El envejecimiento implica una reducción de la masa muscular y la fuerza muscular. El objetivo del estudio fue valorar la efectividad de un protocolo de ejercicios específicos de facilitación neuromuscular propioceptiva (FNP) sobre la fuerza muscular respiratoria.
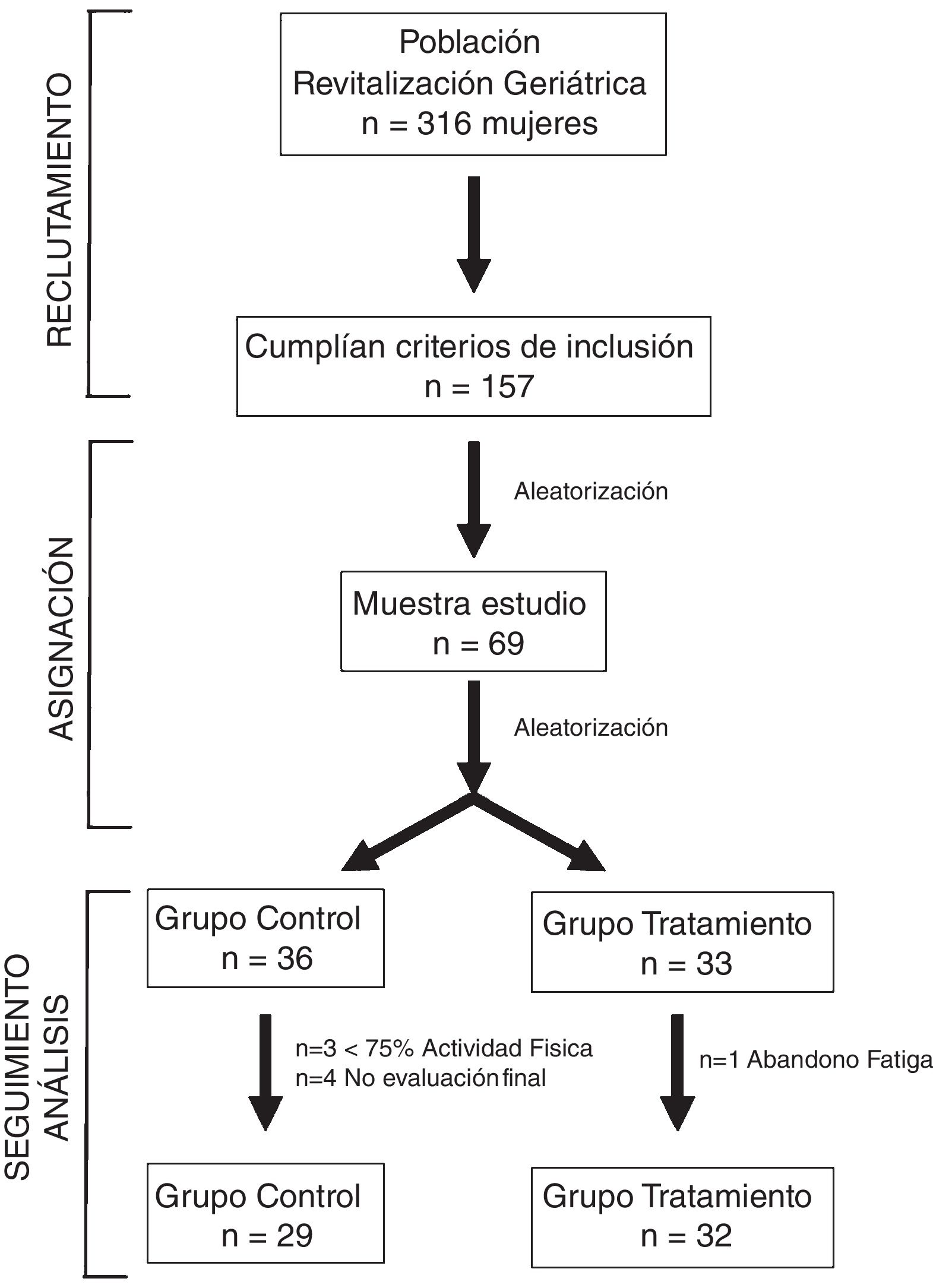
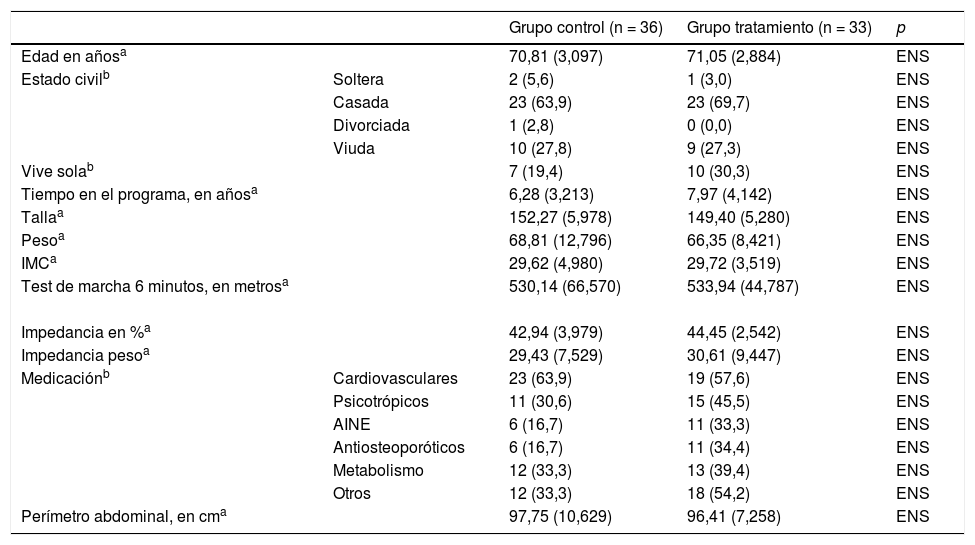
Material y métodoEstudio experimental con 69 mujeres mayores no institucionalizadas y voluntarias participantes en un programa de ejercicio físico. Fueron divididas aleatorizadamente en 2grupos. El grupo intervención recibió un protocolo de tratamiento respiratorio específico basado en metodología de la FNP con 2 sesiones semanales de 50 min durante 8 semanas. El grupo control no recibió intervención adicional. Se evaluó la fuerza de la musculatura respiratoria mediante la presión inspiratoria máxima (PIM) y la presión espiratoria máxima (PEM).
