The incidence of falls in elderly patients in the hospital environment is three times higher than that in the community. The aim was to determine the characteristics of patients who suffered in-hospital falls and their complications.
MethodsThis was a cross-sectional study with patients older than 64 years of age, admitted between 2018 and 2020 to four clinics in Colombia who presented a fall during their stay. Clinical data, reasons for the fall, complications and use of drugs with a known risk for causing falls and with an anticholinergic load were reviewed.
ResultsA total of 249 patients were included. The mean age was 77.5 ± 7.4 years, and there was a predominance of males (63.9%). The patients were hospitalized mainly for community-acquired pneumonia (12.4%) and heart failure (10.4%). Falls occurred most frequently in hospitalization wards (77.1%) and emergency departments (20.9%). Falls were related to standing alone (34.4%) and on the way to the bathroom (28.9%), with 40.6% (n = 102) of falls resulting in trauma, especially to the head (27.7%); the incidence of fractures was low (3.2%). Ninety-two percent of patients had polypharmacy (≥5 drugs), 88.0% received psychotropic drugs, and 37.3% received drugs with an anticholinergic load ≥3 points.
ConclusionsHospitalized adults over 65 years of age suffered falls, mainly in hospitalization wards and emergency departments, especially during the process of solitary ambulation. Most had received psychotropic drugs and medications with a high anticholinergic load. These results suggest that it is necessary to improve risk prevention strategies for falls in this population.
La incidencia de caídas en pacientes ancianos dentro del ambiente hospitalario es tres veces superior a las que se presenta en la comunidad. Se planteó el objetivo de determinar las características de pacientes que sufrieron caídas intrahospitalarias y sus complicaciones en cuatro clínicas de Colombia.
MétodosEstudio transversal con pacientes mayores de 65 años de edad, ingresados entre 2018 y 2020 en cuatro clínicas de Colombia, que presentaron una caída durante su estancia. Se revisaron datos clínicos, motivos de la caída, complicaciones y uso de medicamentos de riesgo conocido para generar caídas y con carga anticolinérgica.
ResultadosSe identificaron 249 pacientes, con edad media de 77,5 ± 7,4 años y predominio masculino (63,9%), internados principalmente por neumonía adquirida en comunidad (12,4%) y falla cardiaca (10,4%); las caídas ocurrieron más frecuentemente en los servicios de hospitalización (77,1%) y urgencias (20,9%). Se relacionaron con procesos de bipedestación en solitario (34,4%), y movilización al baño (28,9%), con traumatismo en 40,6% (n = 102), especialmente de cabeza (27,7%), y baja incidencia de fracturas (3,2%). El 92% de casos tenían polifarmacia ≥5 medicamentos, el 88% recibieron psicofármacos y 37,3% medicamentos con carga anticolinérgica ≥ 3 puntos.
ConclusionesLos adultos mayores de 65 años internados sufrieron caídas, principalmente en los servicios de hospitalización y urgencias, en especial durante el proceso de deambulación en solitario. La mayoría habían recibido psicofármacos y medicamentos con alta carga anticolinérgica. Estos resultados sugieren que es necesario mejorar las estrategias de prevención de riesgo de este tipo de eventos.
What is known
The incidence of falls in elderly patients in the hospital environment is three times higher than that in the community.
What it contributes
This study identified the frequency of falls in older patients that occurred during their stay in four high-complexity hospitals in Colombia, information previously not available for this population of the country. Some of the outcomes associated with falls were reported, as were the main reasons for falls, an aspect that could be useful for designing strategies focused on their prevention.
