To compare the costs and length of hospital stay among patients with a confirmed diagnosis of lung cancer (LC) prior to surgery versus those without confirmation.
MethodsThis retrospective, single-center study was conducted in patients who underwent a surgical procedure for LC, with or without a pathologically confirmed LC diagnosis prior to surgery, between March 2017 and December 2019. The main outcomes were costs and length of hospital stay (LOS).
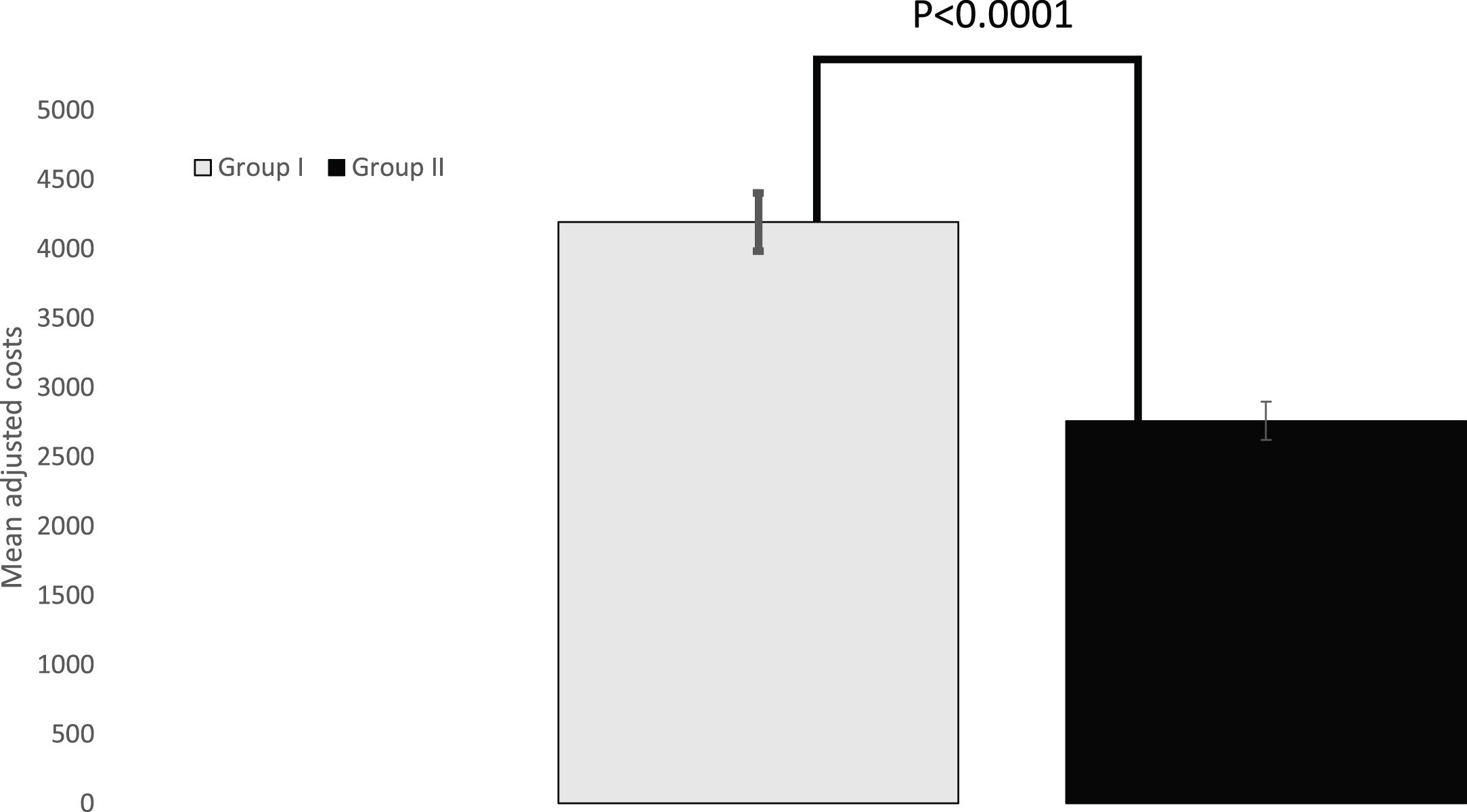
ResultsAmong the 269 patients who underwent surgery for lung cancer between March 2017 and December 2019, 203 (75.5%) patients underwent surgery due to a histopathological diagnosis, and 66 (24.5%) because of a Multidisciplinary Cancer Committee indication. The unadjusted mean cost was significantly lower in Group II (patients with surgery based on Multidisciplinary Cancer Committee criteria) (Є2,581.80 ± Є1,002.50) than in Group I (patients with histopathological diagnosis) (Є4,244.60 ± Є2,008.80), P < 0.0001. Once adjusted for covariables, there was a mean difference of −Є1,437.20 in the costs of Group II, P < 0.0001.
