En 2017 se emprendió el Registro Nacional de Politraumatismos (RNP) a nivel estatal español, cuya finalidad residía en mejorar la calidad de la atención al paciente politraumatizado grave y evaluar el uso de recursos y estrategias de tratamiento. El objetivo de este trabajo es presentar los datos recogidos en el RNP hasta la actualidad.
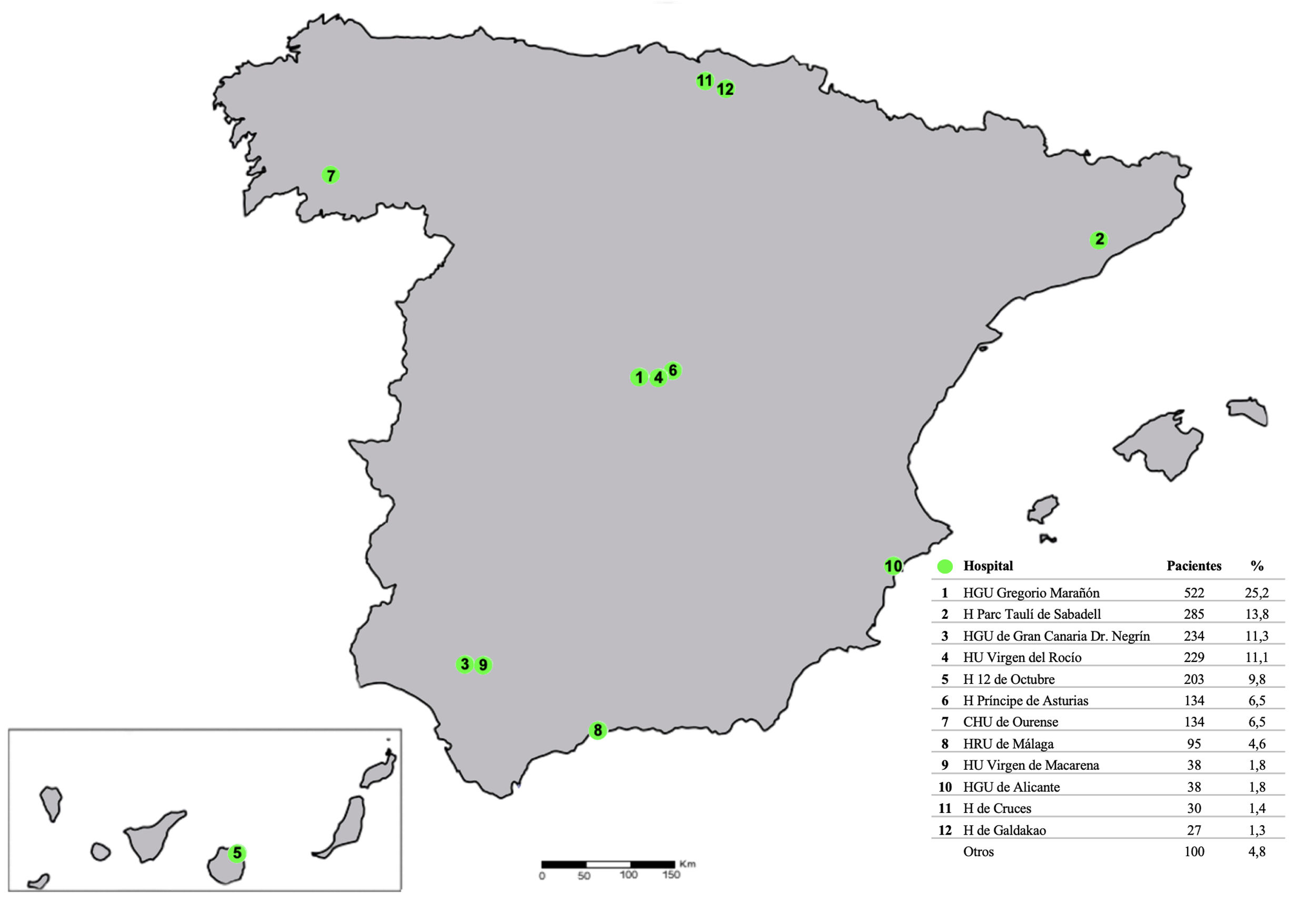
MétodosEstudio observacional retrospectivo a partir de los datos recogidos prospectivamente en el RNP. Se incluyen pacientes mayores de 14 años, con ISS≥15 o mecanismo de trauma penetrante, atendidos en 17 hospitales de tercer nivel de España.