In Colombia, according to the last census carried out in 2018 by the National Administrative Department of Statistics (DANE), 9.8% of the population was older than 65 years,1 and by 2020, 12.6% of Colombians were expected to be over 60 years of age.2 This is important when recognizing a growing population, with a high prevalence of diseases related to aging, including alterations in nutrition, daily physical activity and frailty.3
Frailty has been defined as a multicausal syndrome characterized by a decrease in strength, endurance and some physiological functions, leading to an increase in vulnerability to greater dependence or death.4 Frailty can lead to complications such as falls, which are a very important geriatric syndromes. It has been estimated that up to 30% of older adults require medical attention for an outpatient fall and that 10% suffer fractures and other complications resulting from falls.5 These complications are explained by the aging process and fragility itself, which implies instability, muscular weakness and physical deconditioning (caused by pain, prolonged rest due to an acute or chronic pathology or a lack of exercise and physical activity), situations that are also related to falls themselves and worse outcomes and survival in these patients.6,7
In addition to the characteristics of aging, the consumption of certain medications, especially psychotropics such as benzodiazepines and opioids, among other that have a confirmed anticholinergic load, for example, antidepressants, antipsychotics, and drugs for urinary problems or gastrointestinal diseases, increase the probability of falls and even fractures because these drugs can cause different neurological alterations, producing dizziness, blurred vision, cognitive dysfunction, ataxia or sleep disturbances.8–10
Studies carried out with older adults outside the hospital environment in Colombia identified an increased probability of falls with hip fracture between (OR: 1.97; 1.19–3.27) for drugs with an anticholinergic load and (OR: 4.49; 2.72–7.42) for opioids.11,12 Additionally, comorbidities such as diabetes mellitus in older patients increase the risk of falls, especially in insulin users because of the risk of developing severe hypoglycemia (OR: 1.27; 95% CI: 1.06–1.52).13 In hypertensive patients, there is a risk of falls from symptomatic hypotension when adding a new antihypertensive, especially in the first 24 h after the change in dose or in the first 21 days after starting a diuretic.14
The incidence of falls in patients within the hospital environment is three times higher than that in the community, and for older people, who are especially vulnerable during hospitalization due to acute illness, the need for permanent monitoring and decreased mobility, up to 25% may suffer injuries that require additional medical attention, as well as other complications described as mild to severe trauma, fractures, wounds and sometimes death.15,16 Multiple risk factors associated with falls in hospitalized patients have been identified that are related to medical and nursing care (quantity and quality of training of the nursing staff); the hospital center; patient age, condition, clinical characteristics, comorbidities, capacity for mobility, and family support; architectural barriers; and medications received during hospitalization.17–19 Currently, in Colombia, there is insufficient evidence regarding the clinical characteristics of patients who suffer falls within the hospital environment and a lack of knowledge of the mechanisms of falls. Therefore, the objective of this study was to identify the characteristics of older adult patients with in-hospital falls and secondary complications in four clinics in Colombia between 2018 and 2020.
Materials and methodsDesign and patientsThis was a retrospective cross-sectional study that included patients 65 years of age or older of either sex admitted to hospital care between January 1, 2018, and December 31, 2020, in four different high-complexity hospitals (care of medical specialties and emergency care, surgery, intensive care unit) in southwestern Colombia (Departments of Risaralda, Quindío, Valle del Cauca and Cauca). As of December 2020, the four centers had an availability of 855 beds and treated a total of 530,097 patients over the 4 years.
All the patients who presented a fall during their hospital stay were identified from the mandatory notification registry for falls, which includes sociodemographic information related to the fall, such as the reason, a description of the incident, location and other related data.
Inclusion and exclusion criteriaAs an inclusion criterion, in addition to age, all patients with falls who had data in the mandatory notification registry from each hospital center were considered. There were no exclusion criteria. Once a patient was identified, information was obtained from the patient’s medical history and drug dispensing records during hospitalization; this information was collected for all included patients in a dataset, and the confidentiality of the patients was not compromised. By including all patients with reports that met the inclusion, no sampling was used.
A fall was defined as an event in which the person lost his or her balance and hit the floor or some ground or firm object that stopped him or her; a report was made by the nursing staff of the department where said event occurred (Patient Safety Record20). During care within the hospital, the following variables were collected from the medical history:
- -
Sociodemographic data: age, sex, city of residence, and hospital;
- -
Clinical data: admission diagnosis and comorbidities (International Classification of Diseases version 10 (ICD-10));
- -
Fall: date and location of the fall (emergency department, hospital ward (internal medicine and surgical), surgery room, intensive care unit (ICU), radiology and other), reasons for the fall (walking to the bathroom, during a stay in the bathroom, mobilization in a wheelchair, problems with railings/stretcher) being alone or accompanied, associated trauma, need for care, and presence of fracture and other complications;
- -
Medications: name and pharmacological group of medications prescribed during hospitalization and frequency and proportion of use, not including antimicrobials;
- -
Anticholinergic load: calculated using the anticholinergic risk scale (ARS),21 with 0 points indicating no load, 1 point indicating a low load, 2 points indicating a moderate load, and 3 or more points indicating a high load; and
- -
Polypharmacy: five or more simultaneous medications (Supplementary Table 1 shows the load of each medication based on the ARS).
