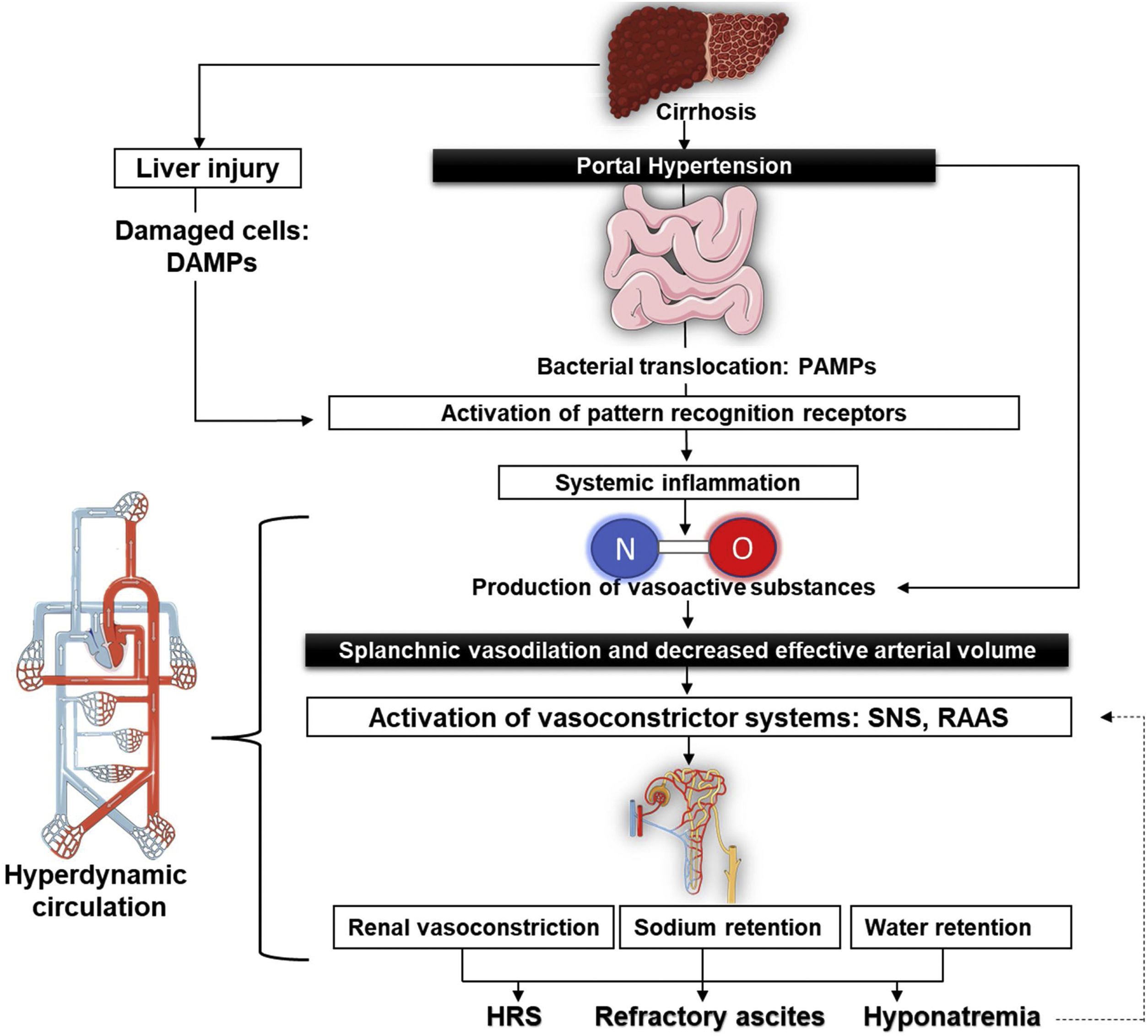
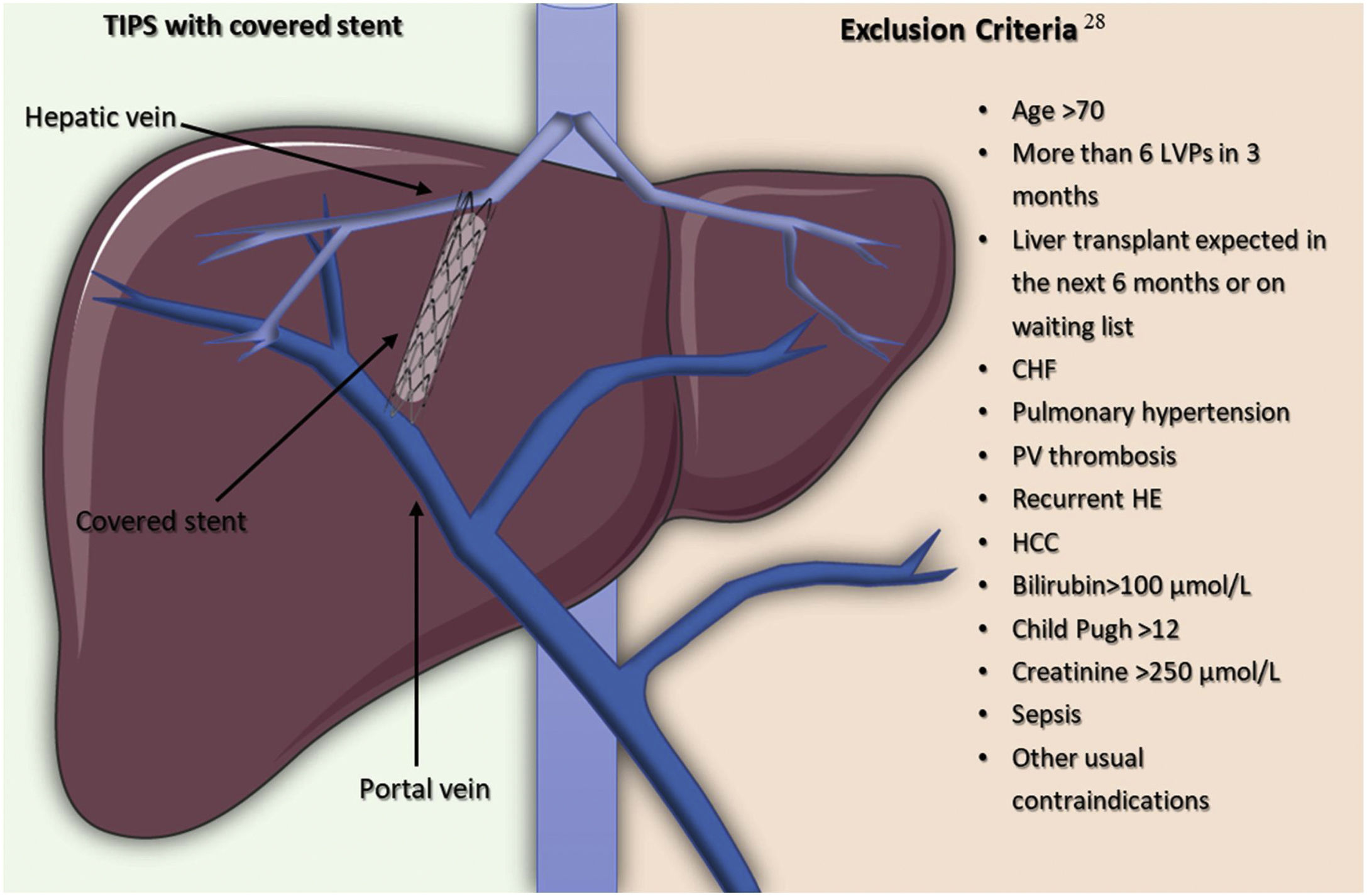
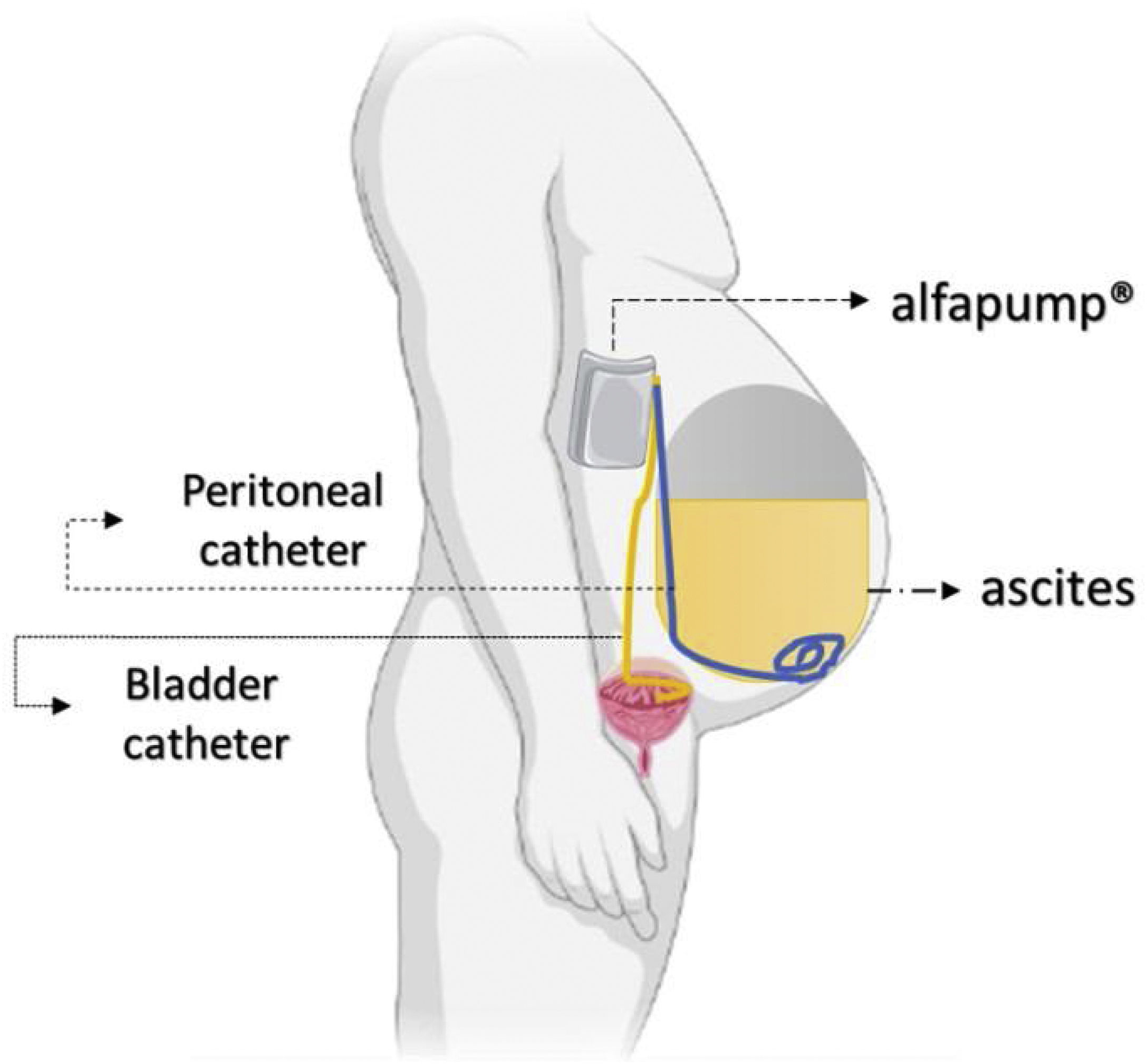
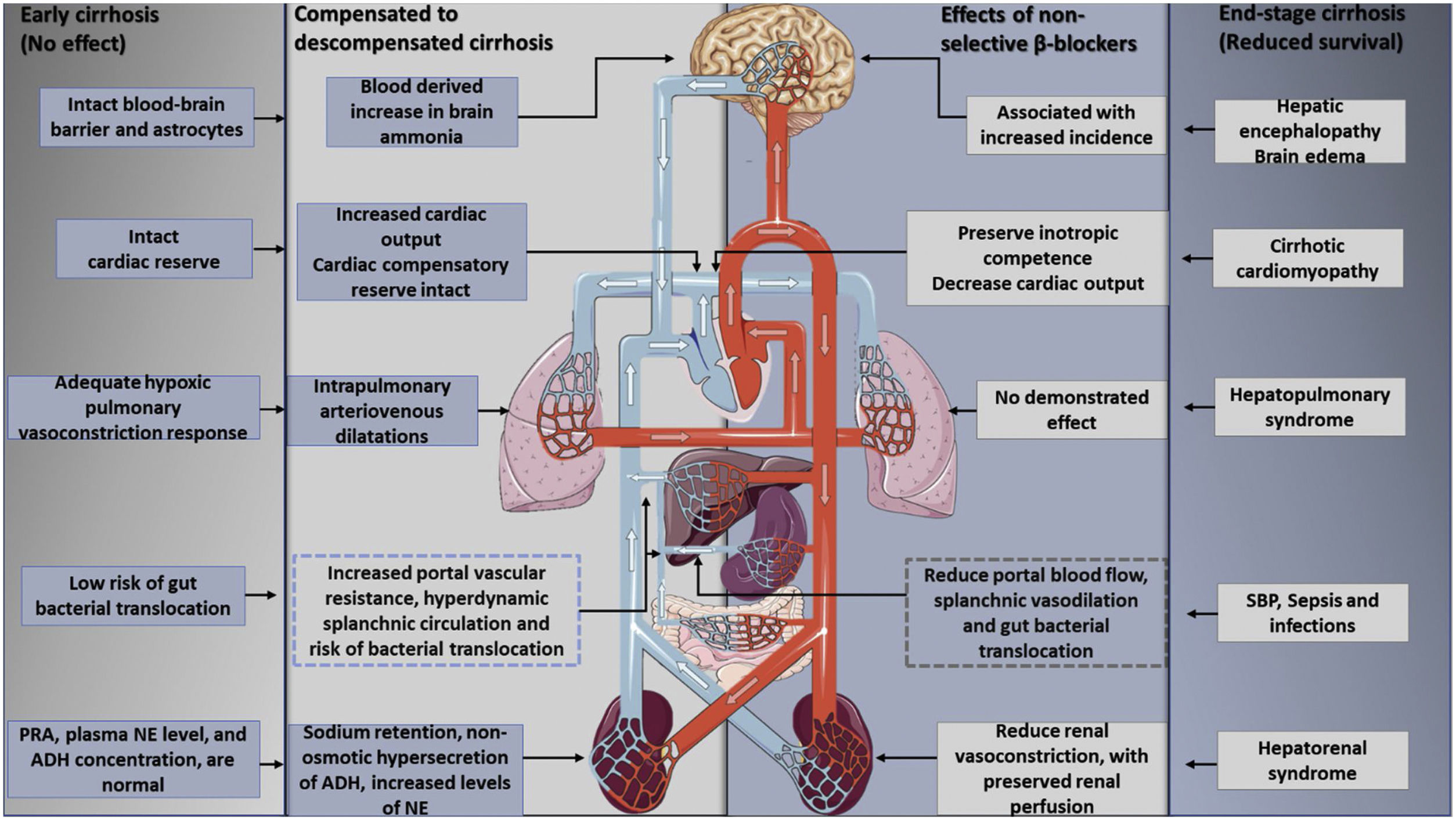
Ascites is the fluid accumulation in the peritoneal cavity, and it is the consequence of a wide variety of entities, being liver cirrhosis the most common one. In this kind of patients, the development of ascites results from splanchnic vasodilation; decreased effective circulating volume; the activation of the sympathetic nervous system and the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system; and a systemic inflammatory process. Its management is diverse and depends on the severity of the hemodynamic disturbance and other clinical manifestations. In recent years, therapeutic strategies have been developed, but they tend to result unconventional, so new evidence demonstrates the advantages of non-selective beta-blockers for the survival rate of patients with end-stage cirrhosis and ascites.
La ascitis es la acumulación de líquido en la cavidad peritoneal, y es consecuencia de una amplia variedad de entidades, siendo la cirrosis la más frecuente. En este tipo de pacientes, el desarrollo de ascitis resulta de la vasodilatación esplácnica, el volumen circulante efectivo disminuido, la activación del sistema nervioso simpático y el sistema renina-angiotensina-aldosterona, así como un proceso inflamatorio sistémico. Su tratamiento es diverso, y depende de la gravedad de la alteración hemodinámica y otras manifestaciones clínicas. En años recientes se han desarrollado estrategias terapéuticas poco convencionales, así como nueva evidencia demuestra los beneficios de los betabloqueadores no selectivos en la tasa de supervivencia de los pacientes con cirrosis en etapa terminal y ascitis.