Based on preliminary studies, it is known that 80% of working mothers fail to make exclusive breastfeeding, on average babies are given formula milk 2–4 months old and stop breastfeeding at 6–18 months of age. Papaya leaves are one of the galactagogues that contain quercetin which can activate the hormone prolactin and help increase breastmilk. The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of giving papaya leaf juice for nursing mothers who work toward increasing levels of the hormone prolactin and infant weight in Tangerang. The research design used was a pre-experimental model with one group pretest–posttest design. Samples taken as many as 10 mothers who have babies aged 0–6 months who have difficulty in breastfeeding because the amount of breastmilk was a little. The study was conducted in several clinics in Tangerang. The intervention was giving papaya leaf juice for 7 consecutive days. The results obtained from this study are as follows: 90% of mothers aged between 20 and 35 years, 70% of mothers have a history of spontaneous labor and have no complications at the time of delivery, 40% of mother's education is junior high school (SMP), and 70% of mothers are primiparas. The average increase in the amount of prolactin after the intervention was 19.59ng/ml, while the average weight gain of the newborn after the intervention was 165g. Wilcoxon test results for increased levels of the hormone prolactin p-value of 0.047<0.05 and for an increase in body weight of newborns p-value of 0.009<0.05.
ConclusionThere is an effect of giving papaya leaf juice for nursing mothers who work on increasing levels of the hormone prolactin and infant weight in Tangerang. Papaya leaf juice can be a galactagogue for mothers who experience problems with a small amount of breastmilk.
World Health Organization stated that only 38% infants in the world gets exclusive breastfeeding,1 and the percentage of mothers that fail to breastfeed is about 10–15%,2 while in Indonesia, based on Indonesian Health Profile in 2017, it is known that only 40.42% infants get exclusive breastfeeding, it means that 59.58% infants has not got exclusive breastfeeding.3 The failure in exclusive breastfeeding caused the cessation of breastfeeding process and early recognition of formula milk.4 The failure in breastfeeding gives bad impacts on infants, such as increasing the incidence of infection like otitis media, gastroenteritis, pneumonia, obesity, diabetes type 1 and 2, leukemia, and sudden death syndrome, while the negative impacts also happen to the mother are increasing the probability of breast cancer before menopause, ovary cancer, overweight, and metabolic syndrome.5
The factors that cause breastfeeding failure are late initiation of breastfeeding, the feeling of insufficient amount of breastfeed from the mother, and no discharge of breastfeed.6,7 The insufficient amount can be caused by some factors, such as the insufficient production of breastfeed, small breast nipples that cause the lack of baby suction.2–8 Based on preliminary studies on March 2018, 80% of 10 mothers that have 6–24 months kids admitted that they failed to breastfeed, in average 2–4 months old infants were given formula milk and stop milking at the age of 6–18 months. This incident was caused by some problems such as the inability to fully breastfeed, the lack of baby suction, and there is even infants that refused to breastfeed even there is a little amount of breastfeed.
Breastfeeding gives metabolic burden on mother's physiology process; it needs a minimum of 480kcal of energy per day to exclusive breastfeeding.9 Therefore, some additional nutrition is needed to increase the production of breastfeed so that mothers can play their role to breastfeeding. The breastfeeding process also assisted by consuming galactogogues, the example of galactogogues that has been studied and succeed to increase the amount of breastfeed are Katuk Leaf,10 green bean juice and fennel,11 papaya fruit boiled water,12 and papaya leaf powder.13 Researcher is attracted to the usage of papaya leaf in increasing the amount of breastfeed, because based on Setyono et al.’s study in 2016,14 Papaya leaf is one of the galactogogues that contain quercetin that can activate the prolactin hormone. The study on the usage of papaya leaf to increase the amount of breastfeed is not much done. In 2015, Turlina et al.15 also studied the effect of giving papaya leaf powder in continuity of breastfeeding also gave a positive impact with p-value of 0.004<p-table.
This research will focus on giving papaya juice because it is easier to do than giving papaya leaf powder. The ease can be used by mother to make papaya juice by herself at home and it does not cost highly, so that the aim of this research is the effects of giving papaya juice to prolactin hormones and infants weight.