The collected variables were recorded in a data file in Microsoft Excel with closed fields, and the information recorded from each of the data sources was validated in search of outliers and inconsistent data, which were confirmed in the original sources. Univariate analyses were performed, and the results are presented a frequencies and proportions for categorical variables and measures of central tendency, position and dispersion for quantitative variables. The statistical package SPSS 28.0 for Windows was used for the analyses.
Bioethics statementEndorsement from the Bioethics Committee of the Universidad Tecnológica de Pereira was obtained; the study was classified as research “without risk” as established by Resolution 8430 of 1993 of the Ministry of Health of Colombia. The principles of justice, beneficence, nonmaleficence and confidentiality of information established by the Declaration of Helsinki were respected.
ResultsDuring the observation period, 249 patients with a fall within the four different clinics in Colombia in the cities of Pereira (n = 103, 41.4%), Cali (n = 77, 30.9%), Popayán (n = 43, 17.3%) and Armenia (n = 26, 10.4%) met the inclusion criteria. The average age of the patients was 77.5 ± 7.4 years, with a predominance of males (n = 159; 63.9%). In 2018, 11 falls were recorded (4.4%), in 2019 a total of 121 (48.6%) and in 2020 a total of 117 (47.0%).
The main reason for admission of the patients was community-acquired pneumonia, followed by decompensated heart failure, systemic infections such as sepsis, and cancer. Table 1 shows the sociodemographic variables, admission diagnoses and comorbidities of the identified patients. Most of the falls occurred in hospitalization wards (medical and/or surgical), followed by emergency departments. Most falls were related to standing alone, without the help of a family member or nursing staff, walking to the bathroom or being in the bathroom itself. In addition, 102 patients (40.6%) presented identifiable associated trauma, mainly to the head, requiring additional medical attention for more than half of the patients (52.6%), the most frequent being radiographs of the trauma site. Table 2 shows the characteristics associated with falls, reasons for falls, trauma, medical attention, presence of fracture and other complications related to falls.
Sociodemographic variables, admission diagnoses and comorbidities in 249 older patients with in-hospital falls in 4 high-complexity centers.
| Variables | n = 249 | % |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years: mean; SD) | 77.5 ± 7.4 | |
| 65−69 years | 39 | 15.5 |
| 70−79 years | 108 | 43 |
| ≥ 80 years | 104 | 41.4 |
| Male sex | 159 | 63.9 |
| Admission Diagnoses (ICD-10a) | ||
| Community-acquired pneumonia | 31 | 12.4 |
| Heart failure | 26 | 10.4 |
| Systemic infection | 26 | 10.4 |
| Cancer | 25 | 10.0 |
| COVID-19 | 21 | 8.4 |
| Acute coronary syndrome | 20 | 8.0 |
| Other admission diagnoses | 18 | 7.2 |
| Ischemic cerebrovascular event | 14 | 5.6 |
| Scheduled surgery | 14 | 5.6 |
| Traumatic fracture | 14 | 5.6 |
| Urinary tract infection | 14 | 5.6 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 7 | 2.8 |
| Cognitive decline/dementia | 6 | 2.4 |
| Major bleeding | 6 | 2.4 |
| Diabetic foot | 4 | 1.6 |
| Hepatic cirrhosis | 3 | 1.2 |
| Comorbidities | ||
| Arterial hypertension | 160 | 64.3 |
| Type 2 Diabetes mellitus | 63 | 25.3 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 54 | 21.7 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 52 | 20.8 |
| Heart failure | 44 | 17.7 |
| Coronary heart disease | 41 | 16.5 |
| Hypothyroidism | 34 | 13.7 |
| Dementia | 16 | 6.4 |
| Active cancer | 16 | 6.4 |
| Stroke | 11 | 4.3 |
| Dizziness | 10 | 4.0 |
| Urinary incontinence | 6 | 2.4 |
| Parkinson’s disease | 3 | 1.2 |
| Epilepsy/Seizures | 3 | 1.2 |
Information related to falls and associated comorbidities in 249 older patients with in-hospital falls in 4 high-complexity centers.
