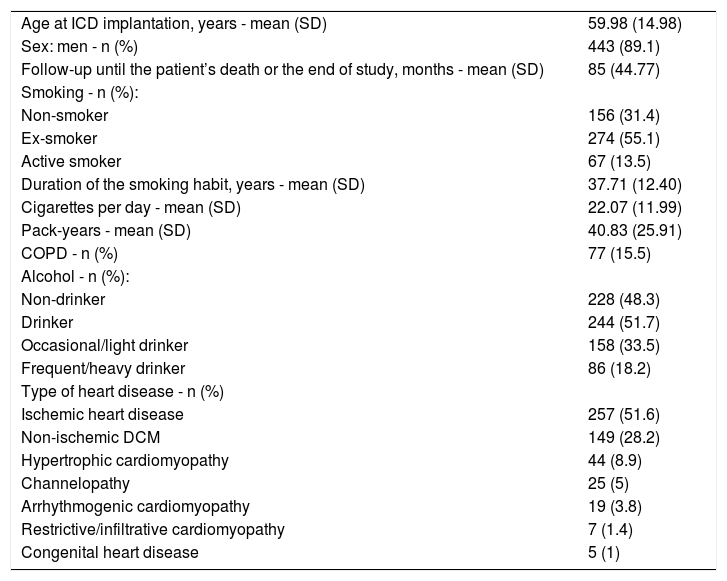
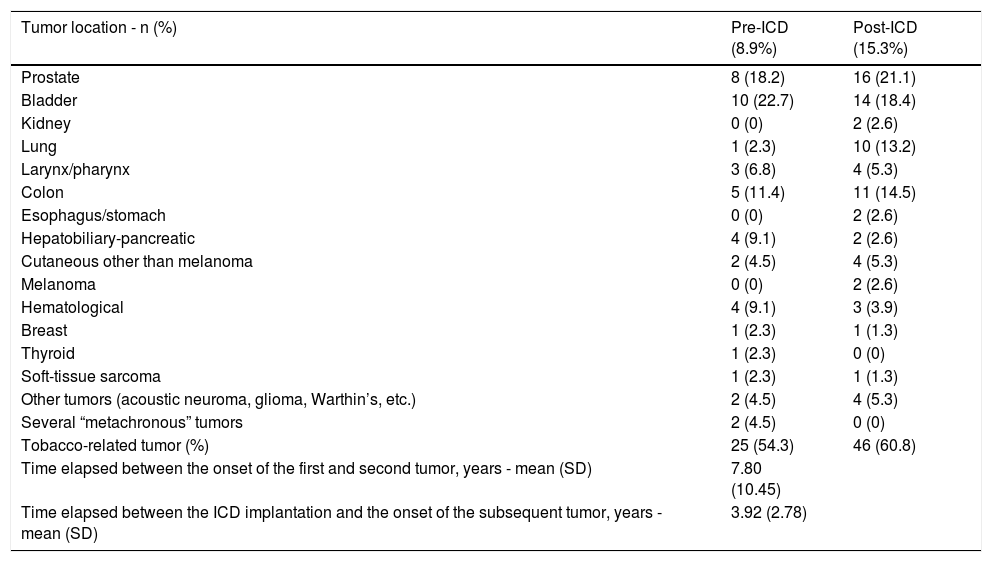
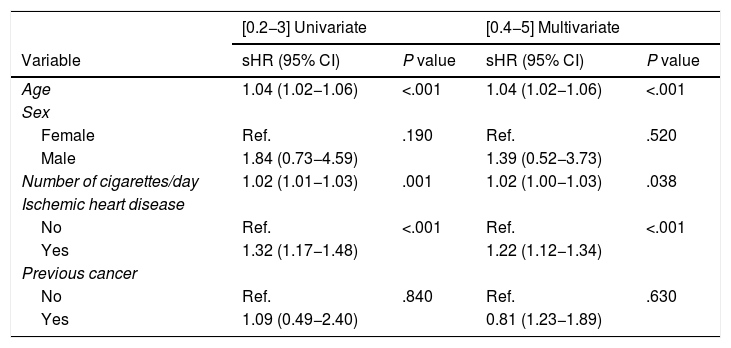
Results497 patients were included, mostly male (89.1%), with a mean age of 59.98 (14.98) years and a proportion of smokers of 67.6% and of ischaemic heart disease of 51.6%. The cancer incidence rate in the sample was 1230.9 per 100.000 person-year. In our study, features associated with cancer were older age, higher tobacco use and ischaemic cardiopathy.
ConclusionsIn our sample of ICD carriers the incidence of cancer is high. This finding mainly seems to be related to tobacco usage and higher age.
El desfibrilador automático implantable (DAI) se ha establecido como terapia en pacientes con elevado riesgo de sufrir arritmias ventriculares malignas.
Algunos estudios plantean un posible efecto oncogénico de materiales protésicos utilizados. Igualmente, existen trabajos que describen mayor incidencia de cáncer en portadores de DAI y plantean una potencial relación causal entre ambos.
El objetivo principal del estudio es describir la incidencia de cáncer en nuestra muestra de pacientes portadores de DAI y compararla con resultados de otras bases de datos.
MétodosEstudio de cohortes retrospectivo de pacientes con DAI que se incluyeron en el Complejo Hospitalario de Navarra entre los años 2000 y 2016 y se siguieron hasta junio de 2018.
Se analizaron variables sociodemográficas, comorbilidades y datos sobre patología oncológica.
Se estimaron tasas de incidencia acumulada (TIA) de cáncer durante el seguimiento que se compararon con datos poblacionales y con datos de otra cohorte de pacientes con insuficiencia cardiaca con FEVI reducida. Se ajustaron modelos de riesgos competitivos para cáncer en el seguimiento.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 497 pacientes, mayoritariamente hombres (89,1%) con una edad media de 59,98 (14,98) años, con una proporción de fumadores del 67,6% y de cardiopatía isquémica del 51,6%. La TIA de cáncer fue 1230,9 por 100.000 personas-año. Las variables que se asociaron significativamente con cáncer fueron mayor edad, mayor consumo de tabaco y cardiopatía isquémica.
ConclusionesLa incidencia de cáncer es elevada en pacientes con DAI. Este hallazgo parece relacionado principalmente con el tabaco y la mayor edad.