To analyze macular choroidal thickness (MCT) in non-arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION).
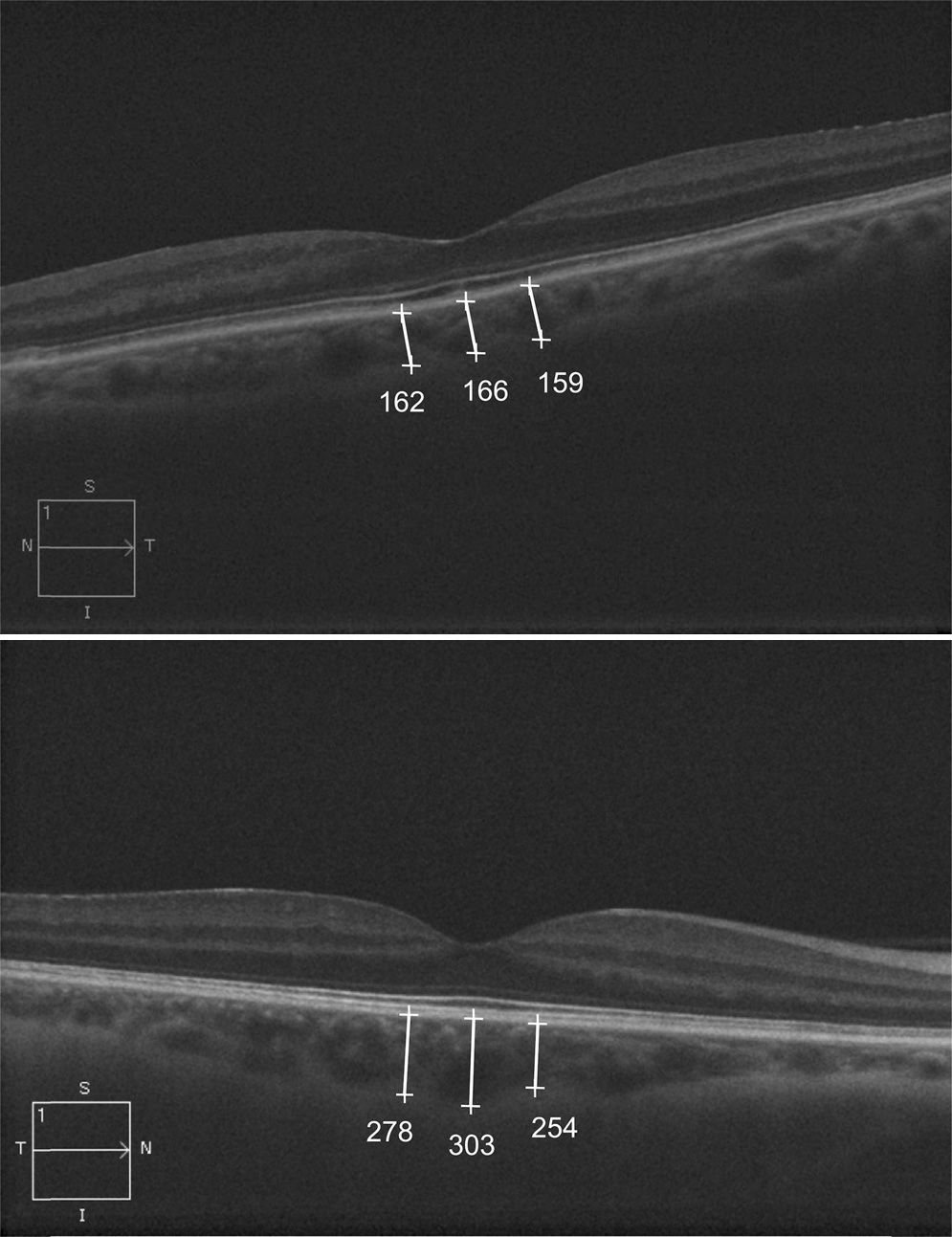
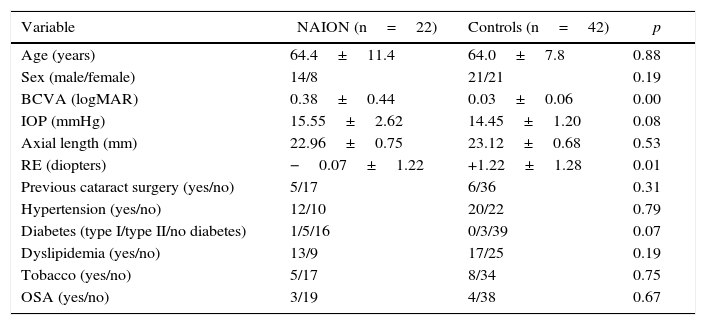
Materials and methodsAn analysis was made on 22 patients diagnosed with NAION (22 eyes) and 42 healthy controls (42 eyes) using enhanced-depth imaging of spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. A horizontal raster scan centered on the fovea was obtained per eye 3 months after the onset of NAION. Three measurements of MCT were obtained from the posterior edge of the retinal pigment epithelium to the choroid-sclera junction at 500μm intervals. Statistical analysis was used to compare the mean MCT and to correlate MCT with other ocular and systemic parameters.