| Variables | n = 249 | % |
|---|---|---|
| Place of the fall | ||
| Hospitalization | 192 | 77.1 |
| Emergency care | 52 | 20.9 |
| Critical Care | 3 | 1.2 |
| Radiology | 2 | 0.8 |
| Reason/Situation associated with the fall | ||
| Standing alone a | 113 | 34.4 |
| Mobilization to the bathroom | 72 | 28.9 |
| Being in the bathroom | 47 | 18.9 |
| Railings Down/Jumping Rails | 75 | 30.1 |
| Wheelchair | 9 | 3.6 |
| Associated trauma | 102 | 40.6 |
| Head | 69 | 27.7 |
| Lumbar/Pelvis | 20 | 8.0 |
| Upper extremity | 17 | 6.8 |
| Lower extremity | 7 | 2.8 |
| No data | 11 | 4.4 |
| Required additional attention | 131 | 52.6 |
| X-rays | 53 | 21.3 |
| Head CT scan | 32 | 12.9 |
| Specialized medicine assessment | 31 | 12.4 |
| Wound Healing/Suture | 13 | 5.2 |
| Other paraclinical | 5 | 2.0 |
| Surgery | 7 | 2.8 |
| Fracture | 8 | 3.2 |
| Hip/femur | 3 | 1.2 |
| Distal ulna | 3 | 1.2 |
| Ulna + Radius | 1 | 0.4 |
| Bone of the nose | 1 | 0.4 |
| Other complications | ||
| Face/scalp hematoma | 9 | 3.6 |
| Altered state of consciousness | 2 | 0.8 |
| Subdural hematoma | 2 | 0.8 |
