The level of recommendation of the robotic approach in liver surgery is controversial. The objective of the study is to carry out a single-center retrospective descriptive analysis of the short-term results of the robotic and laparoscopic approach in liver surgery during the same period.
MethodsDescriptive analysis of the short-term results of the robotic and laparoscopic approach on 220 resections in 182 patients undergoing minimally invasive liver surgery.
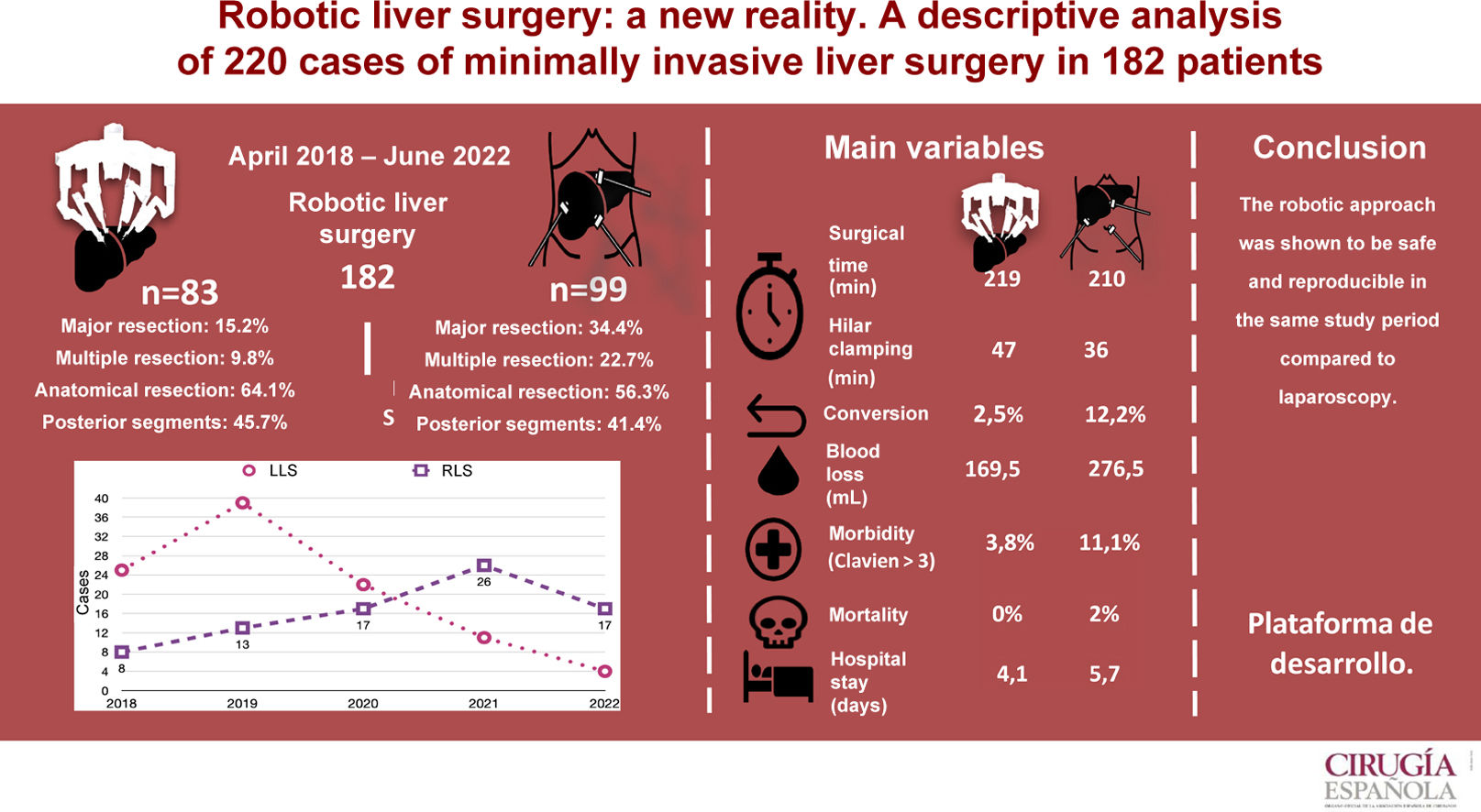
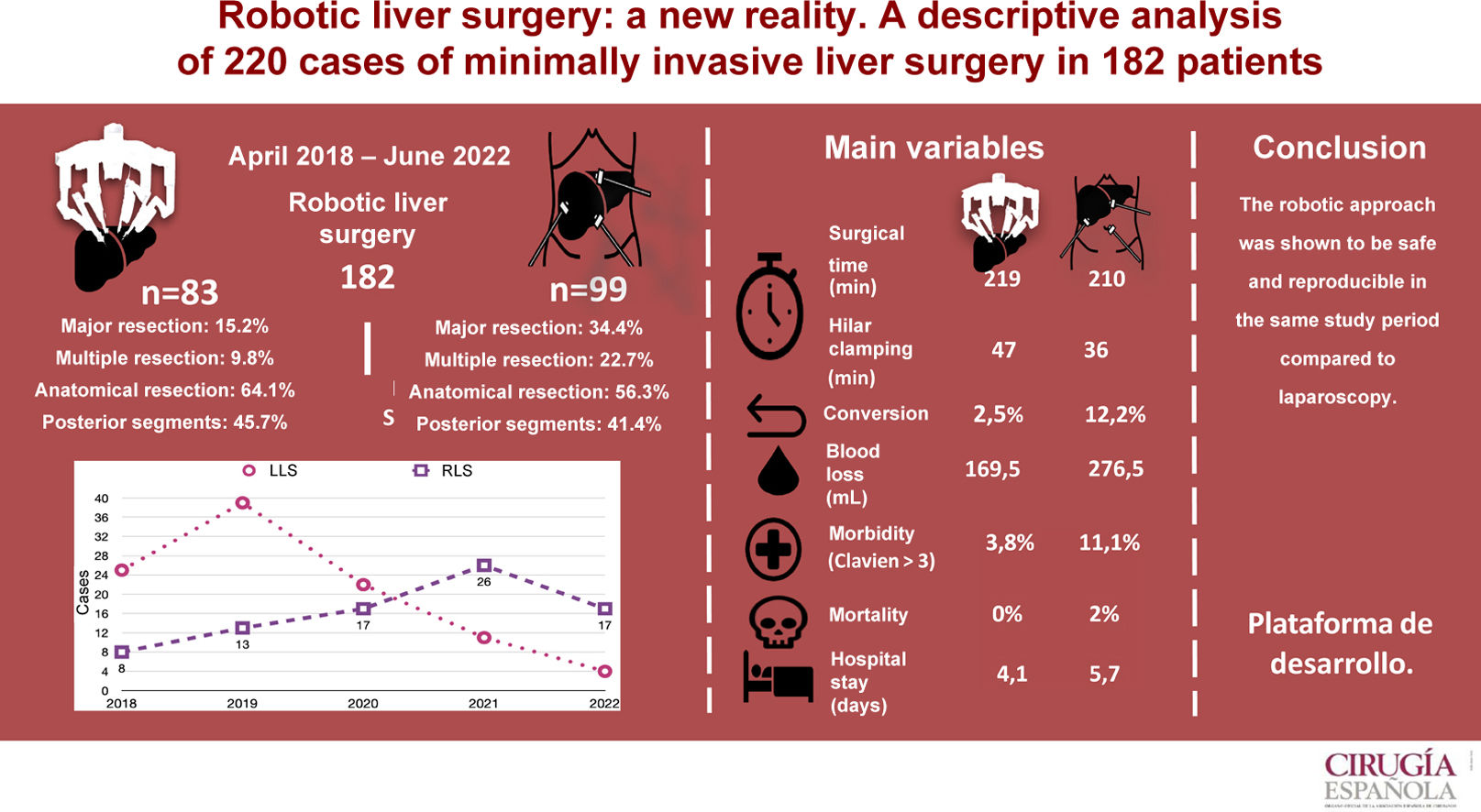
ResultsBetween April 2018 and June 2022, a total of 92 robotic liver resections (RLR) were performed in 83 patients and 128 laparoscopic (LLR) in 99 patients. The LLR group showed a higher proportion of major surgery (P < .001) and multiple resections (P = .002). The two groups were similar in anatomical resections (RLR 64.1% vs. LLR 56.3%). In the LLS group, the average operating time was 212 min (SD 52.1). Blood loss was 276.5 mL (100–1000) and conversion 12.1%. Mean hospital stay was 5.7 (SD 4.9) days. Morbidity was 27.3% and 2% mortality. In the RLS group, the mean operative time was 217 min (SD 53.6), blood loss 169.5 mL (100.900), and conversion 2.5%. Mean hospital stay was 4.1 (SD 2.1) days. Morbidity was 15%, with no mortality.