MethodThe research design that will be used in this research is the pre-experimental which is an experiment study that still affected by external variable that affects the giving of papaya leaf juice with the amount of prolactin hormones and infant's weight (dependent variable). This research uses a group pretest–posttest design approach, which compares the state before treatment and after treatment. The effect is defined by comparing the mean value of the variable before and after treatment. This pre-experimental research is intended to find the mean differences on the group before and after treatment in order to see the changes on the amount of prolactin hormones and infant's weight.
This research is done at two midwife clinics in Tangerang on February to July 2019. The population of this research is 27 working mothers that have 6–24 months baby. From the total of 27 mothers, only 13 of them agreed to become a respondent, and from 13 mothers, 3 of them were excluded because they cannot keep up the process until done. The inclusion criteria of this research are working mother (before and after having babies), that have a 0–6 months baby, which have a problem of the insufficient amount of breastfeed.
This research is conducted when the respondent agreed to participate, the respondents then will be taken blood sample to be checked the amount of prolactin hormone and weigh their infants. Then, some papaya juice was sent to the respondent's home and they were asked to consume it two times a day for seven days. On the eighth day, a blood sample were taken again from each respondent to be checked the amount of prolactin hormone and weigh their infants again.
The papaya leaf juice was made by blending the papaya leaf which has a bitter flavor. In order to neutralize and relieve the smell of the papaya leaf, star fruit water and honey were added. The procedure to made it is: The moderate papaya leaf is selected and then washed with boiled water. The papaya leaf is chopped and then blended with 80cc of boiled water, 20cc of star fruit water and two tablespoons of honey were added.
While the treatment is occurring, the respondents are allowed to draw back if they are feeling uncomfortable on this research. In order to keep the confounding variable, the researcher suggested the respondents to breastfeed their babies as often as possible and stop giving the formula milk, respondents are also asked to sleep earlier and breastfeed at night. Respondents are also asked to minimize their activities and stressful thoughts on these seven days period to help this research to gain a good result.
The data collection is done while the research still takes place. Then, coding, data analysis, and interpretation are conducted. Research ethics that has been used is respect for person, where respondents are free to accept or refuse the treatment on this research. Justice, where all of the respondents are equally treated without any differences. Beneficence and Nonmaleficence, where the role of each respondent is useful to this research.
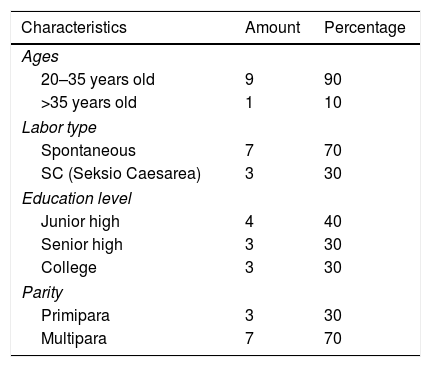
Table 1 shows that 90% of the respondents aged between 20 and 35 years old, 70% deliver spontaneously, 40% of them have Junior high education, and 70% of them are multipara.
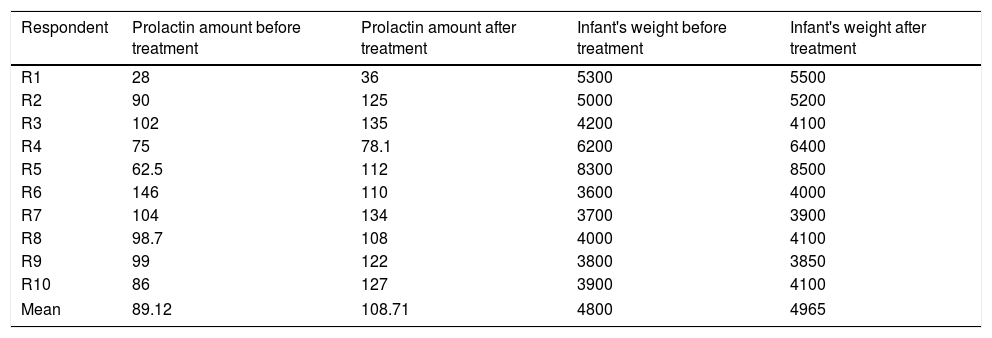
Table 2 shows that 90% of respondent have increased prolactin hormone levels after consuming papaya leaf juice. The average increase of prolactin hormone is 19.59ng/ml. The increase of prolactin hormone can be occurred in just several minutes after breastfeeding,16 infant's suction reflex help to stimulate the production of prolactin hormone. Based on Suksesty's study, green bean juice and fennel can increase the prolactin hormone amount,11 including papaya leaf, Pratiwi's study explain that the 800mg papaya leaf extract can increase the amount of prolactin amount on mothers (Table 3).