| Hemodynamic instability | 2 | 0.8 |
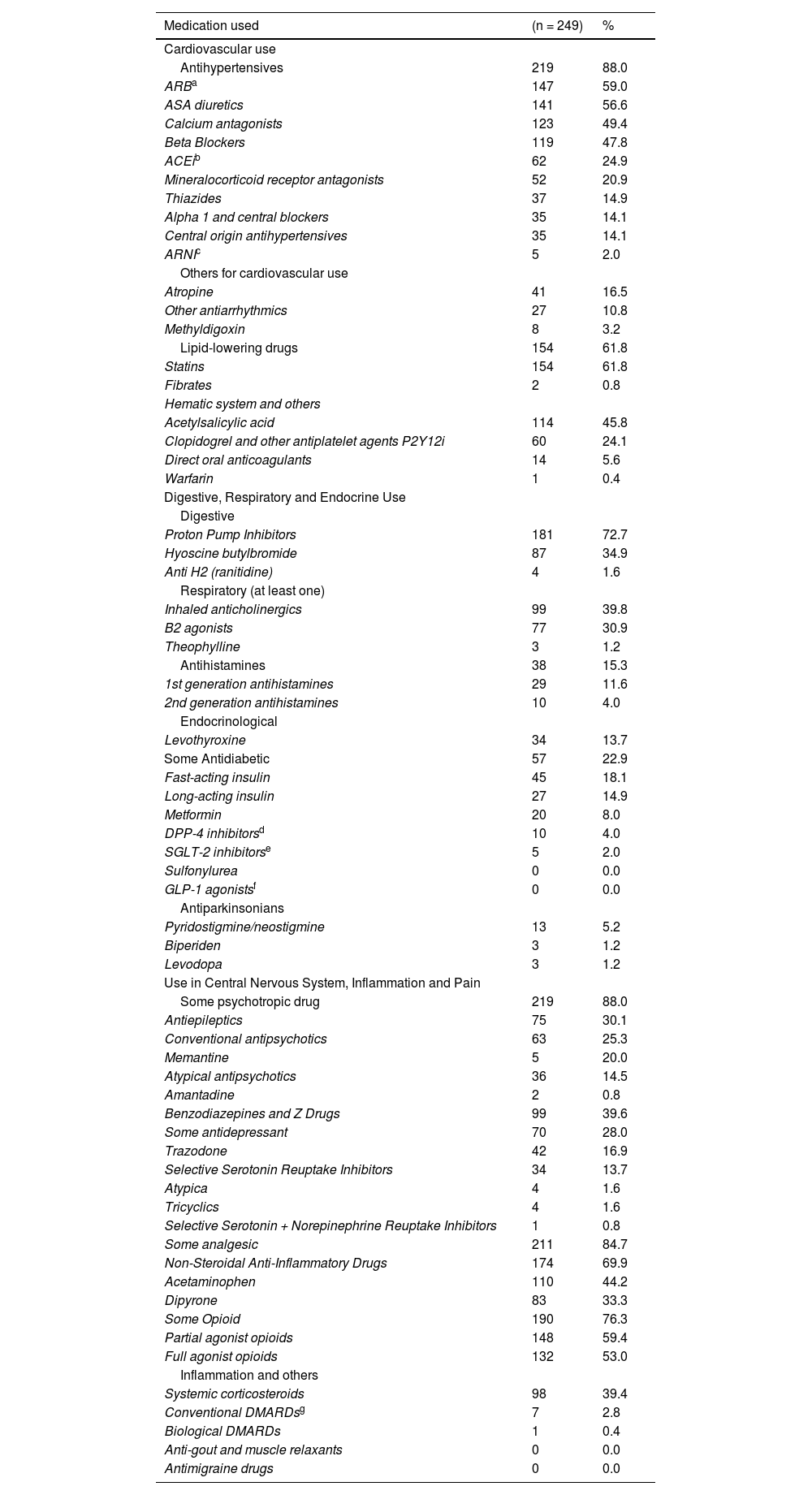
The drugs most frequently used during hospitalization in the group of patients who fell were antihypertensives (88.0%), proton pump inhibitors (72.2%), nonopioid analgesics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (69.9%), lipid-lowering drugs (61.8%), partial (59.4%) and total (53.0%) agonists, antiplatelet drugs (46.8%) and psychotropic drugs such as antipsychotics (30.8%), antidepressants (28.0%) and antiepileptics (25.2%) (Table 3). Of the drugs used, the antimuscarinic load was estimated using the ARS scale (supplementary table), and the mean anticholinergic load score was 2.26 ± 2.25 points. On average, the patients used 11.8 drugs (nonantimicrobial) during the hospital stay, and an estimated 92% had polypharmacy, reaching up to 29.7% with 15 or more medications. A total of 37.3% of the patients had three or more points for anticholinergic load (Table 4).
Medications used during hospitalization in 249 older patients with in-hospital falls in 4 high-complexity centers.