ConclusionMinimally invasive liver surgery is a safe technique, and in particular, RLS allows liver resections to be performed safely and reproducibly; it appears to be a non-inferior technique to LLS, but randomized studies are needed to determine the minimally invasive approach of choice in liver surgery.
El nivel de recomendación del abordaje robótico en la cirugía hepática es controvertido. Se realiza un análisis descriptivo, retrospectivo yunicéntrico de los resultados a corto plazo de la cirugía hepática robótica y laparoscópica en un mismo periodo.
MétodosAnálisis descriptivo del abordaje robótico y laparoscópico sobre 220 resecciones en 182 pacientes sometidos a cirugía hepática mínimamente invasiva.
ResultadosEntre abril de 2018 y junio de 2022 se realizaron 92 resecciones hepáticas robóticas (RHR) en 83 pacientes y 128 laparoscópicas (RHL) en 99 pacientes. Se observaron más resecciones mayores (p < 0,001) y más resecciones múltiples (p = 0,002) en el grupo CHL. El porcentaje de resecciones anatómicas fue similar (RHR: 64,1 vs. RHL: 56,3%). En el grupo CHL el tiempo medio operatorio fue de 212 min (DE: 52,1), las pérdidas hemáticas de 276,5 ml (100-1.000) y la tasa de conversión del 12,1%. La estancia media hospitalaria fue de 5,7 días (DE: 4,9), la morbilidad fue del 27,3%, con un 2% de mortalidad. En el grupo CHR el tiempo medio operatorio fue de 217 min (DE: 53,6), las pérdidas hemáticas fueron de 169,5 ml (100-900) y la tasa de conversión del 2,5%. La estancia media hospitalaria fue de 4,1 días (DE: 2,1) y la morbilidad fue del 15%, con mortalidad nula.
