To analyse the association between the thickness of the circumpapillary retinal nerve fibre layer (cpRNFL) and the thickness of the inner macular layers with the mean deviation of the visual field (MD) in children with primary congenital glaucoma (PCG).
Materials and MethodsA total of 41 children with PGC were included in the study. They all had a complete ophthalmological examination, including visual acuity, intraocular pressure, funduscopy, Octopus™ visual field, as well as circumpapillar and macular spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT). SD-OCT with automated segmentation was used to measure the thicknesses and volumes of the macular retinal nerve fibre layer (mRNFL), ganglion cell layer (GCL), and inner plexiform layer.
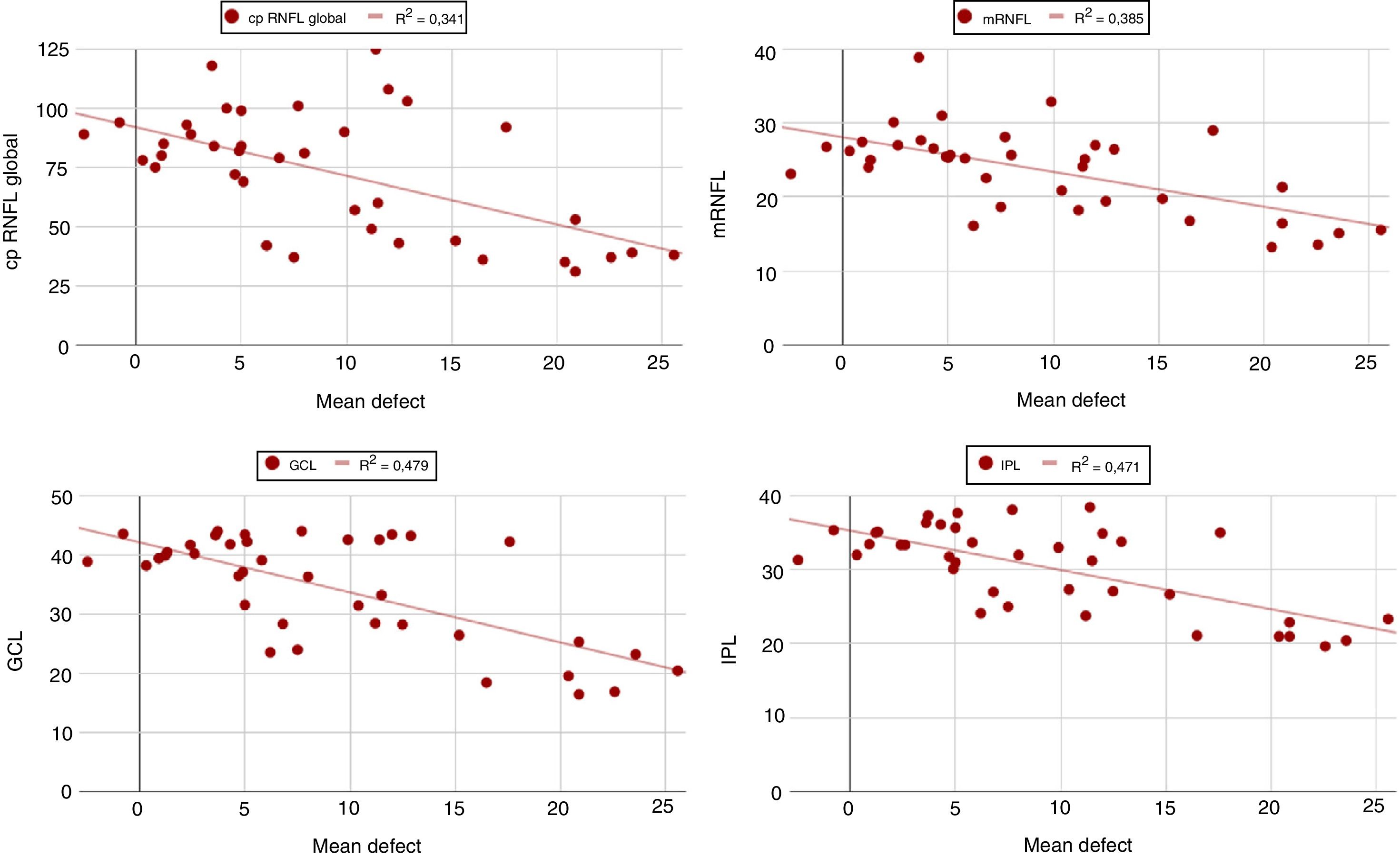
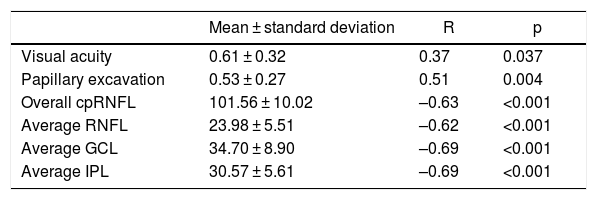
ResultsThe mean age was 11.2 ± 3.86 years, and the mean MD was 8.85 ± 6.76 dB. The visual field was classified as normal in 46% of the patients, and 20% of the patients had a concentrical restriction of the visual field. A positive correlation was found between between the cup-to-disc ratio and the MD, r = 0.51 (P = 0.004). The correlation between the MD and the cpRNFL was r = −0.63 (P < .001), and r = −0.69 (P < .001) with the GCL.
ConclusionsInner macular layers thickness and cpRNFL thickness show a good correlation with the mean deviation of the visual field in children with primary congenital glaucoma.
Analizar la correlación entre el grosor de la capa de fibras nerviosas peripapilar (cpRNFL) y el grosor de las capas internas de la retina con el defecto medio del campo visual (DM) en pacientes con glaucoma congénito primario (GCP).
Material y métodosEn este estudio transversal se incluyeron 41 pacientes diagnosticados de GCP. A todos los pacientes se les realizó una exploración oftalmológica completa incluyendo agudeza visual, presión intraocular, fondo de ojo, campo visual y tomografía de coherencia óptica (OCT) macular y peripapilar. Se utilizo la segmentación automática del OCT Spectralis para medir el grosor de la capa de fibras nerviosas macular (mRNFL), capa de células ganglionares (GCL) y plexiforme interna.
ResultadosLa edad media fue de 11,2 ± 3,86 años y el DM medio fue de 8,85 ± 6,76 dB. En un 46% de los pacientes el campo visual fue clasificado como normal, y un 20% de los pacientes presentaba una restricción concéntrica del campo visual. Se encontró una correlación positiva entre la relación anillo/excavación y el DM (p = 0.004). La correlación ente el DM y el cRNFL fue de r = −0,63 (p < 0.001) y de r = −0,69 con la GCL.
ConclusionesEl grosor de las capas internas de la retina y el cpRNFL tiene una buena correlación con el defecto medio del campo visual en pacientes con glaucoma congénito primario.