Unadjusted mean hospital stay was significantly longer in Group I (5.6 days) than in Group II (3.5 days).
ConclusionsThe results suggest that indicating surgical resection of lung cancer based on Multidisciplinary Cancer Committee criteria, rather than performing CT-guided percutaneous lung biopsy, may result in a significant decrease in cost and length of hospital stay.
Comparar los costes y la duración de la estancia hospitalaria entre los pacientes con un diagnóstico confirmado de cáncer de pulmón (CP) antes de la cirugía frente a los que no lo tienen.
MétodosEstudio retrospectivo y unicéntrico realizado en pacientes que se sometieron a un procedimiento quirúrgico de CP, con o sin diagnóstico de CP confirmado patológicamente antes de la cirugía, entre marzo de 2017 y diciembre de 2019. Los principales resultados fueron los costes y la duración de la estancia hospitalaria (LOHS).
ResultadosEntre los 269 pacientes sometidos a cirugía por cáncer de pulmón entre marzo de 2017 y diciembre de 2019, 203 (75,5%) pacientes se operan por diagnóstico histopatológico y 66 (24,5%) por indicación del Comité Oncológico Multidisciplinar. El coste medio no ajustado fue significativamente menor en el Grupo II (pacientes con intervención quirúrgica basada en criterios del Comité Multidisciplinar del Cáncer) (2.581,8 ± 1.002,5Є) que en el Grupo I (pacientes con diagnóstico histopatológico) (4.244,6Є ± 2.008,8), p < 0,0001. Una vez ajustados por covariables, hubo una diferencia media de −1.437,2Є en los costes del Grupo II, p < 0,0001.
La estancia hospitalaria media no ajustada fue significativamente mayor en el Grupo I (5,6 días) que en el Grupo II (3,5 días).
ConclusionesLos resultados sugieren que indicar la resección quirúrgica del cáncer de pulmón basándose en los criterios del Comité Multidisciplinar del Cáncer, en lugar de realizar una biopsia pulmonar percutánea guiada por TAC, puede suponer una disminución significativa del coste y de la duración de la estancia hospitalaria.
Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer incidence and mortality worldwide.1–3 For both sexes combined, lung cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer (11.6% of the total cases) and the leading cause of cancer death (18.4% of the total cancer deaths).2 In Spain, lung cancer was responsible of 22,930 deaths (20.3% of total cancer deaths) in 2020 year.4
Lung cancer remains as one of the cancers with the poorest prognosis, mainly due to the fact that most patients are diagnosed at an advanced stage.5 Surgery represents a valuable strategy for treating lung cancer patients with curative purposes.6–9 Unfortunately, this strategy is only feasible for a minority of patients, since approximately three quarters of lung cancer patients present when the disease is in advanced stages.10
Early detection would be, therefore, a valuable strategy for diagnosing disease at an earlier, asymptomatic, and potentially curable stage. According to the results of the National Lung Cancer Screening Trial (NLST), low-dose computed tomography (CT) was associated with earlier lung cancer detection, which led to a 20% reduction in lung cancer-related death and an overall all-cause mortality reduction of 6.7%.11 Additionally, the Dutch-Belgian NELSON trial recently confirmed that screening for lung cancer with low radiation dose CT reduces lung cancer mortality.12
Despite their relevance, several issues should be addressed for translating these findings into clinical practice. "Who should be screened"; "How often screening should be performed"; and "For how long" are key questions that need an answer.
Moreover, screening programs entail significant logistic and economic implications. A health economic evaluation of the NLST found that CT screening was associated with an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of $52,000/life-year gained or $81,000/quality-adjusted life year (QALY) gained.13 In a previous study published by our group, surgical treatment was associated with better clinical outcomes and was identified as the most cost-effective lung cancer therapeutic strategy. These results provided evidence supporting the implementation of screening programs in a real setting.14
Special consideration merits the solitary pulmonary nodules, which represent a common problem and are usually a diagnostic challenge. Additionally, implementation of CT screening programs may entail an increase in solitary pulmonary nodules prevalence.15
Among the different methods for obtaining lung tissue before resection, CT-guided percutaneous lung biopsy is widely used.16–18 An alternative strategy is collecting a tissue sampling at the time of surgery. While the patient is under general anesthesia, a small tissue sample is resected and sent to histopathological evaluation. Surgery resumes once diagnosis has been established. If malignancy is diagnosed the patient undergoes a surgical resection; while cases of benign disease typically led to conclusion of the surgery.19
Because the most cost-effective approach has not been established yet, we have considered whether it was necessary to have the diagnosis before the patient enters the operating room.