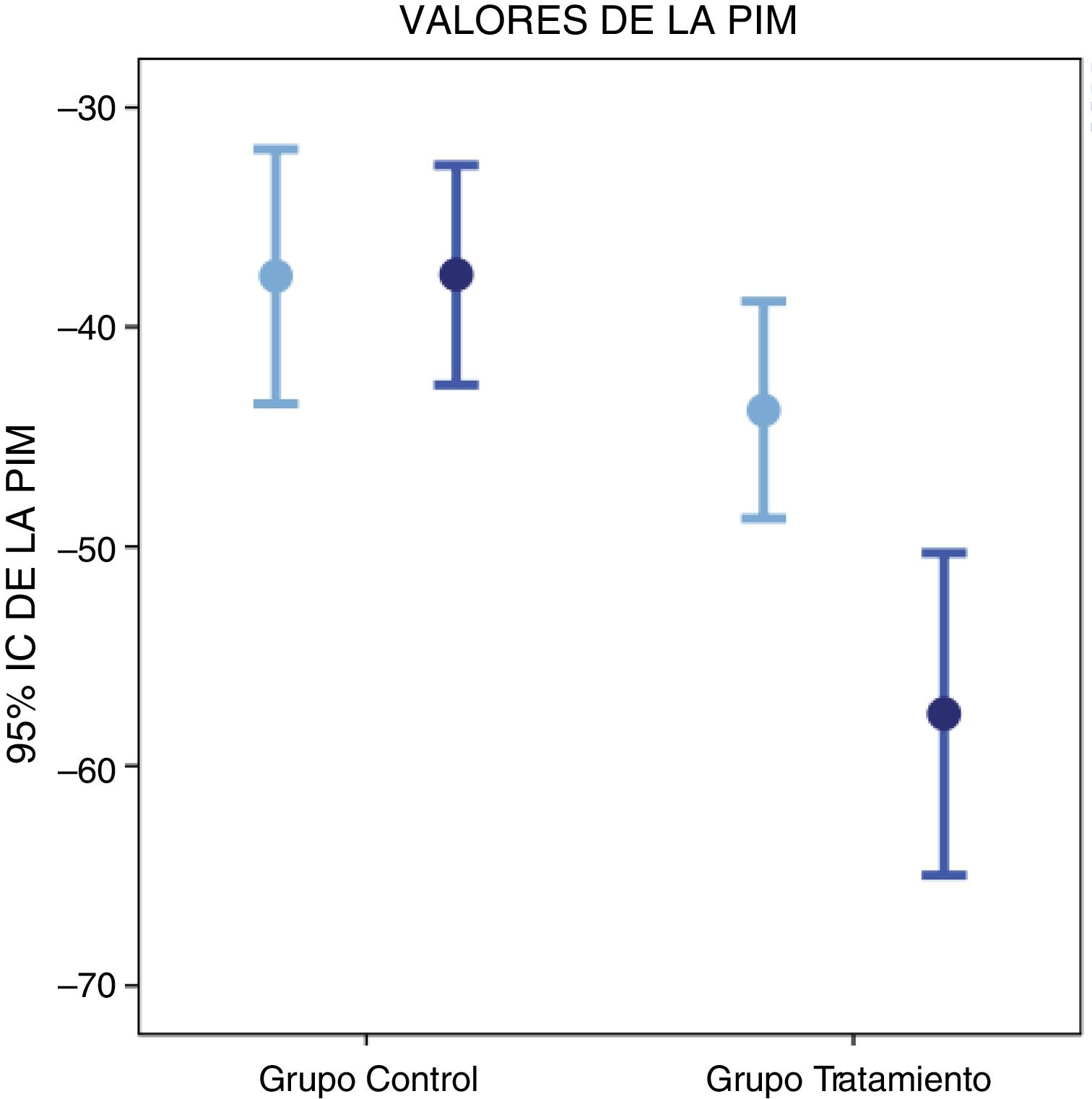
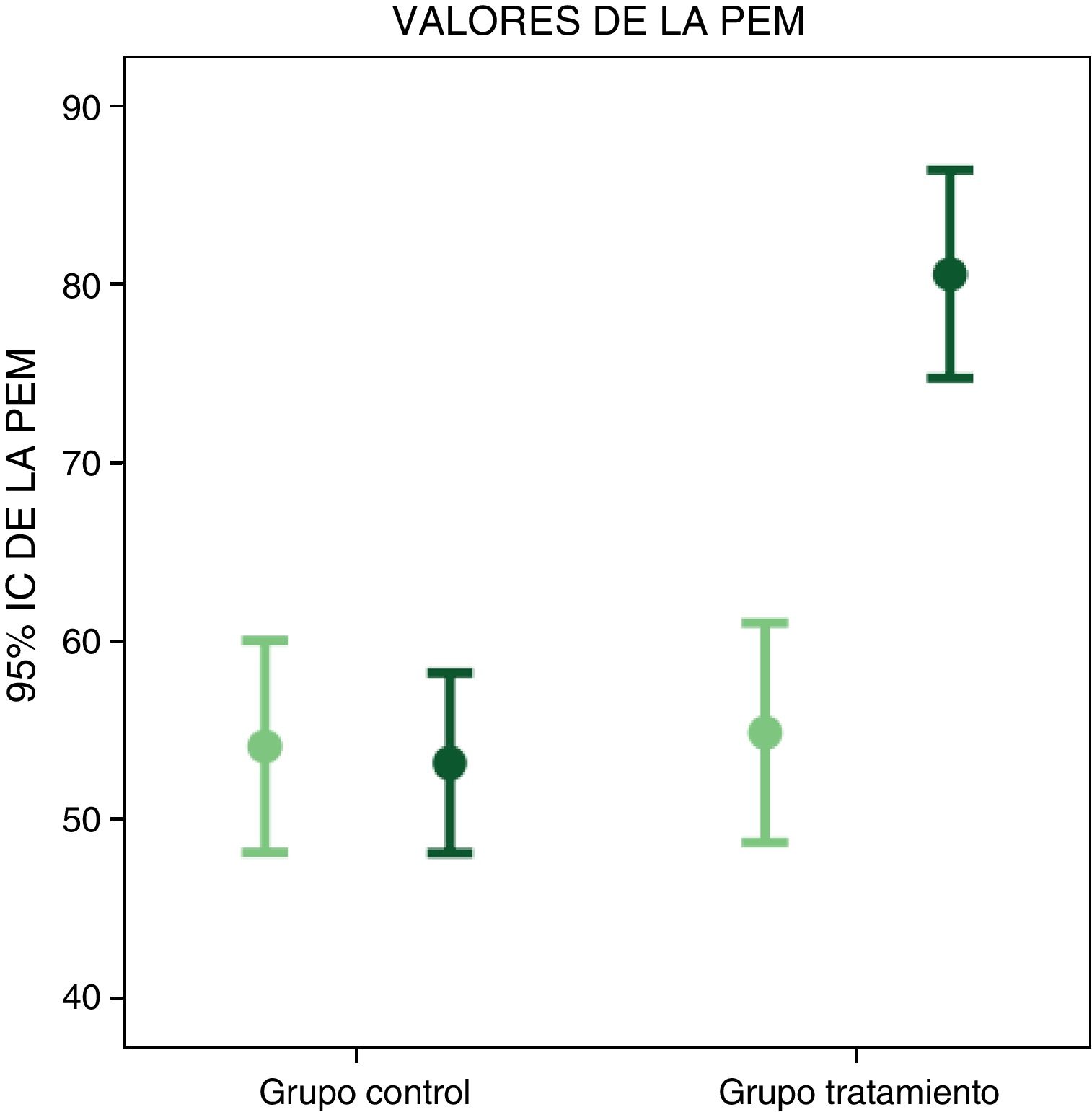
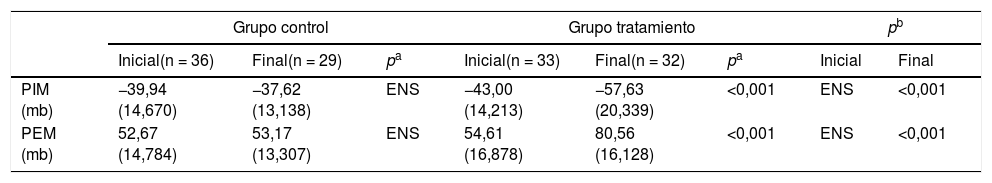
ResultadosSe registró un aumento estadísticamente significativo (p<0,001) y clínicamente relevante en el grupo de intervención en la PIM 13,84mb (IC 95%: 9,017-18,671) y la PEM 25,69mb (IC 95%: 20,373-31,002). Se obtuvieron diferencias con significación estadística entre los grupos: PIM 20,00mb (IC 95%: 11,13-28,88; p <0,001) y PEM 27mb (IC 95%: 19,75-35,012; p < 0,001).
ConclusiónEl trabajo muscular respiratorio específico con FNP mejoró las presiones respiratorias, lo que puede mejorar la fuerza y la función respiratorias en adultos mayores. Este tratamiento