To analyse the state of refractive surgery with Visian ICL phakic lens implantation in Spain, indicating the mean ranges of implanted powers, visual and refractive outcomes obtained and safety and efficacy indices.
MethodThis is a population-based, cross-sectional, descriptive, analytical, retrospective, multicentre study in which each co-author collected data from at least the last 10 patients (up to a maximum of 30) with Visian ICL phakic lens implantation. One eye from each subject was randomly selected for study inclusion, and the variables analysed were: age, gender, visual acuities with and without correction pre and post-surgery, preoperative and residualrefraction, keratometry, endothelial cellular density, anterior chamber depth from endothelium, central corneal pachymetry, intraocular pressure, white-white, implanted lens (power and size), expected and achieved spherical equivalent (SEQ) post-surgery at one month after surgery.
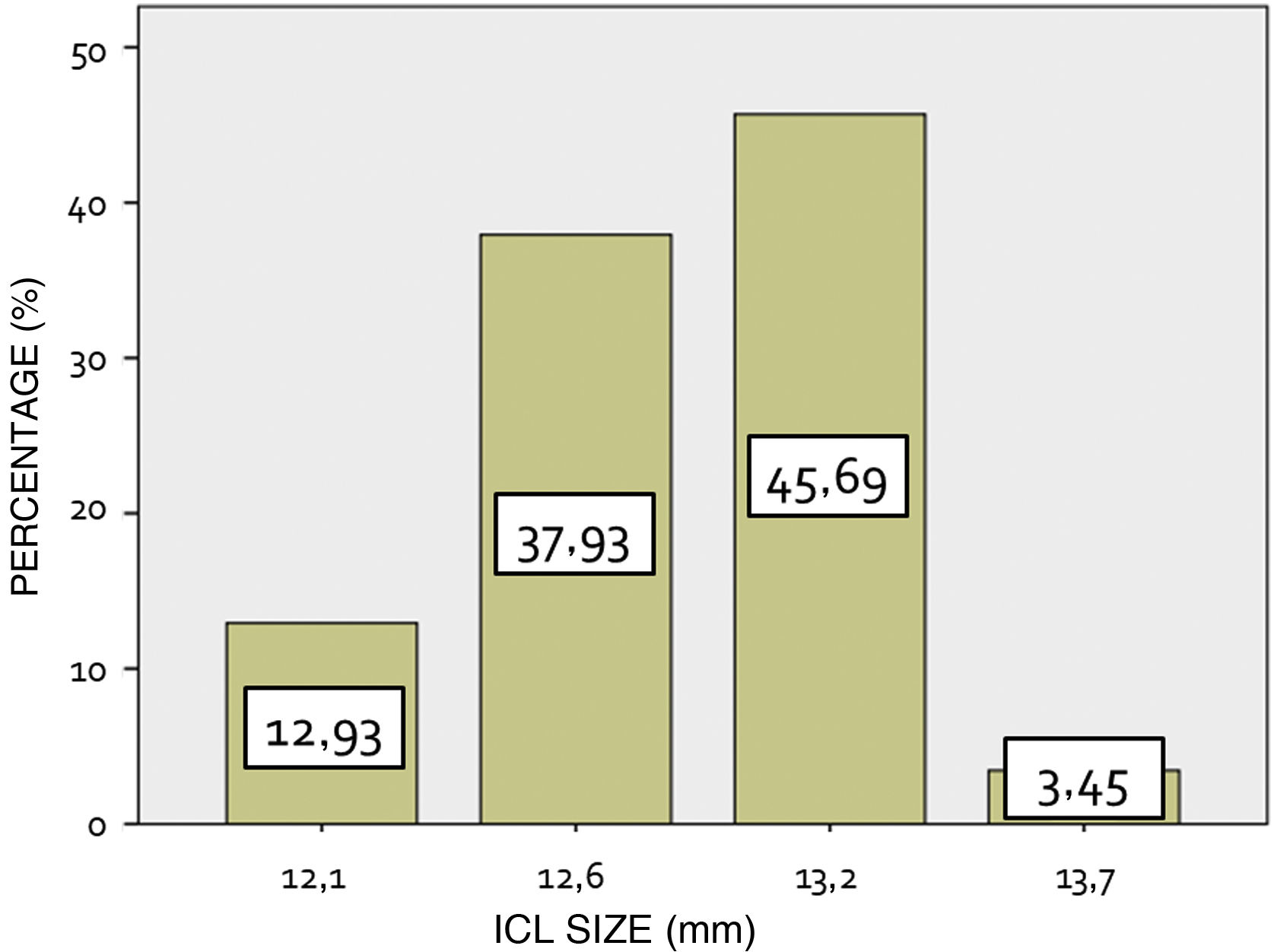
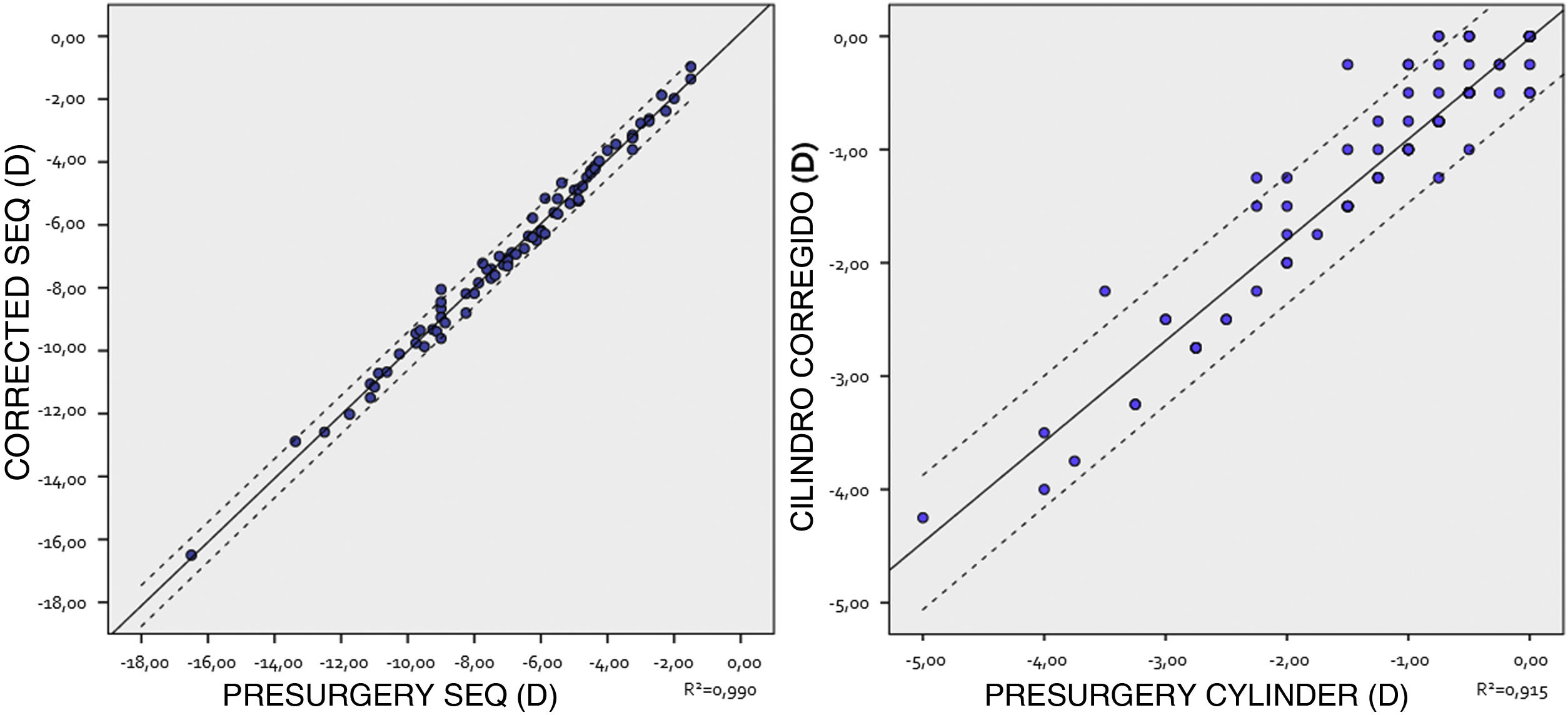
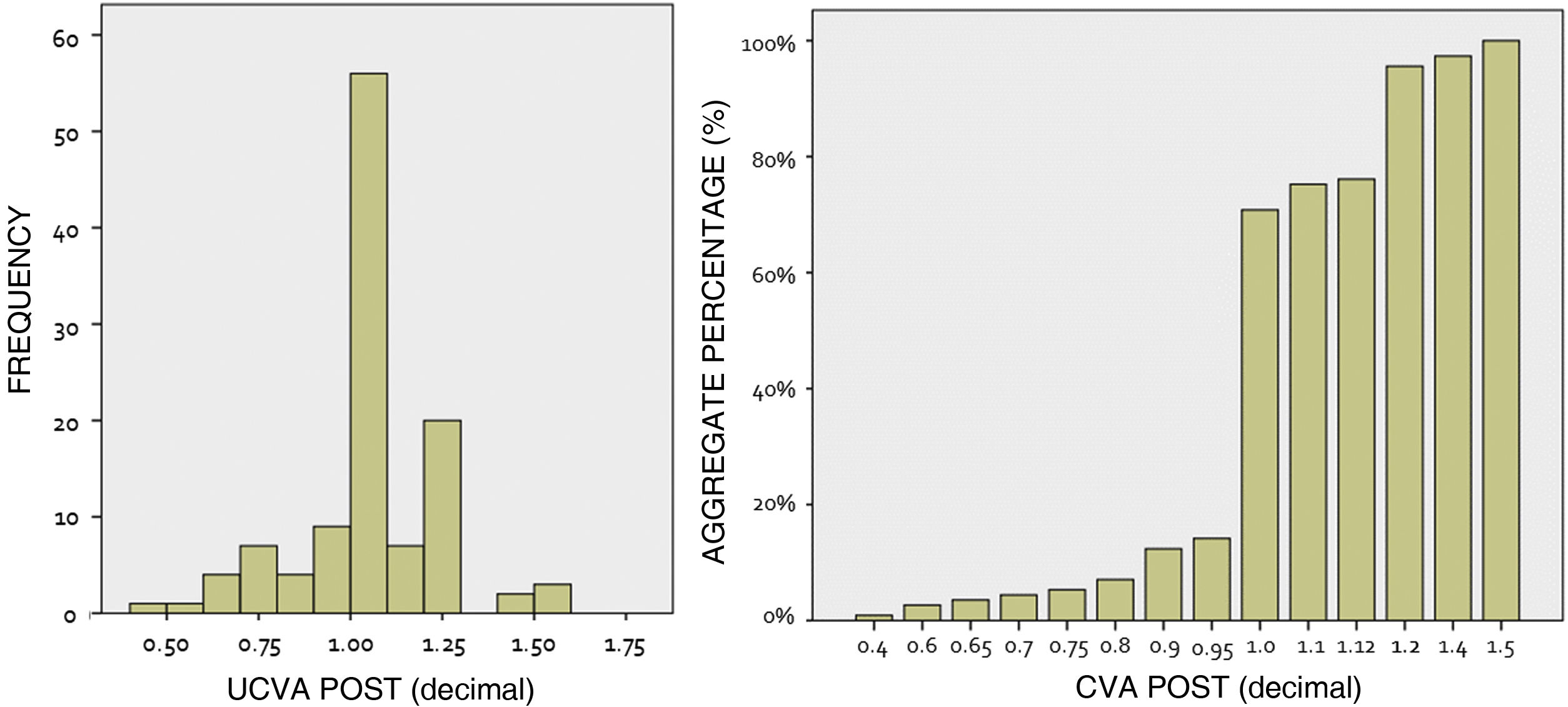
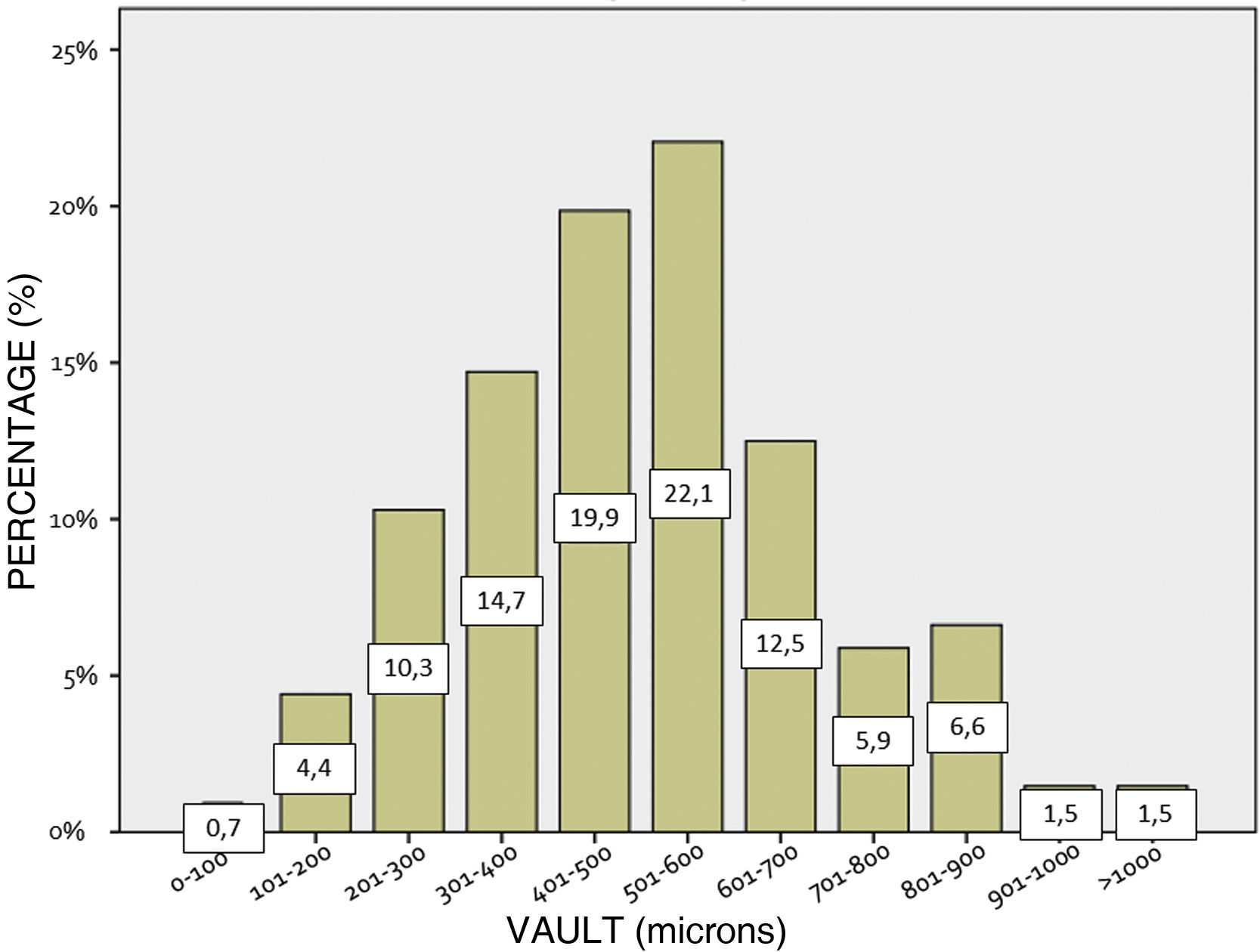
