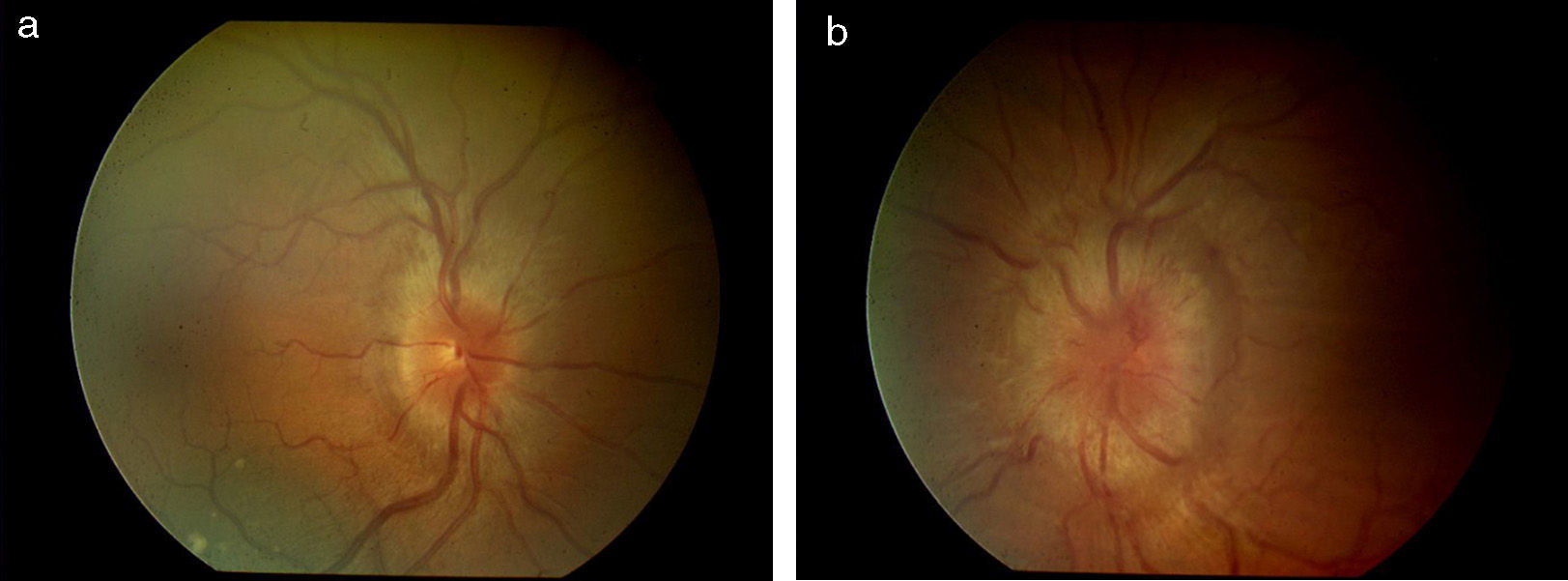
A 46-year-old patient presented with visual loss in the left eye during the previous months. Ophthalmoscopic examination and magnetic resonance angiography found the presence of papilledema due to thrombosis in superior sagittal sinus. The examination findings revealed a mantle cell lymphoma.
DiscussionCerebral venous thrombosis is an unusual cause of papilledema. This type of thrombosis may be secondary to hyper-viscosity within a context of a paraneoplastic syndrome.
Se presenta el caso de un varón de 46 años con disminución de la visión del ojo izquierdo de meses de evolución. Se diagnostica de papiledema por trombosis del seno sagital superior gracias a la angiorresonancia. En busca de la etiología de la trombosis se descubre un linfoma del manto.
DiscusiónLa trombosis venosa cerebral es una causa poco frecuente de papiledema. Puede deberse a cuadros de hiperviscosidad en el contexto de un síndrome paraneoplásico.