This study aimed to compare the costs attributed directly to the surgical procedure between patients who underwent surgery with a prior histopathological diagnosis of lung cancer and those who went to the operating room with a diagnosis of suspected lung cancer according to Multidisciplinary Cancer Committee criteria.
MethodsRetrospective and single center study.
The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Hospital, which waived the need for written informed consent of the participants.
PatientsThe study sample included all the patients who underwent a surgical procedure for lung cancer, independently of diagnosis, between March 2017 and December 2019. The surgical indication was established by the multi-disciplinary LC Committee in our Institution. The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Board of our institution.
Multidisciplinary cancer committee criteriaComprises a core group of specialists from disciplines including medical oncology, pulmonologist, radiation oncology, radiology, haematology, pathology, nuclear medicine, thoracic surgery and nursing. Regular meetings provide a forum for this core group to discuss patient cases in terms of key radiographic and pathological findings; diagnostic and/or therapeutic options and the best approach for each patient; integration of evidence-based guidelines focus on Diagnosis: pathology and molecular testing, Disease staging and treatment options used as criteria; and communication of clinical trial findings.
Direct costsCost analysis was carried out from the perspective of the regional health System Catalonian Institute of Health (CIH).
Cost per hospital day and, therefore, total costs for hospitalization were calculated according to the information supplied by the Hospital.
Besides the cost of the procedure, the different items considered in the model included cost of personnel, equipment, hospital stay, consumables, drugs, laboratory tests, other medical supplies, structure, and perioperative complications.
The data have been considered as a whole and an individualized analysis of the different cost items has not been carried out, beyond the hospital stay.
Other costs, such as transport services, food services, other non-medical materials, etc. have not been taken into account in this study.
Study groupsSubjects were divided into two groups: [I] patients with a histopathology diagnosis before surgery, by using CT-guided fine needle aspiration; [II] Patients with a low-dose CT positive screening result according to the NLST protocol (any non-calcified nodule with a maximum diameter ≥4 mm),11 but without a histopathological diagnosis prior to the surgery. According to the Multidisciplinary Cancer Committee criteria, that comprises a core group of specialists from disciplines including medical oncology, radiation oncology, radiology, pneumonology pathology, nuclear medicine, thoracic surgery, and nursing.Patients were selected for undergoing therapeutic diagnostic surgery based on their clinical and radiologic characteristics.
Study parametersFor patients in group I, data collected included demographics; lung cancer stage, according to the 8th edition of the tumor, node and metastasis (TNM) classification system20; tumor stage; smoking habit; comorbidities; diagnosis; neoadjuvant and adjuvant therapy; forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1), performance access; lung excision procedure; lobectomy procedure site; days of hospital stay; and total cost per patient.
For patients in group II, demographics; smoking habit; histopathological diagnosis (at the time of surgery); TNM classification system20; tumor stage; FEV1; Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) stage, according to the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) committee classification21; performance access; lobectomy procedure site; days of hospital stay; and total cost per patient were assessed.
Statistical analysisMain outcome was the mean cost. Secondary outcome was the length of hospital stay.
Statistical analysis
A standard statistical analysis was performed using the MedCalc® Statistical Software version 19.7.1 (MedCalc Software Ltd, Ostend, Belgium; https://www.medcalc.org; 2021) and the SPSS IBM Corp. Released 2019. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 26.0. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp.
Descriptive statistics number (percentage), mean [standard deviation (SD)], mean [95% confidence interval (95% CI)], mean [standard error (SE)], median (95% CI), or median [interquartile range (IqR)] were used, as appropriate.
Data were tested for normal distribution using a D’Agostino-Pearson test.
The one-way ANOVA test or the Kruskal-Wallis test were used to compare differences between groups. Post hoc analysis for pair wise comparisons were done with the Scheffé's method (ANOVA) or the Conover method (Kruskal-Wallis). The Mann–Whitney U test was used in the evaluation of the pre surgery clinical and demographic parameters between groups.
The analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was used in the evaluation of the total costs and day of hospital stay between study groups. The model included “Study group” as a factor and age, sex, smoking habit, TNM, tumor stage, FEV1, and performance access as covariates.
Categorical variables were compared using a Chi-square test and a Fisher`s exact test, as needed. P value of < 0.05 was considered significant.
