Estudiar la relación entre la espasticidad de la extremidad superior, la función motora gruesa, la habilidad manual y la funcionalidad en las actividades de la vida diaria (AVD).
Material y métodosEstudio descriptivo transversal. En una muestra de 8 niños/as con parálisis cerebral se midió la espasticidad en la musculatura flexora de codo y muñeca a través de la escala Ashworth modificada, la función motora gruesa con la Clasificación de la Función Motora Gruesa, la habilidad manual con la Clasificación de Habilidad Manual y el funcionamiento en las AVD con la escala de habilidades funcionales del Inventario para la Evaluación Pediátrica de la Discapacidad (PEDI).
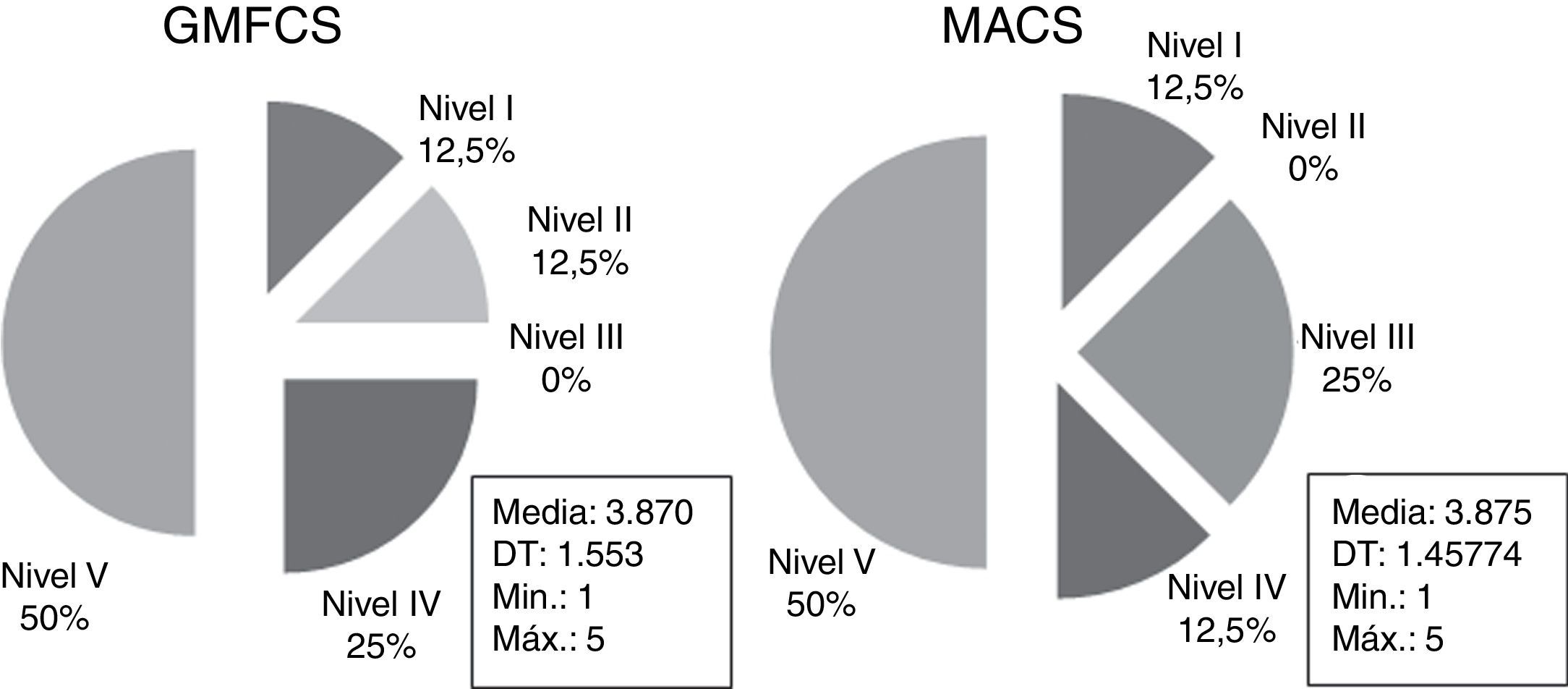
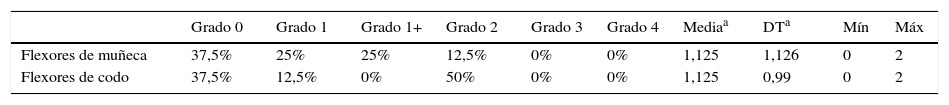
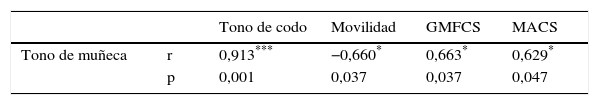
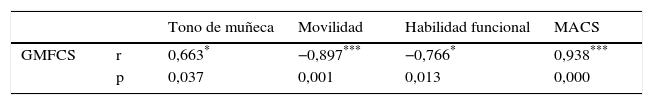
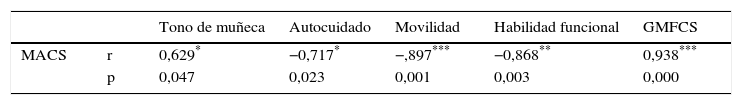
ResultadosLos resultados muestran que el tono de los músculos flexores de la muñeca se correlaciona con el tono de los flexores de codo, con el dominio de movilidad del PEDI, la función motora gruesa y la habilidad manual. Por otro lado, los flexores de codo no guardaron relación con ninguna de las variables estudiadas.
ConclusiónEl aumento de tono en los flexores de muñeca es clave de cara a definir el funcionamiento del niño en las AVD, en su capacidad motora gruesa y su habilidad manual. Sin embargo, el tono de los flexores de codo no ha mostrado su relación con ninguna de las variables estudiadas.
To study the relationship between upper limb spasticity, gross motor function, manual ability and functionality in activities of daily living (ADLs).
Material and methodsDescriptive, observational and cross-sectional study. The spasticity in elbow and wrist flexor musculature was measured through the Modified Ashworth Scale, the gross motor function with the Gross Motor Function Classification System, the manual ability with the Manual ability Classification System and the activity and participation in the ADLs with the functional scales of the Pediatric Evaluation of Disability Inventory (PEDI), in sample of eight children with Cerebral Palsy.
ResultsThe results show that the spasticity in the wrist's flexor muscles is correlated with the spasticity of the elbow's flexors, with the PEDI's mobility domain, the gross motor function and the manual ability. On the other side, elbow's flexors do not keep any connection with any of the studied variables.
ConclusionsThe increased spasticity in the wrist's flexors is crucial in order to define the child's functioning in the AVDs, in his gross motor capacity and in his manual ability. However, the spasticity in the elbow's flexors does not show any relation with any of the studied variables.
Artículo
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".