To demonstrate the genetic influence in the onset of the different age-related macular disease (AMD) subtypes by analysing the genotype distribution of CFH, ARMS2, HTRA1, VEGF-A and VEGF-R polymorphisms in patients with neovascular and atrophic AMD.
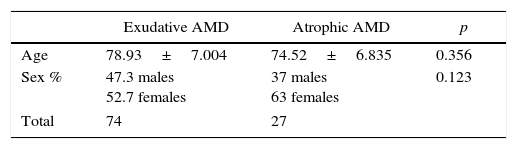
Materials and methodsThe study was conducted on 101 consecutive patients with AMD diagnosis (74 exudative, 27 atrophic) following Wisconsin international classification criteria. The CFH rs1410996, ARMS2 rs10940923, VEGF-A rs833061, rs699947, and VEGF-R rs2071559 polymorphisms were analyzed using real time PCR with taqman probes, and HTRA1 rs112000638 using restriction endonucleases digestion.
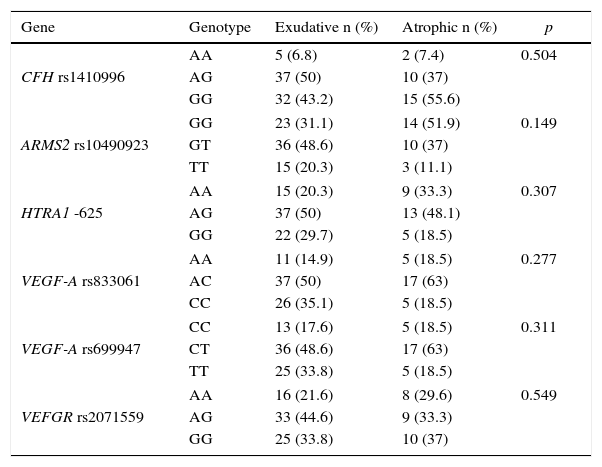
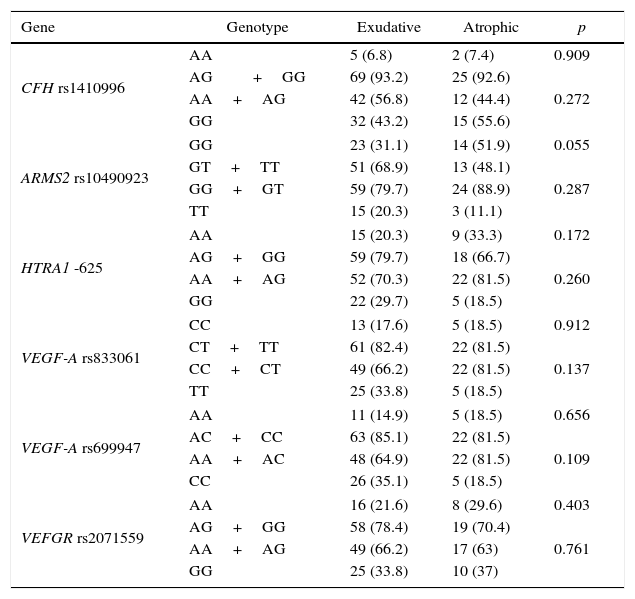
A study was made of the genotype distribution of the different polymorphisms in our group of patients with neovascular AMD and those with the atrophic type, and a comparison was made of the results for each one of the genes studied.
ResultsNo statistically significant differences (p>.05) were found in the genotype distribution of the different polymorphisms between patients with neovascular AMD and patients with atrophic AMD in our population, although the “risk” genotypes tended to appear more frequently in patients with neovascular AMD, despite the lack of statistical significance.
ConclusionsAllelic variants of CFH, ARMS2, HTRA1, VEGF-A or VEGF-R genes are not associated with the different AMD subtypes. This suggests that, although the polymorphisms seem to be associated with the disease susceptibility, they are not involved in the onset of the different clinical variants of AMD. Further studies in different populations, and with a larger cohort of patients, are needed to confirm these results.
Demostrar la influencia genética en el desarrollo de los distintos tipos de degeneración macular asociada a la edad (DMAE) analizando las distribuciones genotípicas de polimorfismos de CFH, ARMS2, HTRA1, VEGF-A y VEGF-R en pacientes con DMAE exudativa y DMAE atrófica.
MétodoSe toman 101 pacientes diagnosticados de DMAE (74 exudativa y 27 atrófica) según las normas del sistema internacional de clasificación Wisconsin. Analizamos los polimorfismos rs1410996 del gen CFH, rs10940923 de ARMA2, rs833061 y rs699947 de VEGF-A y rs2071559 de VEGF-R mediante PCR a tiempo real con sondas Taqman y el HTRA1 rs112000638 mediante digestión con endonucleasas de restricción.
Analizamos la distribución genotípica de los distintos polimorfismos en nuestro grupo de pacientes con DMAE exudativa y los que presentan DMAE atrófica y comparamos los resultados para cada uno de los genes a estudio.
ResultadosNo encontramos diferencias estadísticamente significativas (p>0,05) en la distribución genotípica de los distintos polimorfismos entre pacientes con DMAE atrófica y pacientes con DMAE exudativa en nuestra población, si bien los genotipos considerados «de riesgo» por otros estudios tienden a aparecer de forma más frecuente en la DMAE exudativa, a pesar de no obtener diferencias significativas.
ConclusionesLas variantes alélicas de los genes CFH, ARMS2, HTRA1, VEGF-A o VEGF-R no se asocian con los diferentes subtipos de DMAE, lo que indica que, aunque parece que están implicados en la susceptibilidad a padecer la enfermedad, no están implicados en el desarrollo de las variantes clínicas en nuestra población. Son necesarios nuevos estudios en diferentes poblaciones y con un mayor tamaño muestral para confirmar estos resultados.