ResultsAmong the 269 patients who underwent a surgical procedure for lung cancer between March 2017 and December 2019, 203 (75.5%) patients went into the theater with a histopathological diagnosis and 66 (24.5%) ones with Multidisciplinary Cancer Committee indication.
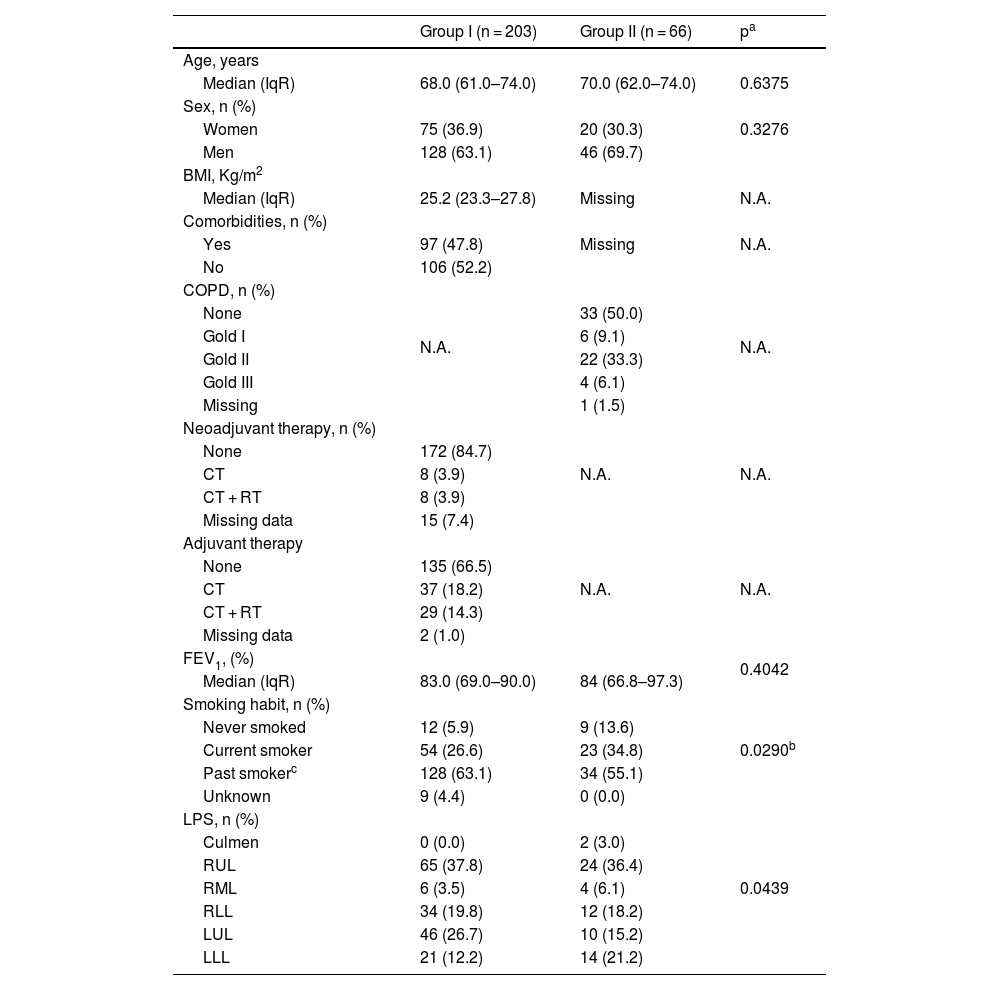
Median age was 68 years (IqR: 61.0–74.0 years) and 70.0 years (IqR: 62.0–74.0) years in the Groups I and II, respectively (Hodges–Lehmann median difference: 1.0 years; 95%CI: −2.0–3.0 years; p = 0.6375). The proportion of women was 36.9% (75/203) in Group I and 30.3% (20/66) in Group II, p = 0.3306. Table 1 summarizes the main presurgical demographic and clinical characteristics.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of the study sample.