| Medication used | (n = 249) | % |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular use | ||
| Antihypertensives | 219 | 88.0 |
| ARBa | 147 | 59.0 |
| ASA diuretics | 141 | 56.6 |
| Calcium antagonists | 123 | 49.4 |
| Beta Blockers | 119 | 47.8 |
| ACEib | 62 | 24.9 |
| Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists | 52 | 20.9 |
| Thiazides | 37 | 14.9 |
| Alpha 1 and central blockers | 35 | 14.1 |
| Central origin antihypertensives | 35 | 14.1 |
| ARNIc | 5 | 2.0 |
| Others for cardiovascular use | ||
| Atropine | 41 | 16.5 |
| Other antiarrhythmics | 27 | 10.8 |
| Methyldigoxin | 8 | 3.2 |
| Lipid-lowering drugs | 154 | 61.8 |
| Statins | 154 | 61.8 |
| Fibrates | 2 | 0.8 |
| Hematic system and others | ||
| Acetylsalicylic acid | 114 | 45.8 |
| Clopidogrel and other antiplatelet agents P2Y12i | 60 | 24.1 |
| Direct oral anticoagulants | 14 | 5.6 |
| Warfarin | 1 | 0.4 |
| Digestive, Respiratory and Endocrine Use | ||
| Digestive | ||
| Proton Pump Inhibitors | 181 | 72.7 |
| Hyoscine butylbromide | 87 | 34.9 |
| Anti H2 (ranitidine) | 4 | 1.6 |
| Respiratory (at least one) | ||
| Inhaled anticholinergics | 99 | 39.8 |
| B2 agonists | 77 | 30.9 |
| Theophylline | 3 | 1.2 |
| Antihistamines | 38 | 15.3 |
| 1st generation antihistamines | 29 | 11.6 |
| 2nd generation antihistamines | 10 | 4.0 |
| Endocrinological | ||
| Levothyroxine | 34 | 13.7 |
| Some Antidiabetic | 57 | 22.9 |
| Fast-acting insulin | 45 | 18.1 |
| Long-acting insulin | 27 | 14.9 |
| Metformin | 20 | 8.0 |
| DPP-4 inhibitorsd | 10 | 4.0 |
| SGLT-2 inhibitorse | 5 | 2.0 |
| Sulfonylurea | 0 | 0.0 |
| GLP-1 agonistsf | 0 | 0.0 |
| Antiparkinsonians | ||
| Pyridostigmine/neostigmine | 13 | 5.2 |
| Biperiden | 3 | 1.2 |
| Levodopa | 3 | 1.2 |
| Use in Central Nervous System, Inflammation and Pain | ||
| Some psychotropic drug | 219 | 88.0 |
| Antiepileptics | 75 | 30.1 |
| Conventional antipsychotics | 63 | 25.3 |
| Memantine | 5 | 20.0 |
| Atypical antipsychotics | 36 | 14.5 |
| Amantadine | 2 | 0.8 |
| Benzodiazepines and Z Drugs | 99 | 39.6 |
| Some antidepressant | 70 | 28.0 |
| Trazodone | 42 | 16.9 |
| Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors | 34 | 13.7 |
| Atypica | 4 | 1.6 |
| Tricyclics | 4 | 1.6 |
| Selective Serotonin + Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors | 1 | 0.8 |
| Some analgesic | 211 | 84.7 |
| Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs | 174 | 69.9 |
| Acetaminophen | 110 | 44.2 |
| Dipyrone | 83 | 33.3 |
| Some Opioid | 190 | 76.3 |
| Partial agonist opioids | 148 | 59.4 |
| Full agonist opioids | 132 | 53.0 |
| Inflammation and others | ||
| Systemic corticosteroids | 98 | 39.4 |
| Conventional DMARDsg | 7 | 2.8 |
| Biological DMARDs | 1 | 0.4 |
| Anti-gout and muscle relaxants | 0 | 0.0 |
| Antimigraine drugs | 0 | 0.0 |
Polypharmacy, frequency of use of drugs with a higher risk of falls and anticholinergic load using the ARS scale for 249 older patients with in-hospital falls in 4 high-complexity centers.
| Variables | n = 249 | % |
|---|---|---|
| Quantity of drugs - hospitalization (days, mean; SD) | 11.8 ± 1.1 | |
| Polypharmacy (5 or more drugs) | 229 | 92 |
| Drug frequency distribution | ||
| Between 0–4 medications | 20 | 8 |
| Between 5–9 medications | 78 | 31.3 |
| Between 10–14 medications | 77 | 30.9 |
| Between 15–19 medications | 50 | 20.1 |
| Between 20 and more medications | 24 | 9.6 |
| Medications with risk of falls | ||
| Antihypertensives (n, mean; SDb) | 2.9 ± 1.9 | |
| Use of at least one antihypertensive | 219 | 88 |
| Antidiabetics (n, mean; SD) | 0.4 ± 0.9 | |
| Use of at least one antidiabetic | 57 | 22.9 |
| Antidepressants (n, mean;SD) | 0.3 ± 0.6 | |
| Use of at least one antidepressant | 70 | 28.1 |
| Psychotropic drugsa(n, mean;SD) | 2.5 ± 0.3 | |
| Use of at least one psychotropic drug a | 219 | 88 |
| Anticholinergic Load (ARS scale)c(n, mean;SD) | 2.26 ± 2.25 | |
| 0 Points (zero risk) | 69 | 27.7 |
| 1 Points (low risk) | 53 | 21.3 |
| 2 Points (moderate risk) | 34 | 13.7 |
| 3 Points or more (high risk) | 93 | 37.3 |
This study identified the frequency of falls in older patients that occurred during their stay in four high-complexity hospitals from the south-west of Colombia, information previously not available for this population of the country. Some of the outcomes after falls were reported, as were the main reasons for falls, an aspect that could be useful for designing strategies focused on their prevention.
