Glucocorticoids are vital in treating COVID-19, but standard dosage for noncritical patients remain controversial. To determine the optimal glucocorticoid dosage for noncritical COVID-19 patients, we analyzed factors influencing dosage and developed a predictive model.
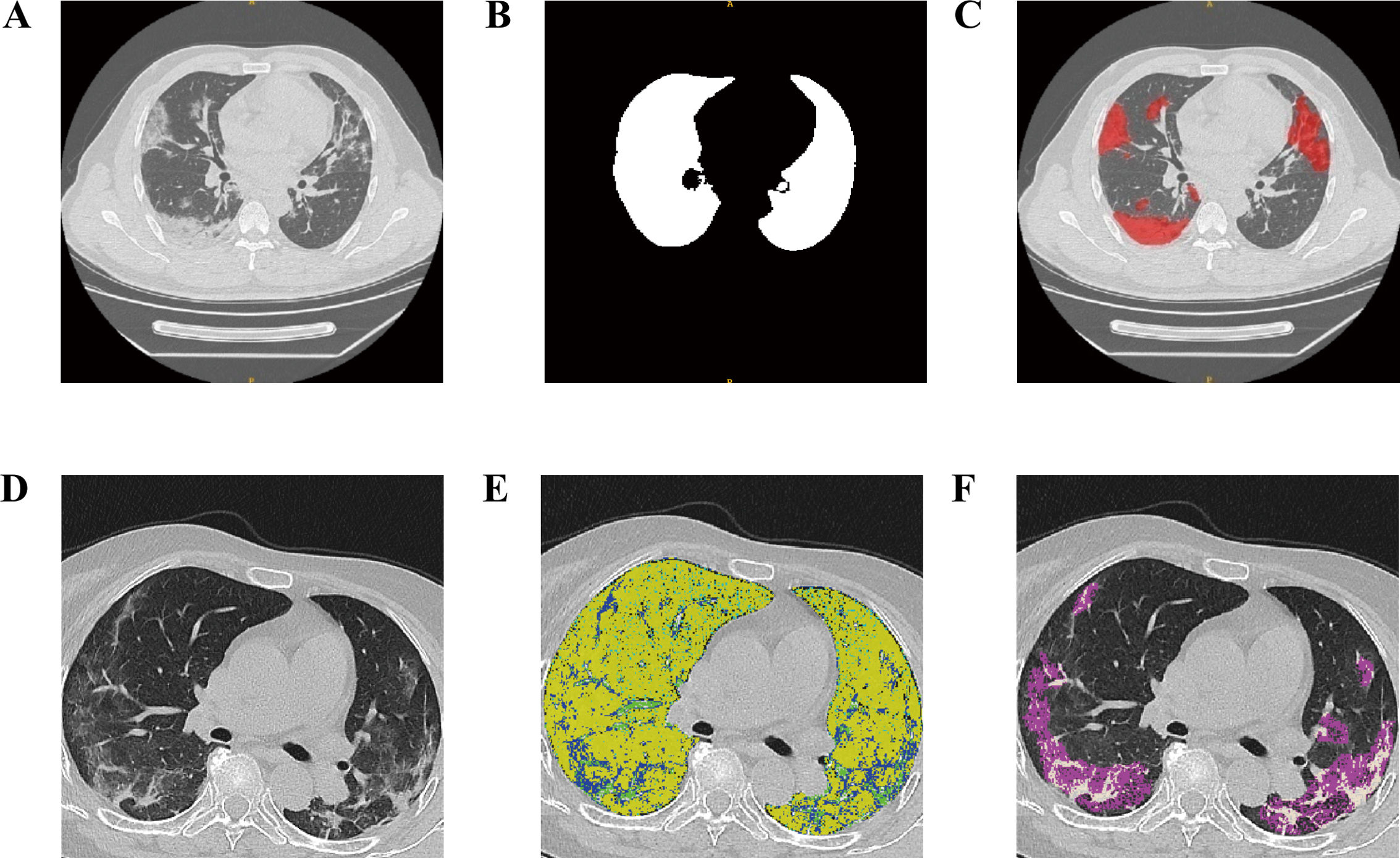
MethodsWe retrospectively analyzed 273 noncritical COVID-19 pneumonia patients underwent pulmonary CT and treated with glucocorticoids in a tertiary hospital (12/2022–01/2023). Patients were divided into low and high glucocorticoid dosage groups based on a daily 40mg methylprednisolone or equivalent. Artificial intelligence (AI)-based deep learning was utilized to assess pulmonary CT images for accurate lesion area, which then analyzed through multivariable logistic regression to explore their correlation with glucocorticoid dosage. A predictive model was developed and validated for dosage prediction.
ResultsThe primary analysis included 243 patients, with 168 in the training set and 75 in the validation set. High-dose treatment was administered to 139 patients (82.7%) and low-dose to 29 patients (17.3%) in the training cohort. A predictive model incorporating normally inflated ratio, ground-glass opacity (GGO) ratio, and consolidation ratio accurately predicted selection of high- or low-dose, in both training (AUC=0.803) and validation cohorts (AUC=0.836), respectively. In 30 patients with post-CT adjusted dosages, the predicted dosages highly matched with the actual adjusted dosages.
ConclusionGlucocorticoid dosages for noncritical COVID-19 pneumonia treatment are influenced by pulmonary CT features. Our predictive model can predict glucocorticoid dosage, however, should be validated by larger, prospective studies.
Los glucocorticoides son esenciales en el tratamiento de la COVID-19, pero la dosificación estándar para pacientes no críticos sigue siendo controvertida. Para determinar la dosificación óptima, analizamos los factores que influyen en ella y desarrollamos un modelo predictivo.
MétodosAnalizamos retrospectivamente a 273 pacientes con neumonía por COVID-19 no crítica tratados con glucocorticoides en un hospital terciario (de diciembre de 2022 a enero de 2023). Se dividieron en grupos de dosis baja y alta, según una dosis diaria de 40mg de metilprednisolona o equivalente. Se utilizó aprendizaje profundo basado en inteligencia artificial (IA) para analizar imágenes pulmonares y evaluar el área de lesión, correlacionada con la dosificación mediante regresión logística multivariable.
ResultadosIncluimos 243 pacientes: 168 en entrenamiento y 75 en validación. El 82,7% recibió dosis altas y el 17,3% dosis bajas. Un modelo predictivo basado en la proporción de inflamación normal, opacidad en vidrio esmerilado y consolidación predijo con precisión dosis altas o bajas (AUC=0,803 en entrenamiento, AUC=0,836 en validación). En 30 pacientes con dosis ajustadas post-TC las predicciones coincidieron con las dosis reales.
ConclusiónLas dosis de glucocorticoides están influenciadas por características pulmonares en la TC. El modelo predictivo es prometedor, pero requiere validación en estudios más amplios.
Article
Socio de la Sociedad Española de Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología Clínica

Para acceder a la revista
Es necesario que lo haga desde la zona privada de la web de la SEIMC, clique aquí
Para realizar los cursos formativos
La actividad estará abierta para socios de la SEIMC. IMPORTANTE, recuerde que requiere registro previo gratuito. Empezar aquí