| Group I (n = 203) | Group II (n = 66) | pa | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | |||
| Median (IqR) | 68.0 (61.0–74.0) | 70.0 (62.0–74.0) | 0.6375 |
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Women | 75 (36.9) | 20 (30.3) | 0.3276 |
| Men | 128 (63.1) | 46 (69.7) | |
| BMI, Kg/m2 | |||
| Median (IqR) | 25.2 (23.3–27.8) | Missing | N.A. |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | N.A. | ||
| Yes | 97 (47.8) | Missing | |
| No | 106 (52.2) | ||
| COPD, n (%) | N.A. | N.A. | |
| None | 33 (50.0) | ||
| Gold I | 6 (9.1) | ||
| Gold II | 22 (33.3) | ||
| Gold III | 4 (6.1) | ||
| Missing | 1 (1.5) | ||
| Neoadjuvant therapy, n (%) | N.A. | N.A. | |
| None | 172 (84.7) | ||
| CT | 8 (3.9) | ||
| CT + RT | 8 (3.9) | ||
| Missing data | 15 (7.4) | ||
| Adjuvant therapy | N.A. | N.A. | |
| None | 135 (66.5) | ||
| CT | 37 (18.2) | ||
| CT + RT | 29 (14.3) | ||
| Missing data | 2 (1.0) | ||
| FEV1, (%) | 0.4042 | ||
| Median (IqR) | 83.0 (69.0–90.0) | 84 (66.8–97.3) | |
| Smoking habit, n (%) | 0.0290b | ||
| Never smoked | 12 (5.9) | 9 (13.6) | |
| Current smoker | 54 (26.6) | 23 (34.8) | |
| Past smokerc | 128 (63.1) | 34 (55.1) | |
| Unknown | 9 (4.4) | 0 (0.0) | |
| LPS, n (%) | 0.0439 | ||
| Culmen | 0 (0.0) | 2 (3.0) | |
| RUL | 65 (37.8) | 24 (36.4) | |
| RML | 6 (3.5) | 4 (6.1) | |
| RLL | 34 (19.8) | 12 (18.2) | |
| LUL | 46 (26.7) | 10 (15.2) | |
| LLL | 21 (12.2) | 14 (21.2) |
IqR, Interquartile range; BMI, Body mass index; COPD, Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CT, Chemotherapy; RT, Radiotherapy; FEV1, Forced expiratory volume in 1 s; LPS, Lobectomy procedure site; RUL, Right upper lobule; RML, Right middle lobule; RLL, Right lower lobule; LUL, Left upper lobule; LLL, Left lower lobule; NA, Not applicable.
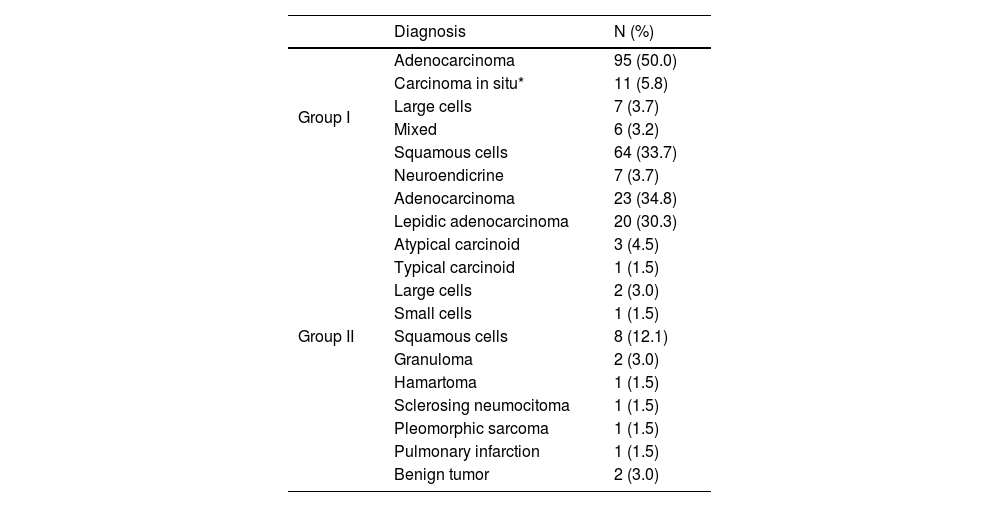
Regarding diagnosis, adenocarcinoma was the most frequently diagnosed cancer in both groups; followed by squamous cell in the Group I and Lepidic adenocarcinoma in group II (Table 2). In the Group II, 8 (12.1%) patients had a final histopathological diagnosis of benign lesions.