ResultsA sample of 140 eyes was obtained from 140 patients with a mean age of 31.35 ± 7.28 years. Mean preoperative SEQ was −6.33 ± 3.69D, mean CDVA was 0.96 ± 0.16, ACD was 3.30 ± 0.29 mm, WTW 12.02 ± 0.40 mm, CCT 535.03 ± 37.68 µm, ECD 2684.37 ± 313.74 cels/mm2 and IOP 14.84 ± 2.59 mmHg. 66.4% of the implanted lenses were spherical ICLs and 33.6% toric, with a mean power of −7.81 ± 4.09D and a mean cylinder of 2.27 ± 1.23D. 5.7% of the implanted lenses were hypermetropic. The mean SEQ target selected was +0.04 ± 0.27D. 48.92% of the implanted lenses were of size 13.2 mm, with the remaining 36.69, 10.79 and 3.60% being of sizes 12.6, 12.1 and 13.7 mm, respectively. At one month after surgery a residual SEQ of −0.01 ± 0.31D was obtained. The efficacy and safety indices were 1.06 ± 0.18 and 1.10 ± 0.19, respectively. The mean central vault was 508.80 ± 201.04 µm. The accuracy between the calculated SEQ and the obtained SEQ was 99.3% for spherical lenses and 88.2% for Cyl correction. The mean ECD at 1 month after surgery was 2805.53±273.30céls/mm2, which was a difference from preoperative of 0.11% (p = 0.922), similarly, the mean IOP was 13.98 ± 2.57 mmHg, which was a difference of −0.92 ± 2.80 mmHg.