ConclusiónLa cirugía mínimamente invasiva hepática es una técnica segura y reproducible. La CHR permite realizar resecciones hepáticas con seguridad y parece ser una técnica no inferior a la CHL, pero para determinar el abordaje mínimamente invasivo de elección en cirugía hepática se requieren estudios aleatorizados.
The first laparoscopic liver surgery (LLS) in the world was published in 1991,1 and the first in Spain was in 2000.2 This minimally invasive surgery was subsequently validated in several international consensus documents,3–8 which granted LLS a high degree of acceptance and recommendation and after which its indications were expanded until it was almost on par with open liver surgery (OLS).9–11
Robotic liver surgery (RLS) was introduced in 200112–14 following the approval of the Da Vinci Surgical System15 by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). It consists of an interface console between the surgeon and a remote 4-arm articulated robot (the surgeon must be previously trained in laparoscopy16). Its use is currently very limited,17 but it is increasing around the world.10,18
Despite the fact that the oncological results appear to be similar to LLS for selected patients,19,20 the level of recommendation of RLS is still low; therefore, the creation of prospective registries is currently being proposed.19,21
The main objective of this study is to perform a descriptive analysis of the clinical indications and short-term surgical results of RLS and LLS in the same time period and in the same hospital by the same surgical team.
MethodsWe conducted a single-center retrospective descriptive analysis of minimally invasive liver surgery with intention to treat, using a prospective registry of cases. The study period began in April 2018 (when RLS was initially introduced at our hospital) and ended in June 2022. All patients were operated on at the same hospital and by the same group of 8 surgeons. Most patients were treated by the same surgeon, although 3 other surgeons in the group also have console certification. Our study included all cases of liver surgery, both malignant and benign, that were treated with liver resection. The liver resection nomenclature was recorded according to the Brisbane 2000 classification.22 Postoperative complications were recorded according to the Dindo–Clavien classification23 during the first 90 days after the procedure, including readmissions within the same period. The Comprehensive Complication Index (CCI)24 was calculated for all patients.
Selection criteriaThe inclusion criteria were common for both RLS and LLS, with no restrictions for ASA grade. Patients under 18 years of age and those who had undergone 2 or more previous laparotomies were excluded.
IndicationsThe indications for surgery were similar to those for OLS: liver resection for benign tumors only for symptomatic lesions or when radiological evaluation raised reasonable doubt; and liver resection for colorectal liver metastases in the absence of peritoneal carcinomatosis or unresectable disease. In patients with cholangiocarcinoma, lymphadenectomy of the hepatic hilum was included. In patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, only patients with well-compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh class A, 5 points) were included.
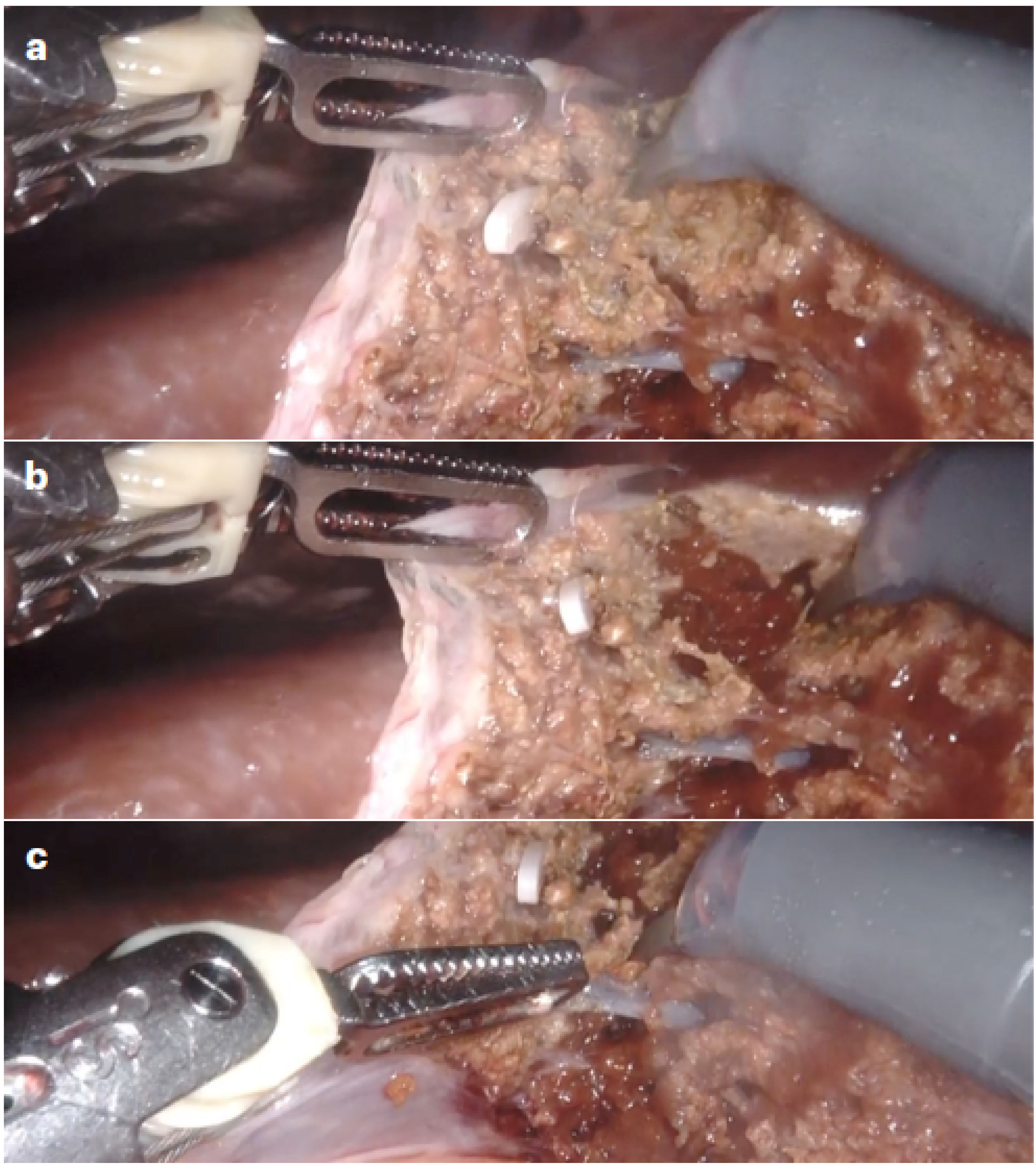