Overview of the histopathological diagnosis.
| Diagnosis | N (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Group I | Adenocarcinoma | 95 (50.0) |
| Carcinoma in situ* | 11 (5.8) | |
| Large cells | 7 (3.7) | |
| Mixed | 6 (3.2) | |
| Squamous cells | 64 (33.7) | |
| Neuroendicrine | 7 (3.7) | |
| Group II | Adenocarcinoma | 23 (34.8) |
| Lepidic adenocarcinoma | 20 (30.3) | |
| Atypical carcinoid | 3 (4.5) | |
| Typical carcinoid | 1 (1.5) | |
| Large cells | 2 (3.0) | |
| Small cells | 1 (1.5) | |
| Squamous cells | 8 (12.1) | |
| Granuloma | 2 (3.0) | |
| Hamartoma | 1 (1.5) | |
| Sclerosing neumocitoma | 1 (1.5) | |
| Pleomorphic sarcoma | 1 (1.5) | |
| Pulmonary infarction | 1 (1.5) | |
| Benign tumor | 2 (3.0) |
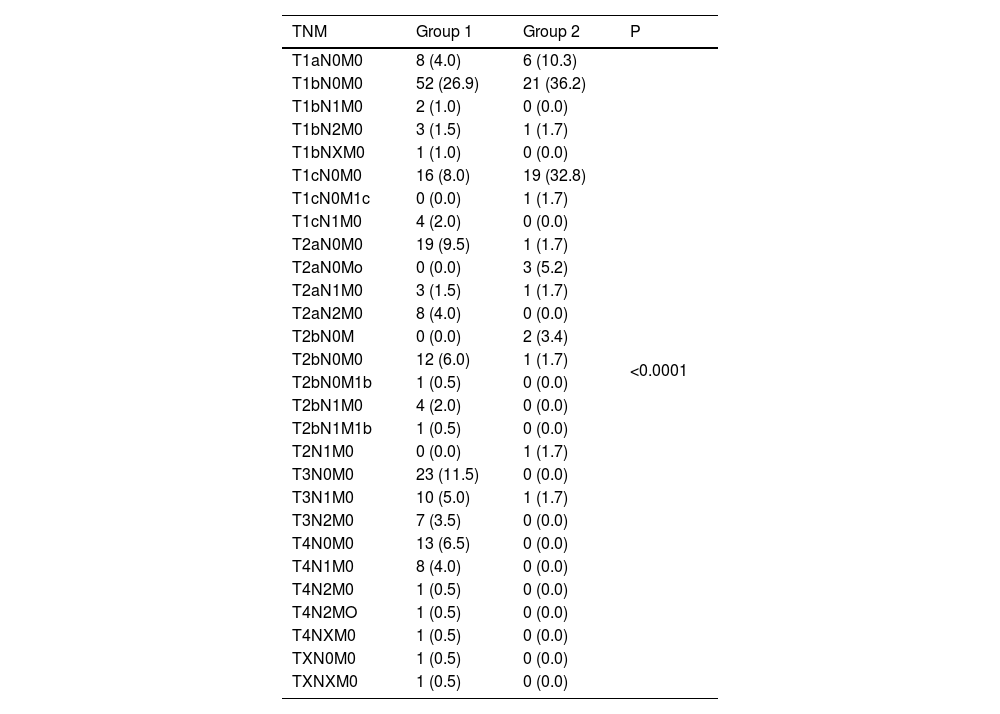
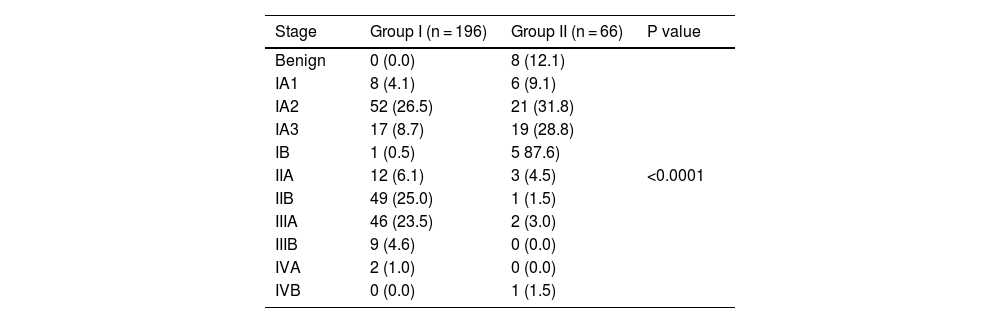
The Tables 3 and 4 show the tumor stage.