ConclusionsICL phakic lens surgery is an effective, safe and predictable procedure. There were no significant changes in endothelial cell count or intraocular pressure measurement one month after surgery.
Analizar la situación actual de la cirugía refractiva con implante de lente fáquica Visian ICL en España, señalando los rangos medios de potencias implantadas, resultados visuales y refractivos obtenidos e índices de seguridad y eficacia.
MétodoSe trata de un estudio de población, transversal, descriptivo, analítico, retrospectivo, multicéntrico, en el que cada coautor recopiló los datos de, al menos, los 10 últimos pacientes (hasta un máximo de 30) con implante de lente fáquica Visian ICL. Se elegió aleatoriamente un ojo de cada sujeto para incluirlo en el estudio, y se analizaron las variables: edad, género, agudezas visuals sin corrección y con corrección pre y postquirúrgica, refracción preoperatoria y residual, queratometrías, contaje endothelial, profundidad de cámara anterior desde endotelio, paquimetría corneal central, presión intraocular, blanco-blanco, lente implantada (potencia y talla) y equivalente esférico esperado y obtenido (SEQ) esperado y obtenidoposquirúrgico al mes de la cirugía.
ResultadosSe obtuvo una muestra de 140 ojos de 140 pacientes con una edad media de 31,35 ± 7,28 años. El SEQ preoperatorio medio fue de −6,33 ± 3,69, la agudeza visualcon corrección media de 0,96 ± 0,16, la profundidad de cámara anterior desde endoteliode 3,30 ± 0,29 mm, distancia blanco-blanco 12,02 ± 0,40 mm, paquimetría corneal central 535.03 ± 37.68 µm, recuento endotelial 2.684,37 ± 313,74 céls/mm2 y presión intraocular 14,84 ± 2,59 mmHg. El 66,4% de las lentes implantadas fueron ICL esféricas y el 33,6% tóricas, con una potencia media de −7,81 ± 4,09 D y un cilindro medio de 2,27 ± 1,23D. El 5,7% fueron hipermetrópicas. El 45,69% de las lentes implantadas eran de la talla 13,2 mm, siendo el 37,93, 12,93 y 3,45% restante de las tallas 12,6, 12,1 y 13,7 mm, respectivamente. Al mes de la cirugía se obtuvo un SEQ residual de −0,01 ± 0,31 D. Los índices de eficacia y seguridad fueron de 1,06 ± 0,18 y 1,10 ± 0,19, respectivamente. El vault central medio fue de 508,80 ± 201,04 µm. La precisión entre el SEQ calculado y el SEQ obtenido fue del 99,3% en el caso de las lentes esféricas y del 88,2% para la corrección del cilindro. El ECD medio al mes de la cirugía fue de 2805,53 ± 273,30 céls/mm2. La presión intraocular media fue de 13,98 ± 2,57 mmHg.
ConclusionesEn este grupo de análisis se ha demostrado que el implante de ICL es un procedimiento seguro en el corto plazo con una alta predictibilidad refractiva.