The mean age of the patients in this study was higher than that of the patients in a study by Lyu et al.,22 in China between 2018 and 2022 that identified that approximately 50% of patients with falls were older than 70 years,but similar to that reported (84.4%) in a study by Mikos et al.,23,24 in Poland, in which the average age was 77.9 years and there was predominance of males. The foregoing highlights the risk conferred by advanced age and the use of medications in the hospital environment.
A study by López et al.,25 in a city in Colombia in 2010 identified falls in the hospital setting among patients of any age, mainly men. Fifty-four percent were over 60 years old, and the main causes of hospital admission in this group were neurological (27.6%), cardiovascular (18.6%) and respiratory problems (13.1%). In the present study, the reasons for admission were different, with community-acquired pneumonia and heart failure, probably because it was an exclusive study in older adults, but also systemic infections, cancer and COVID-19, prevailing as the most frequent causes of hospitalization and complications.26 In addition, SARS-CoV-2 infection became one of the main reasons for hospitalization for older adults during the year 2020, which, added to frailty and the same age-related comorbidities, contributed to being a risk factor for falls during hospitalization.27,28
Lack of accompaniment, either by health care personnel or a family member (37.5% of cases), and moving on wet ground (35%) were common findings in the study by López et al.25 from 2010. Additionally, the most recent relevant report, by Rodríguez et al.,29 in Bogotá, Colombia, during 2021 with adult patients, 65.5% of patients were older than 35 years, 39.4% of falls were associated with getting out of bed, and 18% of falls occurred in the bathroom. The importance of the company of responsible people who help the patient in these two critical moments is highlighted. This finding agrees with the data found in this study, in which 34.4% of falls occurred when getting out of bed alone or moving alone, followed by falls during trips to the bathroom. By identifying the frequency of these situations, effective accompaniment strategies can be generated in hospitals to prevent falls.30
Importantly, in Colombia, there are clear guidelines from the Ministry of Health regarding patient safety and the prevention of falls as well as the evaluation of the quality of nursing care, starting with the correct identification of the patient, maintaining permanent accompaniment for those considered high risk, such as older individuals, and ensuring sufficient staff and adequate transportation.31,32 These situations can fail for different reasons and explain a large number of preventable events through the adoption of support measures by family members and health personnel, effective call systems for nursing centers, easy-to-use fasteners, and floor slip resistance, among other protection strategies.30
The low proportion of fractures (3.2%) that occurred when falling within the hospitals among this cohort of older patients, despite their advanced age and the comorbidities they suffered, is notable because in other reports, they are present in 52.6% of cases, with other trauma accounting for 40%, a finding that may be related to the mechanisms of falls and the possible mitigation measures for the effects of this in each health care center. In addition, these same studies identified deaths associated with this type of fall (1.3% of 9753 patients) in Japan33 and in the subsequent 30 days after the event and up to 21.1% in the following year, according to Newgard et al. in the United States,34 findings that may be influenced by advanced age, being a man and having a higher rate of Charlson comorbidities, in addition to the use of medications with a potential increase in the risk of falls.13,14,35
Importantly, the potential impact of drugs on the mental and alert state can generate and the impact of those that can generate episodes of hypoglycemia or severe hypotension (secondary to changes in dose or the start of a new antihypertensive) can lead to an increased likelihood of falls.13,14 In previous studies in Colombia, there was a higher risk of falls in ambulatory older people who had a high anticholinergic load or were users of benzodiazepines or opioids.11,12 These groups of drugs in particular should be prescribed with great caution to the older patients due to their risks and need for greater monitoring and evaluation by clinicians of possible adverse reactions and risks to which patients are exposed, in addition to preventable situations such as family support, nursing care and circulation barriers affecting the patient and leading to intrahospital falls.11,12,36–38
The most widely used drugs were antihypertensive drugs, a finding that is consistent with the comorbidities of the patients included as well as with studies of patients with in-hospital falls in Iran or Brazil.38,39 The frequency of prescription of drugs described by their risk, such as benzodiazepines, accounting for almost 40%, was higher than that described in the study by Silva et al.,39 i.e., 19.7% in patients with hospital falls, somewhat lower than the 51.9% reported in the Najafpour study38 in Iran, and much higher when compared with the results of studies of falls in outpatients with hip fracture in Colombia in which the prescription of benzodiazepines was observed in 4.2% of cases,11 benzodiazepines are more widely used in hospitalized versus outpatient patients and may be related to falls in older adults.