Lung cancer stage, according to the 8th edition of the tumor, node and metastasis (TNM) classification system.
| TNM | Group 1 | Group 2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1aN0M0 | 8 (4.0) | 6 (10.3) | <0.0001 |
| T1bN0M0 | 52 (26.9) | 21 (36.2) | |
| T1bN1M0 | 2 (1.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| T1bN2M0 | 3 (1.5) | 1 (1.7) | |
| T1bNXM0 | 1 (1.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| T1cN0M0 | 16 (8.0) | 19 (32.8) | |
| T1cN0M1c | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.7) | |
| T1cN1M0 | 4 (2.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| T2aN0M0 | 19 (9.5) | 1 (1.7) | |
| T2aN0Mo | 0 (0.0) | 3 (5.2) | |
| T2aN1M0 | 3 (1.5) | 1 (1.7) | |
| T2aN2M0 | 8 (4.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| T2bN0M | 0 (0.0) | 2 (3.4) | |
| T2bN0M0 | 12 (6.0) | 1 (1.7) | |
| T2bN0M1b | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | |
| T2bN1M0 | 4 (2.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| T2bN1M1b | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | |
| T2N1M0 | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.7) | |
| T3N0M0 | 23 (11.5) | 0 (0.0) | |
| T3N1M0 | 10 (5.0) | 1 (1.7) | |
| T3N2M0 | 7 (3.5) | 0 (0.0) | |
| T4N0M0 | 13 (6.5) | 0 (0.0) | |
| T4N1M0 | 8 (4.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| T4N2M0 | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | |
| T4N2MO | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | |
| T4NXM0 | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | |
| TXN0M0 | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | |
| TXNXM0 | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) |
P value was calculated by using Chi-squared test.
Lung cancer stage.
| Stage | Group I (n = 196) | Group II (n = 66) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | 0 (0.0) | 8 (12.1) | <0.0001 |
| IA1 | 8 (4.1) | 6 (9.1) | |
| IA2 | 52 (26.5) | 21 (31.8) | |
| IA3 | 17 (8.7) | 19 (28.8) | |
| IB | 1 (0.5) | 5 87.6) | |
| IIA | 12 (6.1) | 3 (4.5) | |
| IIB | 49 (25.0) | 1 (1.5) | |
| IIIA | 46 (23.5) | 2 (3.0) | |
| IIIB | 9 (4.6) | 0 (0.0) | |
| IVA | 2 (1.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| IVB | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.5) |
Unadjusted mean cost was significantly lower in the Group II (patients with surgical intervention based on Multidisciplinary Cancer Committee criteria) (2,581.8 ± 1,002.5Є; 95% CI: 2,335.3–2,828.2) than in the Group I (patients with histopathological diagnosis) (4,244.6Є ± 2,008.8; 95% CI: 3,966.6–4,522.6), p < 0.0001. Once adjusted by covariates, there was a mean difference of −1,437.2Є (standard error of the mean: 291.2Є; 95% CI: −2,010.8 to −863.7Є) in the Group II costs, p < 0.0001 (Fig. 1).
Unadjusted mean hospital stay was significantly longer in the Group I (mean 5.6 days; 95% CI: 5.4–5.8 days) than in the Group II (3.5 days; 95% CI: 3.4–3.7 days), (Mean difference 2.1 days; 95% CI: 1.7–2.5 days, p < 0.0001). Once adjusted by covariates, as compared to Group II, Group I was associated with a significantly higher length of hospital stay (mean difference 1.7 days; 95% CI: 1.3–2.1 days; p < 0.0001).
In our study, performance access was significantly associated with both length of hospital stay and total costs. Unadjusted mean of hospital stay and costs were 4.6 ± 1.5 days and 3,456.1 ± 1854.9Є, respectively, in patients who underwent video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) versus 6.0 ± 1.6 days and 4,511.3 ± 1938.6Є, respectively, in patients who underwent open thoracotomy, p < 0.0001 each, respectively.
Moreover, after adjusting by covariates (age, sex, smoking habit, TNM, tumor stage, FEV1, lobectomy procedure site, and study group) VATS was associated with a significantly shorter hospital stay (mean difference: −0.75 days; 95% CI: −1.13 to −0.37 days); p = 0.0001) and lower total costs (mean difference: −503.1Є; 95% CI: −1,003.4 to −2.8; p = 0.0487) (adjusted by age, sex, age, sex, smoking habit, TNM, tumor stage, FEV1, lobectomy procedure site, length of hospital stay, and study group).
DiscussionThe results of the current study suggested that indicating lung cancer surgical resection based on the Multidisciplinary Cancer Committee criteria, instead of performing CT-guided percutaneous lung biopsy, may result in a significant decrease in cost and length of hospital stay.
These results disagree from those reported by Barnett et al.,19 who found that in patients with solitary pulmonary nodules, pre-surgical CT guide percutaneous lung biopsy was the most effective strategy.
Nevertheless, the results of our study were in agreement with those published by Cho et al.,22 who found that in nodular ground-glass opacities with high suspicious of malignancy, surgery resection without previous tissue histopathological diagnosis was more cost-effective and reduced the length of hospital stay.