Prolactin hormone frequency distribution before and after treatment.
| Respondent | Prolactin amount before treatment | Prolactin amount after treatment | Infant's weight before treatment | Infant's weight after treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 28 | 36 | 5300 | 5500 |
| R2 | 90 | 125 | 5000 | 5200 |
| R3 | 102 | 135 | 4200 | 4100 |
| R4 | 75 | 78.1 | 6200 | 6400 |
| R5 | 62.5 | 112 | 8300 | 8500 |
| R6 | 146 | 110 | 3600 | 4000 |
| R7 | 104 | 134 | 3700 | 3900 |
| R8 | 98.7 | 108 | 4000 | 4100 |
| R9 | 99 | 122 | 3800 | 3850 |
| R10 | 86 | 127 | 3900 | 4100 |
| Mean | 89.12 | 108.71 | 4800 | 4965 |
Setyono's study in developing papaya leaf powder drink and red ginger with brown sugar, cinnamon powder, salt, pandan leaves, and water that processed to become powder which is given to breastfeeding mothers and then the color, smell, and texture are examined,14 while Turlina's15 study that gave papaya leaf powder to breastfeeding mother and gave positive impacts to the continuity of breastfeeding.
Papaya leaves are a part of papaya plant with Latin name Carica papaya. This plant is a small tree with 2–10m height. Perpendicular hollow trunk without branches, but branches can be made. Single shaped 5–9 fingers leaves. Hollow petiole with 50–100cm length. Usually papaya leaves appear on the mid of the branches.17 The papaya leaves contain carpain alkaloid, carpinine, pseudocarpaine, dehydrocarpaine I, dehydrocarpaine II, vitamin B, C, E, and mineral Zn, Ca, Fe, K, Na, and Mg.18,19 Phytochemical profile of the carica papaya reveals the presence of phytocompounds that active with pharmacological, alkaloid, phenolic, and amino acid.20 A moreover study can be conducted to identify and isolate the most active bioconstituents that connected the compounds in increasing the prolactin hormone.
Some studies explained that papaya leaves have medical properties, such as antibacterial, accelerate wound healing, diuretic, increasing uterine contractions, anti-fungus, contraception, anti-tumor, and anti-coagulant.18,19
The increasing amount of breastfeeding mother that consumes papaya leaf juice offset by reduced breastmilk viscosity. The breastmilk becomes thinner and clear (foremilk) on day 9 until day 12 post consuming. The research assumed that papaya leaves can decrease the amount of fats that consumed by mothers. Thick breastmilk (hindmilk) have a high amount of fats, while thin breastmilk contains more protein and lactose,16 both breastmilk is allowed to be given to their infants.
Table 2 explains that 10% of the respondents have decreasing amount of prolactin hormone. This can be caused by the decreasing frequency of breastfeeding. In this research, respondents that have a decreasing amount of prolactin hormone experienced pain while breastfeeding, this has caused stress to the respondents while breastfeeding. This condition then obstruct the breastmilk production on mothers and resulting in decreased confidence on mothers because their breastmilk is decreasing.
Table 2 also shows that 90% of the infant's weight is increasing by the mean of 165g. The increasing of weight for 0–6 months baby can be affected by mother's weight during pregnancy, parent's genetic, nutrition during pregnancy and puerperium, and baby's intake.21 The papaya leaf juice gave a positive impact on infant's weight to the mother who consumed it 2 times a day. The increasing of baby's weight is one of a baby's growth indicator whether if it goes on well or not. Besides, weighing the baby also defined the baby's nutritional status.22
Based on this research, it shows that every baby weight normally, which means that the babies grow well. This will help their growth in the future, gross motor and fine motor development, and academic achievement in 15 years in the future.23
There is an effect on giving papaya leaf juice to breastfeeding and working mothers in increasing the amount of prolactin hormone and infant's weight in Tangerang. Papaya leaf juice can be used as galactogogues to help breastfeeding mother. A further research can be conducted by including control group.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Peer-review under responsibility of the scientific committee of the 3rd International Conference on Healthcare and Allied Sciences (2019). Full-text and the content of it is under responsibility of authors of the article.