In this study, 76.3% of the patients received an opioid during hospitalization associated with the fall, a figure very similar to that found in Iran (77.3%)38 but much higher than that reported in Brazil (25.0%) and in the study of falls in outpatients in Colombia.11,39 These findings show the differences in the patterns of drug use between hospitals and countries and the high risk of falls that this group of hospitalized older adults, allowing the opportunity in future studies to identify the risks associated with the drugs for the Colombian population and actions plans to mitigate it. Opioids also increase the total score for anticholinergic load, as measured using the ARS scale, as do antidepressants and antihistamines, among others, reaching an average of 2.26 points in this group of patients with falls, findings that are similar to those reported for Colombia in outpatients who had falls (2.2 points).12 The data that are consistent with this study show the risk to which these patients with hospital falls are exposed, as the level of risk is similar to the anticholinergic load to which they were exposed and could influence the risk of falling. Situations should lead to increasing the processes of care for older patients as well as seeking greater identification of the drugs used and the risks associated with them.40
This study has some limitations. The severity of the pathologies that led to hospitalization was not known. All the clinics or hospitals included were located in the western center of Colombia and were of a private nature; therefore, the conclusions cannot necessarily be interpreted in the same way for hospitals in different regions or countries. Finally, the information available on each fall event was obtained from the registry of each hospital, being retrospective in nature; therefore, it is possible that data were omitted or not available, as well as the possibility of incomplete information limiting the total number of people included. Strengths include the identification of information related to all reports of falls as each hospital as well as the participation of four reference centers in southwestern Colombia and the identification of the use of medications in this population with falls.
ConclusionsWith the above findings, it can be concluded that in-hospital falls in this group of older adults are an important problem related to patient safety; falls increase the requirements of care because of the high occurrence of associated traumas. In addition, falls occur more frequently in men of advanced age, suffering from pneumonia, heart failure or systemic infections, who get out of bed alone, wander alone or unaccompanied to the bathroom; however, they were identified with low proportion of fractures. Furthermore, polypharmacy and the use of medications that potentially increase the probability of falling were frequently identified. It is necessary to continue with this line of research to identify other possible risk factors associated with falls, such as the use of medications with hypnotic and sedative or hypotensive effects that can influence the alertness, mental state, balance and posture of adult patients.
Statements & declarationsCompeting interests: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This study is part of the development of the doctoral thesis in pharmacology of MEMD at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona.
Author contributions: MEMD participated in the conceptualization, drafting, data collection, data analysis, description of results and discussion. LC participated in the supervision, discussion critical revision of the article. MS participated in the supervision, discussion critical revision of the article. JEMA participated in the, supervision, discussion, critical revision of the article, and evaluation of the final version of the manuscript.
Ethics approval: The protocol was approved by the Bioethics Committee of the Universidad Tecnológica de Pereira in the category of “risk-free research” (approval number 02 - 14/12/20). The principles established by the Declaration of Helsinki were respected.
Consent to participate. No applicable, is a retrospective observational study.
Consent to publish: all authors consent to participate.
Data availability statementAvailability of data and material: protocolos.io
Code availability: https://www.protocols.io/private/8E09F5D3226111EE9F2D0A58A9FEAC02.
FundingMachado-Duque ME has a doctoral scholarship provided by Colfuturo.