Although it has been published that CT-guided fine needle aspiration may save money by preventing unneeded surgery,23 this was based on the assumption that rates of resection of nonmalignant lung nodules are high. In addition, collecting a tissue sampling at the time of surgery may be associated with lengthening of the operating room time in approximately 45 min.19 However, despite this fact, and after adjusting by different covariates, in our study this strategy was more cost-effective than CT-guided fine needle lung biopsy.
Current guidelines emphasize a systematic approach to pulmonary nodules evaluation, with probability assessment based on clinical and radiographic characteristics.17,24,25 Pulmonary nodules may be classified according to their probability of malignancy. Those with a high probability of malignancy should be evaluated aggressively and considered for surgical resection.24 Low-dose chest CT scanning has been suggested as a screening tool, especially in the presence of high-risk factors for lung cancer. Although this procedure has been associated with a significant reduction in lung cancer-related mortality rates,11,12 it might be affected by a large rate of false positives.11 However, the use of validated clinical malignancy probability models can help to discriminate benign from malignant nodules, guiding clinicians and patients when making management decisions.26 And going further, and look into the future, we mustn’t forget about artificial intelligence (AI). It is being increasingly used in the diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer. AI algorithms can help in image analysis for the early detection of lung cancer through CT scans, making it more accurate and efficient compared to manual interpretation. Additionally, AI can assist in the analysis of molecular and genetic data, helping to personalize treatment plans and predicting patients' response to various therapies. However, it's important to note that AI is not a substitute for human expertise and judgment in medical decision-making and should be used as an aid.
On average, approximately 25 % of the thoracic surgical procedures performed during the various randomized controlled lung cancer screening trials were done for benign nodules.27 Nevertheless, in our study, only 8 (12.1%) had a confirmed histopathological diagnosed of benignity. It should be highlighted that the definition of a positive screening result may differ substantially among the different protocols, which critically impacts on the number of false-positive scans.
Although in Group II, benign processes were associated with lower costs (Hodges–Lehmann median difference: 319.4Є; 95% CI: −215.0–863.0Є), such a difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.3163).
In a previous study, we have found that implementation of lung cancer screening programs is beneficial for both patients and health care systems.14 Additionally, it has been observed that survival time decreases significantly with progression of disease, with a 5-year survival time declining from 50 % for clinical stage IA to 43%, 36%, 25%, 19%, 7% and 2% for stages IB, IIA, IIB, IIIA, IIIB and IV, respectively.28
VATS lobectomy for patients with early-stage lung cancer is a standard surgical treatment, and is associated with lower morbidity and improved survival rates compared with open thoracotomy.29 Additionally, VATS is potentially more cost-effective than thoracotomy.30,31 Although in our study, VATS was performed in subjects with less advanced cancer stages, after adjusting by different covariates, including age, sex, tumor stage, FEV1, lobectomy procedure site, and study group, VATS was associated with lower costs and shorter hospital stay than open thoracotomy.
Among the different limitations of the current study, its retrospective design may be the most important one. Selection bias and confounding factors are inherent to retrospective studies. As second limitation, the accuracy of the Multidisciplinary Cancer Committee criteria has not been assessed. Nevertheless, in the current study 58 (87.9%) patients had a confirmed histopathological diagnosed of malignancy. In fact, Multidisciplinary Cancer Committee approach may be the best way for managing cancer patients, especially the more complex cases. However, it should be noted that requires behavior changes and specific logistic requirements.32–35 Additionally, our study took into account only the direct medical costs related to lung cancer treatment. Other costs, such as transportation services, food expenses, non-medical materials, and working time lost, were not considered. However, providing comprehensive data on expenditures of lung cancer care is highly complex because treatment strategies and survival need to be taken into consideration.
Despite these limitations, this study suggests that indicating lung cancer surgery based on Multidisciplinary Cancer Committee criteria is more costs effective than do it based on pre-surgical CT guide biopsy. Additionally, our study also found that independently of the cancer stage and demographic variables, VATS was associated with lower costs than open thoracotomy.
Further studies are needed for establishing the positive and negative likelihood ratios of our Multidisciplinary Cancer Committee criteria, as well as their positive and negative predictive values.
Author contributionAll authors met the ICMJE authorship criteria. All authors made substantial contributions to conception, design, analysis and interpretation of data, contributed to writing the article, provided critical revision of the manuscript, and approved the final version.
Availability of materials and dataThe datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of interestNone of the authors have any conflict of interest to declare.
Ethics declaration“All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The local ethics committee waived the need for written informed consent of the participants for the study”.
Ethics approvalThis study was approved by the local ethics committees and was performed with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Statistics assistance was provided by Antonio Martinez (MD) of Ciencia y Deporte ltd.