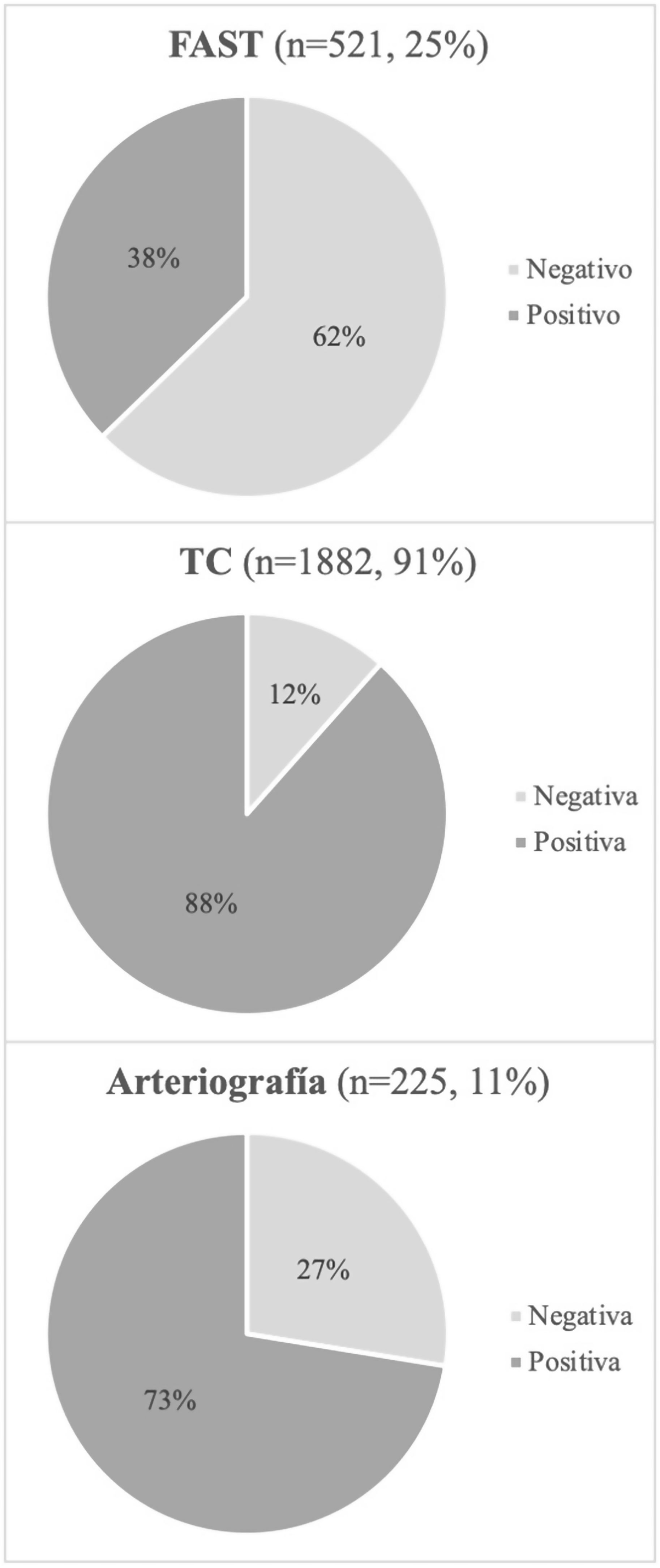
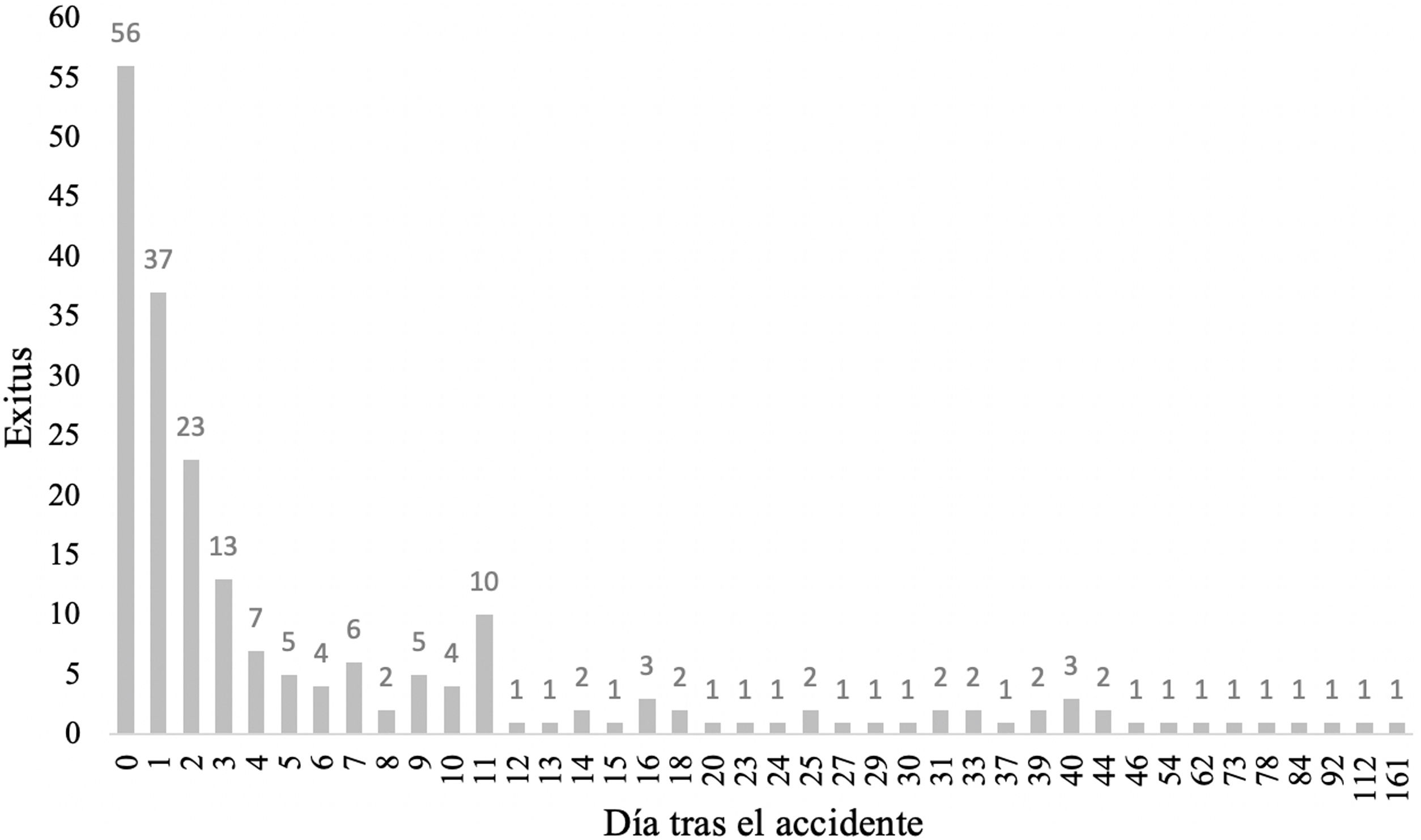
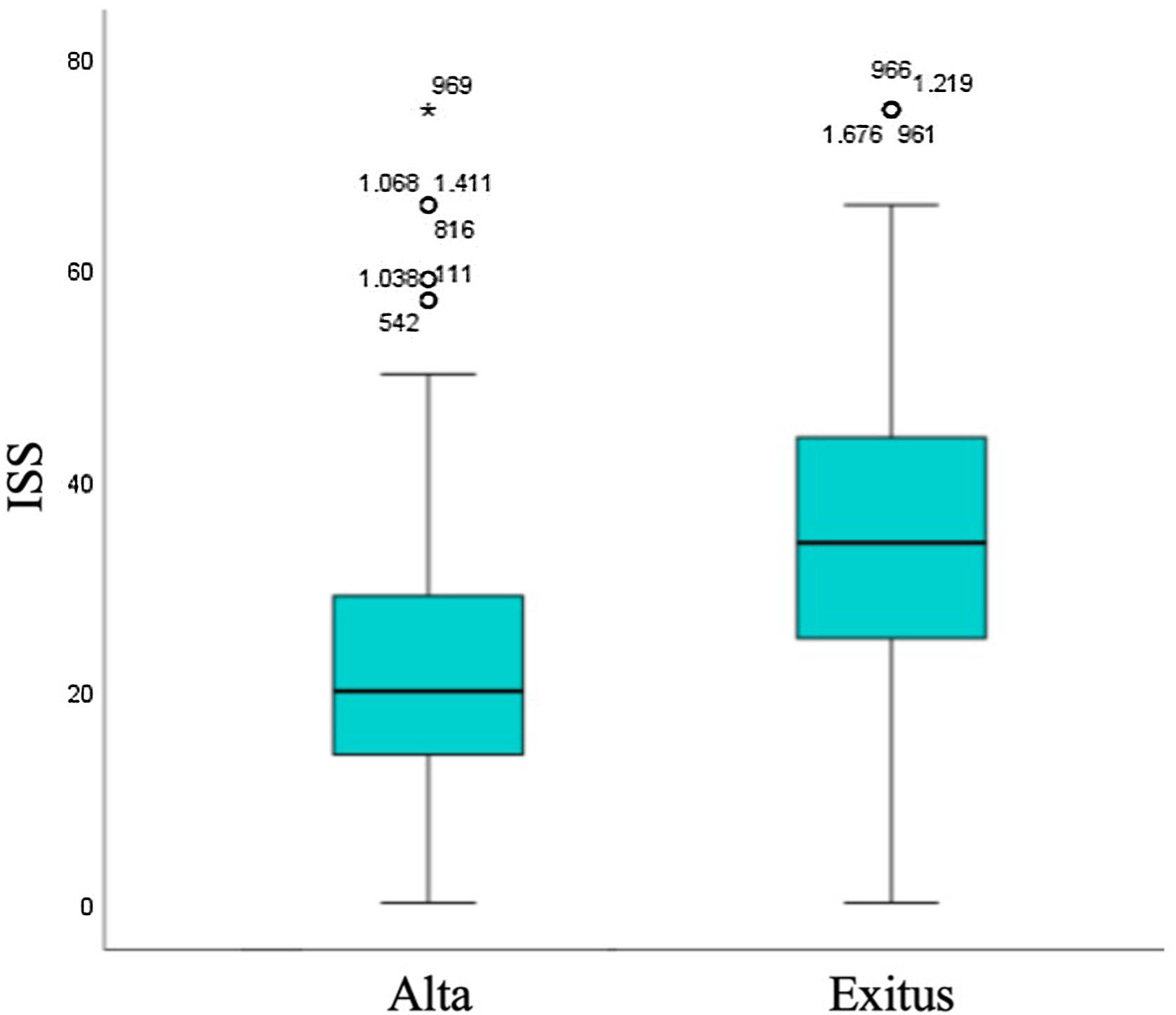
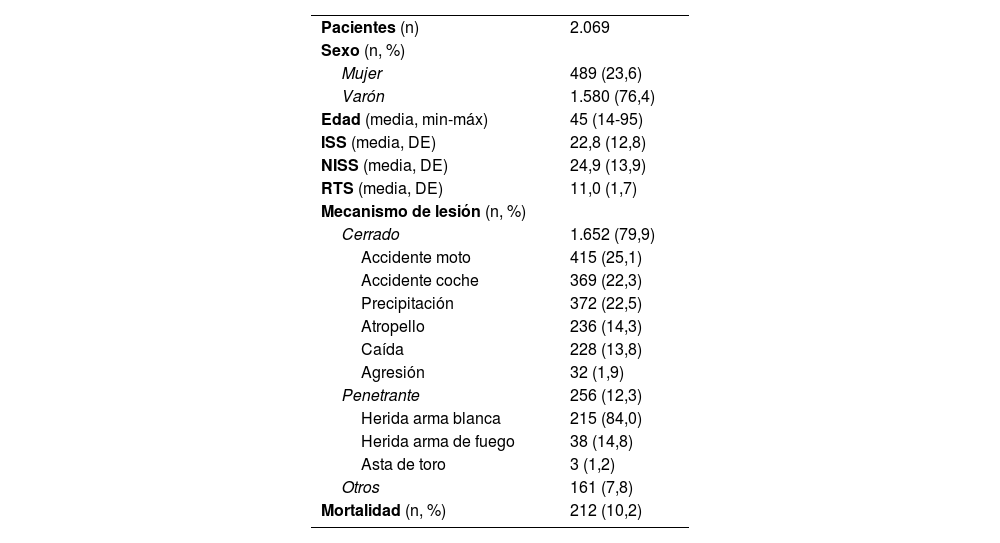
ResultadosDel 1/1/17 al 1/1/22 se han registrado un total de 2.069 pacientes politraumatizados. El 76,4% son varones; edad media: 45 años; ISS medio: 22,8 y mortalidad: 10,2%. El mecanismo de lesión más frecuente es el cerrado (80%) con mayor incidencia de accidentes de moto (23%). Un 12% de los pacientes sufren un traumatismo penetrante, por arma blanca en el 84%.