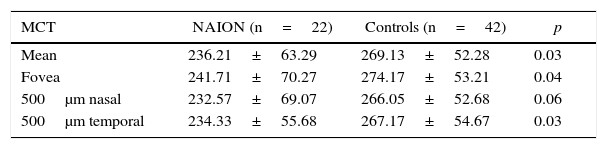
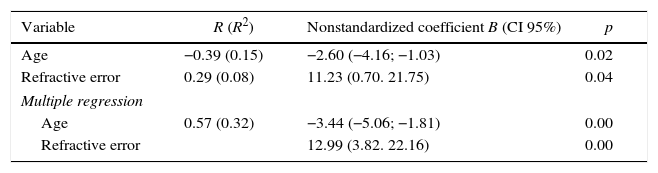
ResultsExcept for refractive error (p=.01), there were no statistically significant differences between both groups in axial length (p=.53), age (p=.88) and other epidemiological and ocular parameters. Mean MCT in NAION eyes and control group was 236.21±63.29μm and 269.13±52.28, respectively. Mean MCT was significantly thinner in NAION eyes than in healthy eyes (p=.03). Thinner MCT, adjusted for refractive error, was associated with the diagnosis of NAION (p=.04).
ConclusionsEyes affected by NAION showed significantly thinner MCT compared with healthy control eyes after adjusting for refractive error.
Analizar el grosor coroideo macular (GCM) en la neuropatía óptica isquémica anterior no arterítica (NOIA-NA).
Material y métodosUn total de 22 pacientes diagnosticados de NOIA-NA (22 ojos) y 42 sujetos sanos (42 ojos) fueron estudiados usando tomografía de coherencia óptica con técnica Enhanced Depth Imaging (EDI-OCT). Se realizó un escáner de una línea horizontal centrado en la fóvea 3 meses después del inicio de NOIA-NA. Se tomaron 3 medidas desde la parte posterior del epitelio pigmentario hasta la unión esclerocoroidea a intervalos de 500μm en las 1.500μm centrales de la mácula. Los resultados fueron analizados estadísticamente comparando la media de GCM entre grupos y correlacionando el GCM con otros parámetros oculares y sistémicos.
ResultadosExcepto en el error refractivo (p=0,01), no hubo diferencias significativas en longitud axial (p=0,53), edad (p=0,88) ni en otros parámetros oculares ni epidemiológicos entre grupos. La media de GCM en la NOIA-NA y en el grupo control fue 236,21±63,29μm y 269,13±52,28, respectivamente. La media del GCM fue significativamente más delgada en ojos con NOIA-NA que en sanos (p=0,03). El adelgazamiento del GCM estuvo asociado con el diagnóstico de NOIA-NA después de ajustar por error refractivo (p=0,04).
ConclusionesLos ojos afectos con NOIA-NA mostraron un GCM significativamente más adelgazado que en sujetos sanos, después de ajustar por error refractivo.