Robotic techniqueThe surgical protocol in RLS with the Da Vinci Xi Surgical System (Intuitive Surgical, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) included supine decubitus in French position, table at 15º anti-Trendelenburg, closed pneumoperitoneum (12 mmHg) and trocars above the umbilicus following a straight transverse line with the robot approaching from the patient’s right. For posterior lesions, the patient was positioned in a 90º left lateral decubitus position, and the table inclination was adjusted on demand by synchronizing the robotic arms with the surgical table. Docking was on the right of the patient with bipolar forceps (T1), 30° camera (T2), monopolar scissors (T3), and “tip up” grasping forceps (T4), plus a 12-cm accessory trocar between T2 and T3. “Pure” robotic parenchymal transection was performed without a vessel sealer but instead using a “microfracture-coagulation” system with bipolar forceps (port 1) and monopolar scissors (port 3), defined by microdislaceration of the parenchyma and the selective use of bipolar and monopolar energy, which provides for the selective isolation of the vascular pedicles, obtaining a blood-free plane equivalent to that obtained by laparoscopy (Fig. 1). Second-order portal radicals were divided with robotic Hem-o-loks and endostapler (Endowrist®; Intuitive) using a 45-mm white cartridge for the suprahepatic veins (or portal vein in the intra-Glissonian approach) and a 60-mm blue cartridge for the first-order portal radicals (in the extra-Glissonian approach).
Robotic transection of liver parenchyma using “microfracture-coagulation”.
Hepatic parenchyma transection using robotic “microfracture-coagulation” through the combined application of monopolar and bipolar energy: A) Initial position of the bipolar forceps and monopolar scissors; B) Microfracture action on the parenchymal surface to deepen the transection; C) Selective coagulation action after deep transection.
For LLS, the protocol included the patient in supine decubitus on a vacuum mattress in the French position, the table in 15º anti-Trendelenburg, closed pneumoperitoneum (12 mmHg) and 5 trocars at 60º working angles. Parenchymal transection was performed with an ultrasonic dissector-aspirator (CUSA; Integra®), for selective isolation of vascular and pedicular elements, and selective use of radiofrequency coagulation (Aquamantys®; Medtronic), obtaining a blood-free parenchymal transection plane. Division of third-order portal radicals was done with bipolar sealing (Ligasure® Bluntip; Covidien) and second-order radicals with robotic Hem-o-loks and articulated endostapler (Echelon Flex®; Ethicon), with a 45-mm white cartridge for suprahepatic veins (or portal vein in the intra-Glissonian approach) and a 60-mm blue cartridge for first-order portal radicals (in the extra-Glissonian approach).
In all cases, extracorporeal hilar clamping was performed by passing a tape through the epiploic foramen through a 5 mm trocar incision on the side contralateral to the resection, which allows for manual adjustment of the pressure on the hepatic pedicle. The specimen was extracted in an XL endobag through an accessory Pfannenstiel incision or by enlarging one of the trocars. We only closed the aponeurosis of the 11-mm (or reduction) trocars and the incision for specimen extraction. All patients followed the same “fast-track” postoperative recovery protocol,25 which included both preoperative multimodal prehabilitation26 and an enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) protocol.27
Statistical analysisWe applied either the Student’s t or Mann–Whitney U test for continuous variables, while Fisher’s exact test and Pearson’s chi-squared were applied for categorical variables. Variables were expressed by measures of frequency (percentage) for the qualitative variables, measures of central value for the quantitative variables, and mean (standard deviation) or median (range), according to their distribution. Double-tailed statistical significance was P < .05. All analyses were performed using SPSS software (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY).