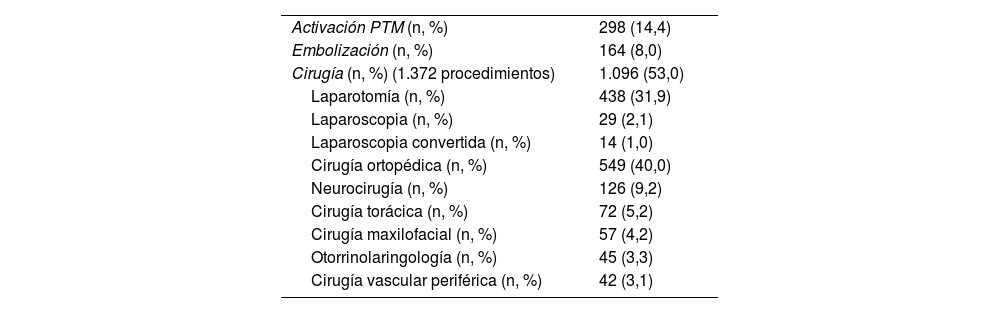
Un 16% de los pacientes ingresa hemodinámicamente inestable en el hospital. Activando el protocolo de transfusión masiva en el 14% de los pacientes e interviniendo quirúrgicamente a un 53%. La estancia hospitalaria mediana es de 11 días. Precisando ingreso en la UCI un 73,4% (estancia media: 5 días).
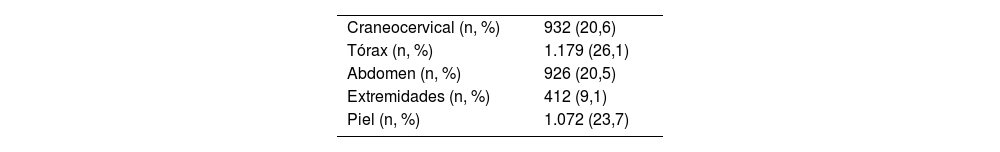
ConclusionesLos pacientes politraumatizados registrados en el RNP son mayoritariamente varones de mediana edad, que sufren traumatismos cerrados y presentan una elevada incidencia de lesiones torácicas. La detección y el tratamiento dirigido de este tipo de lesiones probablemente permitirá mejorar la calidad asistencial del politraumatizado en nuestro medio.
In 2017 the Spanish National Polytrauma Registry (SNPR) was initiated in Spain, its goal was to improve the quality of severe trauma management and evaluate the use of resources and treatment strategies. The objective of this study is to present the information obtained with the SNPR since it was initiated.
MethodsObservational study with prospective data collection from the SNPR. Trauma patients included are older than 14 yeas, with ISS ≥ 15 or penetrating mechanism. In total 17 hospitals from Spain have participated.
ResultsFrom 1/1/17 to 1/1/22, 2069 trauma patients were registered. The majority were men (76.4%); mean age: 45 years; mean ISS: 22.8 and mortality: 10.2%. The most common mechanism of injury was blunt trauma (80%), being motorbike accident the most frequent (23%). Penetrating trauma is presented in 12% of patients, being stab wound the most common (84%).
Sixteen percent of patients are hemodynamically unstable on hospital arrival. Massive transfusion protocol is activated in 14% of patients and 53% are operated. Median hospital stay is 11 days. There is a 73.4% of patients who need intensive care unit (ICU) admission, with a median ICU stay of 5 days.
ConclusionsTrauma patients registered in the SNPR are predominantly middle-aged males who experience blunt trauma with a high incidence of thoracic injuries. Early and addressed detection of these kind of injuries would probably improve trauma quality of care in our environment.