puede utilizarse como una intervención preventiva para minimizar las implicaciones del envejecimiento sobre la pérdida de masa y fuerza muscular.
Aging results in reduced muscle mass and strength. The aim was to evaluate the effectiveness of a proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) exercise protocol on respiratory muscle strength.
Material and methodsAn experimental study of 69 elderly, non-institutionalized female volunteers who participated in a physical exercise programme. They were randomly divided into 2groups. The intervention group performed a specific respiratory treatment protocol using the PNF technique. The control group did not receive an additional intervention. The PNF treatment consisted of 2weekly sessions lasting 50minutes over an 8-week time period. Respiratory muscle strength was measured for both groups by maximal inspiratory pressure (MIP) and maximal expiratory pressure (MEP).
ResultsThere was a statistically significant (P<.001) and clinically relevant increase in the intervention group in MIP 13.84mb (95%CI: 9.017-18.671) and MEP 25.69mb (95%CI: 20.373-31.002). There was also a statistically significant difference between groups: MIP 20.00mb (95%CI: 11.13-28.88; P<.001) and PEM 27mb (95%CI: 19.75-35.012; P<.001).
ConclusionsThe PNF respiratory treatment improved respiratory pressures, which may improve respiratory strength and function in older adults. This treatment can be used as prevention to minimize the loss of muscle mass and strength as a result of aging.
Article
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".