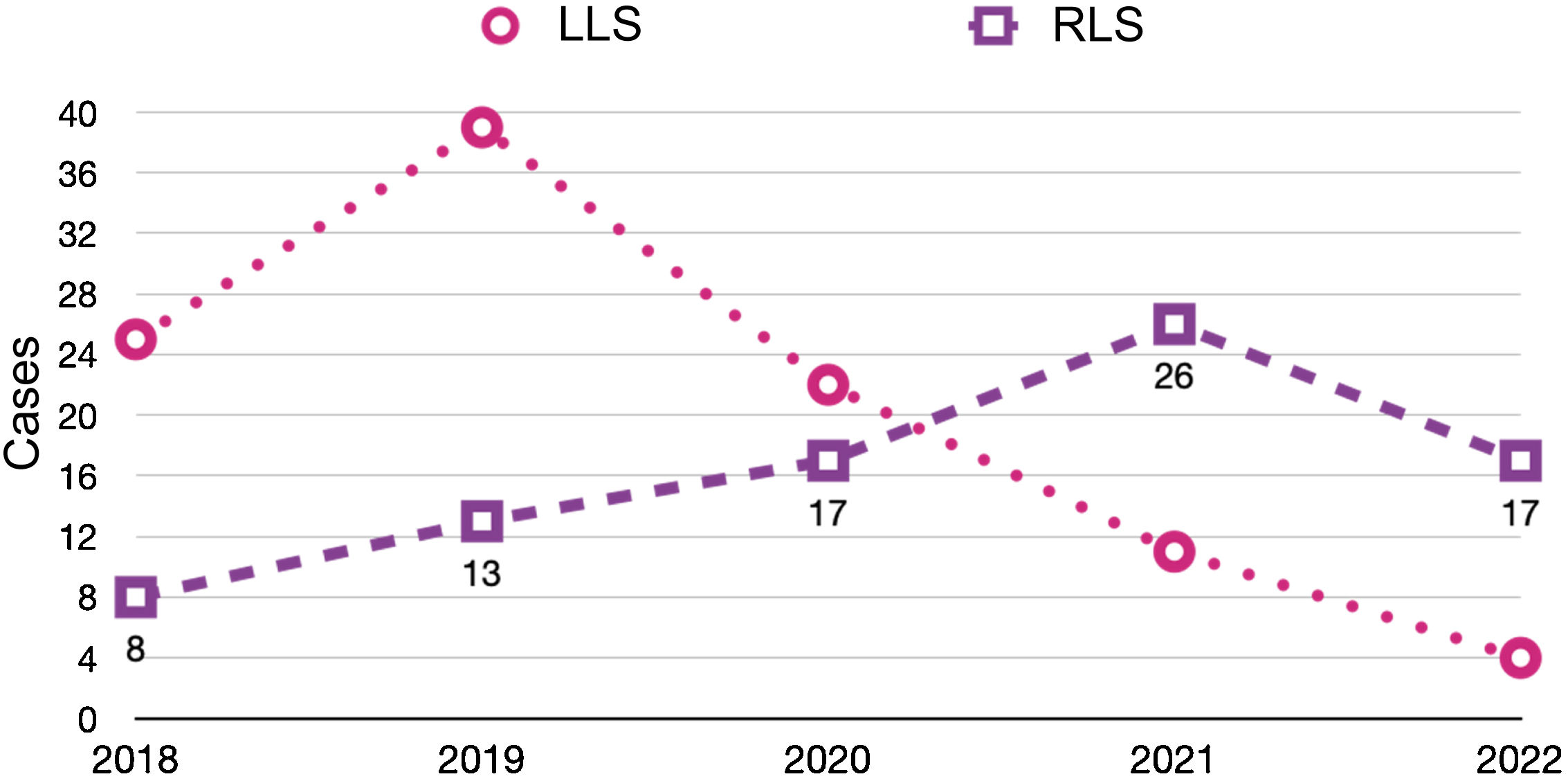
ResultsA total of 182 liver surgery patients were prospectively collected between April 2018 and June 2022, 83 of whom had been treated robotically (RLS) and 99 laparoscopically (LLS) (Fig. 2).
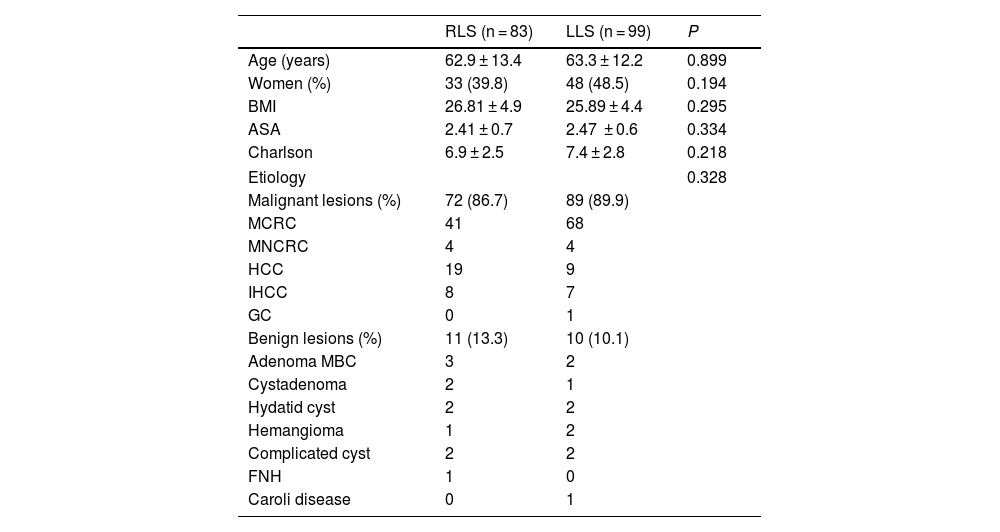
Patient characteristics are shown in Table 1 and demonstrate that the variables referring to age, sex, BMI, ASA and the Charlson index were similar for both groups. As for the etiological diagnosis (also found in Table 1), similar percentages of malignant pathology are observed (RLS 86.7% vs LLS 89.9%). Surgery for metastasis of colorectal origin is the most frequent in both groups, while a greater number of hepatocellular carcinomas treated by robotic surgery is observed.
Demographic and etiological data.
| RLS (n = 83) | LLS (n = 99) | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 62.9 ± 13.4 | 63.3 ± 12.2 | 0.899 |
| Women (%) | 33 (39.8) | 48 (48.5) | 0.194 |
| BMI | 26.81 ± 4.9 | 25.89 ± 4.4 | 0.295 |
| ASA | 2.41 ± 0.7 | 2.47 ± 0.6 | 0.334 |
| Charlson | 6.9 ± 2.5 | 7.4 ± 2.8 | 0.218 |
| Etiology | 0.328 | ||
| Malignant lesions (%) | 72 (86.7) | 89 (89.9) | |
| MCRC | 41 | 68 | |
| MNCRC | 4 | 4 | |
| HCC | 19 | 9 | |
| IHCC | 8 | 7 | |
| GC | 0 | 1 | |
| Benign lesions (%) | 11 (13.3) | 10 (10.1) | |
| Adenoma MBC | 3 | 2 | |
| Cystadenoma | 2 | 1 | |
| Hydatid cyst | 2 | 2 | |
| Hemangioma | 1 | 2 | |
| Complicated cyst | 2 | 2 | |
| FNH | 1 | 0 | |
| Caroli disease | 0 | 1 | |
Legend: RLS: robotic liver surgery; LLS: laparoscopic liver surgery; MCRC: metastatic colorectal cancer; MNCRC: metastatic non-colorectal cancer; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; IHCC: intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; GC: gallbladder cancer; MBC: mutated beta-catenin; FNH: focal nodular hyperplasia.
Data are expressed as means and standard deviation or as percentages.
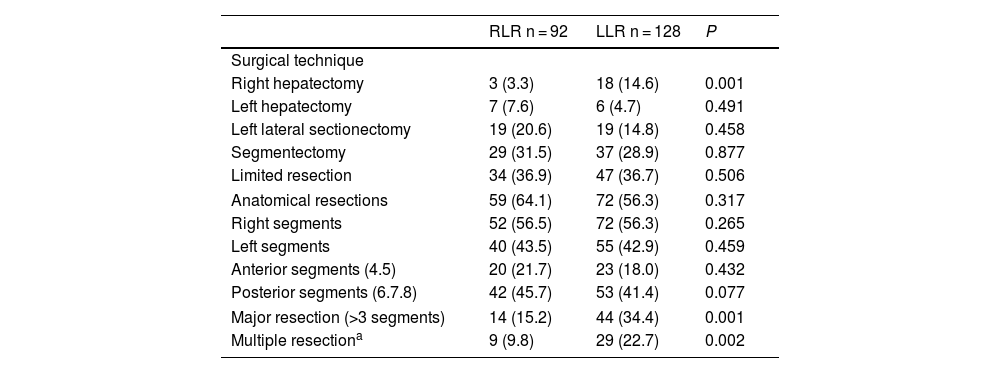
We analyzed 92 RLR and 128 LLR. More major resections (P = .001), right hepatectomies (P = .001), and multiple resections (P = .002) were performed in the LLS group. However, the percentages of left hepatectomies, left lateral sectionectomies, segmentectomies, limited resections, and anatomic resections performed were similar in both groups. The percentages of resections of right segments, left segments, posterior segments (6–8) and anterior segments were also similar.
Surgical technique. Operative and postoperative results.
| RLR n = 92 | LLR n = 128 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical technique | |||
| Right hepatectomy | 3 (3.3) | 18 (14.6) | 0.001 |
| Left hepatectomy | 7 (7.6) | 6 (4.7) | 0.491 |
| Left lateral sectionectomy | 19 (20.6) | 19 (14.8) | 0.458 |
| Segmentectomy | 29 (31.5) | 37 (28.9) | 0.877 |
| Limited resection | 34 (36.9) | 47 (36.7) | 0.506 |
| Anatomical resections | 59 (64.1) | 72 (56.3) | 0.317 |
| Right segments | 52 (56.5) | 72 (56.3) | 0.265 |
| Left segments | 40 (43.5) | 55 (42.9) | 0.459 |
| Anterior segments (4.5) | 20 (21.7) | 23 (18.0) | 0.432 |
| Posterior segments (6.7.8) | 42 (45.7) | 53 (41.4) | 0.077 |
| Major resection (>3 segments) | 14 (15.2) | 44 (34.4) | 0.001 |
| Multiple resectiona | 9 (9.8) | 29 (22.7) | 0.002 |
RLR: robotic liver resection; LLR: laparoscopic liver resection. Data expressed in frequencies and in percentages.
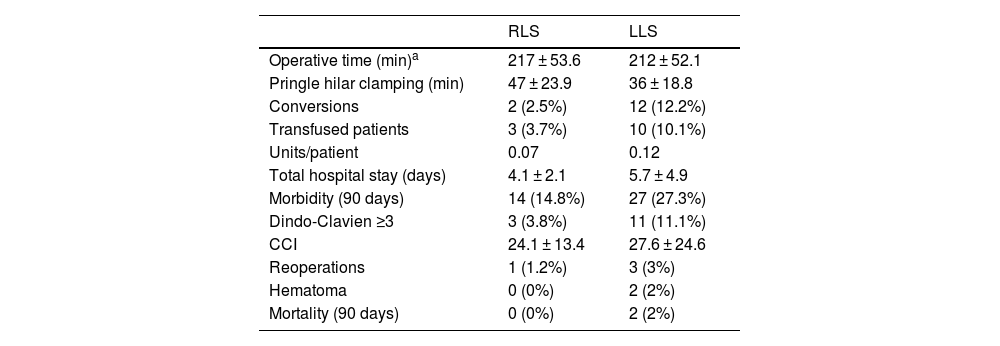
Mean surgical time was 217 min (SD 53.6), with a mean Pringle time of 48.5 min (SD 23.9). Blood loss was 169 mL (SD 126), including 44 cases of negligible bleeding recorded as equivalent to 100 mL, with a perioperative transfusion rate in the first 24 h of 3.7% (mean 0.07 units/patient). One case was converted to laparoscopic surgery due to irrecoverable failure of the energy system, which made it necessary to carry out the entire resection using the laparoscopic approach. Another case was converted to open surgery due to adhesion syndrome. Fourteen (14.8%) patients presented some type of morbidity, with a mean CCI of 24.1 (SD 13.4), 3 of which (3.8%) were Dindo–Clavien ≥3, including one case of reoperation for injury due to denudation of a loop during adhesiolysis maneuvers for trocar placement prior to docking. There were no cases of mortality. Mean hospital stay was 4.1 (SD 2.1) days.
Descriptive operative and postoperative results.
| RLS | LLS | |
|---|---|---|
| Operative time (min)a | 217 ± 53.6 | 212 ± 52.1 |
| Pringle hilar clamping (min) | 47 ± 23.9 | 36 ± 18.8 |
| Conversions | 2 (2.5%) | 12 (12.2%) |
| Transfused patients | 3 (3.7%) | 10 (10.1%) |
| Units/patient | 0.07 | 0.12 |
| Total hospital stay (days) | 4.1 ± 2.1 | 5.7 ± 4.9 |
| Morbidity (90 days) | 14 (14.8%) | 27 (27.3%) |
| Dindo-Clavien ≥3 | 3 (3.8%) | 11 (11.1%) |
| CCI | 24.1 ± 13.4 | 27.6 ± 24.6 |
| Reoperations | 1 (1.2%) | 3 (3%) |
| Hematoma | 0 (0%) | 2 (2%) |
| Mortality (90 days) | 0 (0%) | 2 (2%) |
RLS: robotic liver surgery; LLS: laparoscopic liver surgery. Data expressed as frequencies and percentages, means and standard deviation.
Mean operating time was 212 (SD 52.1) min with a mean Pringle time of 35 (SD 18.9) minutes. A blood loss of 276 (SD 256) mL was recorded (including negligible bleeding in 27 cases, recorded as equivalent to 100 mL), with a perioperative transfusion rate of 10.1% (mean 0.28 units/patient). Conversion to laparotomy was necessary in 12 patients (12.1%), 5 due to hemodynamic intolerance with dislocation of the right hepatic lobe (2), intolerance to hepatic reperfusion after hilar unclamping, or intraoperative bleeding (2), and 7 because of lack of progression of surgical dissection due to adhesions (2), invasion of the diaphragm, risk of tumor capsule rupture, technical difficulty in accessing the dissection site (2), and difficulty to locate a lesion. Twenty-seven (27.3%) patients presented some type of morbidity, with a mean CCI of 27.6 (SD 24.6), 11 of which (11.1%) were Dindo–Clavien >3. One reoperation was performed for postoperative stenosis of the bile duct after right hepatectomy, one due to evisceration of the laparotomy after conversion to OLS, and another due to intestinal obstruction caused by an adhesion band, requiring intestinal resection. There were 2 (2.1%) cases of 90-day mortality (one due to pulmonary progression of the unresected disease, and another due to postoperative liver failure after the second stage of ALPPS-type liver resection). The mean hospital stay was 5.7 (SD 4.9) days.
DiscussionEven though minimally invasive liver surgery presents better results than OLS,9–11 RLS has been the subject of controversy since its inception due to the absence of typical liver surgery instruments,12–16 such as the CUSA ultrasonic dissection device, radiofrequency coagulator, or bipolar sealer. However, it presents other advantages, such as the articulated instruments that allow the Glisson pedicles to be surrounded (especially on the left side) and facilitate sutures at bleeding points.16
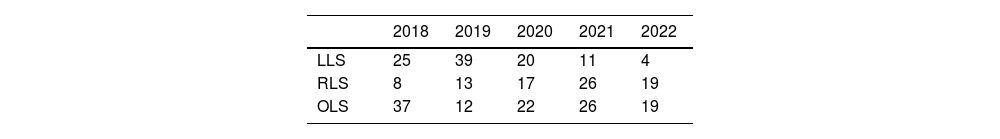
Recently published articles in RLS28–38 have described the feasibility and safety of robotic procedures with results equivalent to LLS in selected patients and in high-volume centers.39–43 Thus, the assessment of RLS has been that is it inferior to the laparoscopic approach.7,8 In our experience, use of the robotic approach has increased year after year, to the detriment of the laparoscopic approach, whose use has decreased (Table 4). Although the use of RLS is still very limited internationally,17 it is increasing worldwide,18 perhaps favored by a shorter learning curve44 that allows complex resections to be performed earlier,39 recording even minor complications45 and managing to complete a greater number of surgeries in a minimally invasive manner,40 optimizing parenchyma preservation55 and even reducing hospital stay.56 Our experience is consistent with recently published series that have reported a lower conversion rate to OLS.41,49,50
Evolution of the approaches used in elective liver surgery according to the year of the study period (April 2018–June 2022).
| 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLS | 25 | 39 | 20 | 11 | 4 |
| RLS | 8 | 13 | 17 | 26 | 19 |
| OLS | 37 | 12 | 22 | 26 | 19 |
RLS: robotic liver surgery; LLS: laparoscopic liver surgery; OLS: open liver surgery.
Total values include major and minor resections.
While LLS is in stage 3 IDEAL46 for Surgical Innovations (“early adopter”), RLS is currently in stage 2a (“pioneer”). Its development relies on the lessons already learned in LLS: the caudal approach to the hepatic hilum,47 the isolation of the pedicles following the Laennec capsule48 or the “cone unit”,49 allowing more precise and anatomical resections. Its development represents a sort of back-to-the-future moment for surgeons, since the lack of specific material for parenchyma transection has been compensated with the use of bipolar forceps and scissors, resembling the well-known kellyclasia of OLS.
The literature shows that the methodology of robotic parenchymal transection has not been systematized, and several series describe a hybrid method. In our case, we have used a purely robotic systematized procedure consisting of “microfracture-coagulation”, without utilizing instruments external to the platform (Fig. 1), thereby demonstrating that the standard robotic features are sufficient to reproduce internationally accepted results. In this manner, parenchyma transection could be somewhat slower than in the laparoscopic approach, resulting in longer hilar clamping time, which in turn could have contributed to obtaining little blood loss and a very low transfusion rate in the RLS group.
After surpassing the learning curve, experience in LLS enables the surgeon to perform a greater number of multiple and larger resections. Even so, using the robotic system, major resections have been achieved earlier than with LLS, such as the first major hepatectomy among the first 10 cases (the first left hepatectomy was the 3rd procedure performed, and the first right hepatectomy was the 6th) and the first ALPPS in situ liver bipartition before reaching 100 cases (82nd procedure). The fact that there were 10 major hepatectomies in the RLS group (3 right hepatectomies) but 24 in the LLS group (18 right hepatectomies) reflects the differing surgical complexity of the 2 groups, which precludes a comparative analysis of the results. This difference is possibly because, initially, the most complex cases were preferably treated laparoscopically. Later, however, the performance of major RHR increased as experience accumulated (Fig. 2), and the speed with which these were carried out for the first time has become notorious.
It should be noted that, despite the fact that the mean hospital stay was shorter for RLS, perhaps favored by having fewer major resections, in the LLS group there were 12 conversions that increased the overall hospital stay. The higher number of conversions in this group could be due to a better selection of patients in the RLS group.
It is surprising that, despite a longer hilar clamping time in the RLS group, the operative time in both groups was similar, perhaps due to the bagging time and/or the time spent on the revision of hemostasis. Although these data were not recorded, a future analysis could be of interest.
With regards to the limitations of this study, it should be noted that the 2 treatment groups are not comparable due to the higher incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma cases in the RLS group versus the LLS group and due to the higher incidence of major hepatectomies and multiple resections in the LLS group, so the comparative analysis of postoperative results is not possible. Although patient registry was carried out prospectively, the analysis of the results was retrospective. Furthermore, the limited number of major RHR did not allow for matching or subgroup analysis. Although this fact may bias the interpretation of the results, it should be noted that the rapid implementation of RLS made it possible to collect a similar number of cases in the same period of time.
Technically, the robot offers several “metahuman” capabilities, such as the ergonomic console, easy switching to indocyanine green (ICG) vision51 from the console controls whenever the surgeon desires, 10× magnification stereoscopic vision, 7° of movement, very good bipolar and monopolar energy, and elimination of essential tremor, all of which may influence the comparable proportion of anatomic or posterior segment resections (6–8) that are considered difficult laparoscopically.52–54 As indicated in the pan-European survey on liver surgery,57 up to 70% of liver surgeons stated that liver surgery will be performed using minimally invasive techniques in the future, and up to 30% favored the robotic route, even though 85% of surgeons have currently never performed RLS and 40% have never performed complex LLS.45
Thus, following the path of pioneers, the robot is utilized as a platform to integrate new and multidisciplinary technologies, such as intraoperative navigation with intraoperative ultrasound, ICG,51 3D models (virtual and physical)58,59 and their intraoperative consultation from the console, as well as augmented reality (AR),60 telemedicine61 and/or artificial intelligence (AI). The robotic platform also offers an unending data source, which will play a very decisive role in remote surgery and in AI-assisted surgery protocols. In the next 10–30 years, we anticipate that the coexistence of AI, AR, Big Data, and quantum computing will result in a disruptive leap forward in technology,62 giving robotic platforms unknown future potential, in which we surgeons we must get involved.
In conclusion, robotic surgery enables surgeons to perform liver resections safely and reproducibly with results not inferior to laparoscopic resections. In addition, as the learning curve could be shorter than in laparoscopic surgery, the robotic platform would also allow surgeons to perform complex resections earlier. The evolution of the robotic platform leads us to believe that robotic surgery will become established as the minimally invasive approach of choice in the immediate future, and randomized studies are necessary.
Conflict of interestsThe authors have no conflicts of interests to declare regarding the content of this manuscript.