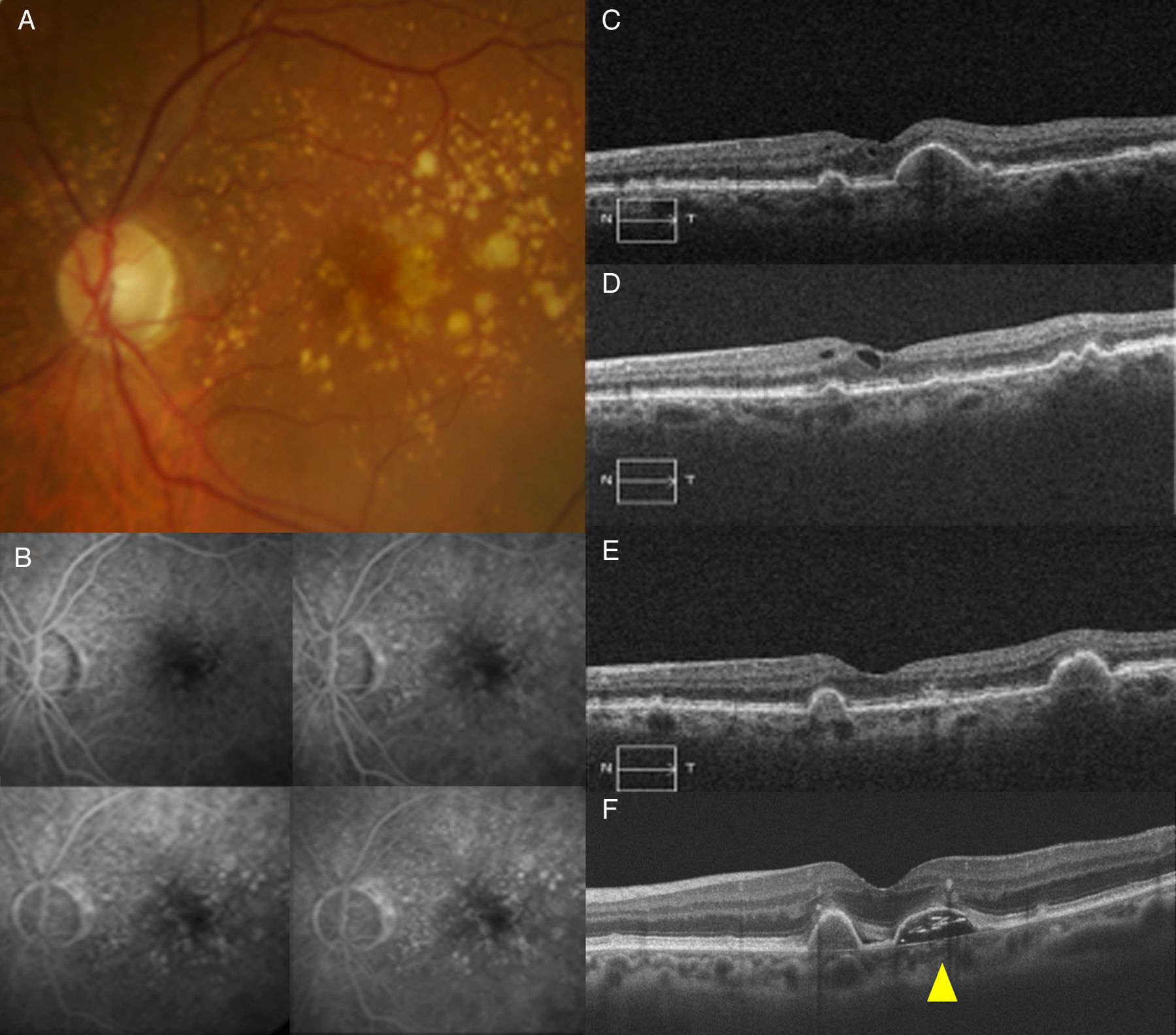
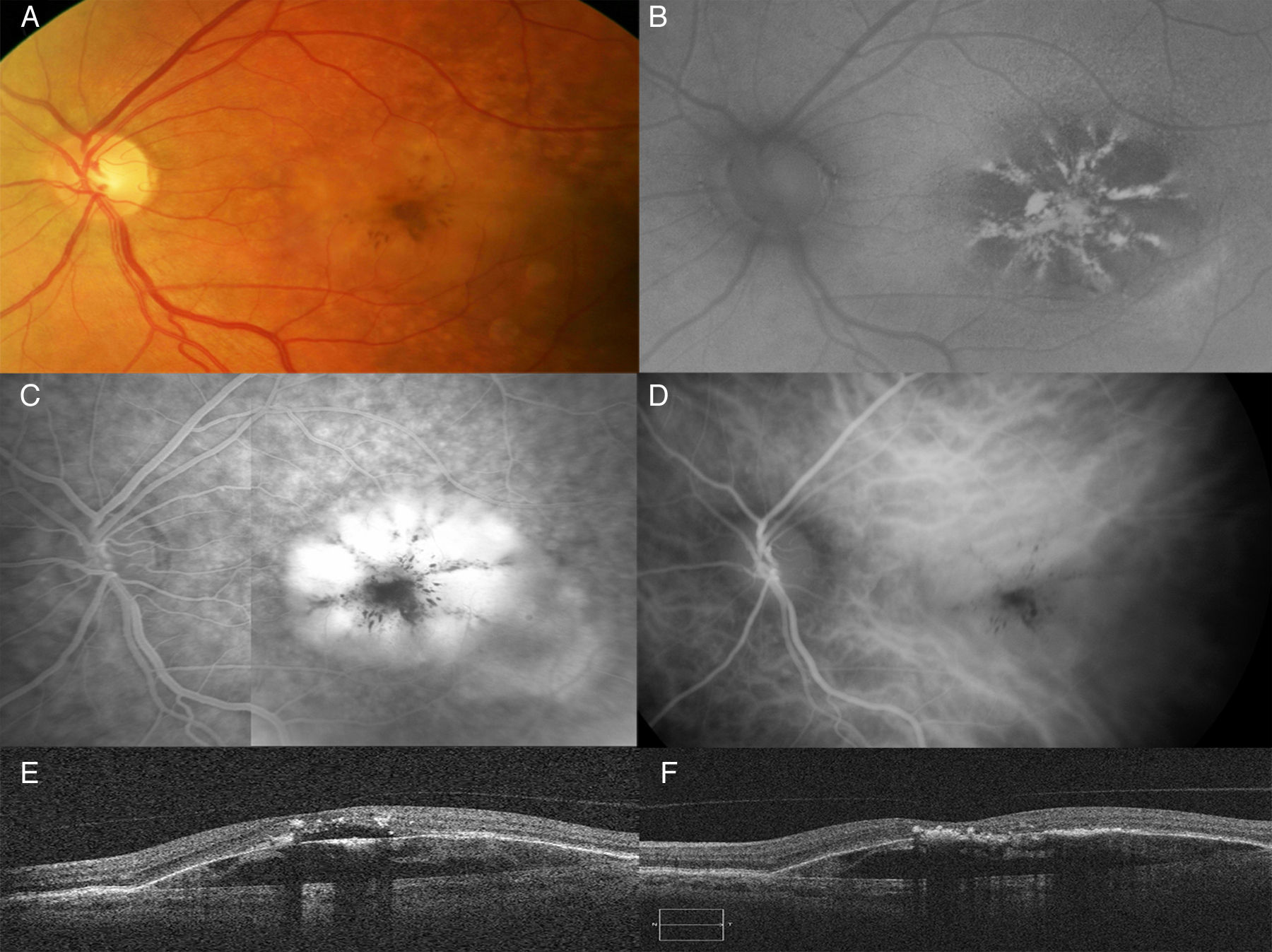
To evaluate the efficacy of intravitreal therapies in cases of atrophic age-related macular degeneration (AMD) with subretinal or intraretinal fluid.
MethodsA retrospective review was made of the clinical charts of patients diagnosed with atrophic AMD with subretinal or intraretinal fluid. Fundus photographs and spectral-domain optical coherence tomography images were examined, and an analysis was made on the presence of fluid and its density. Neovascularisation was ruled out by fluorescein and/or indocyanine green angiography.
ResultsThe study included 14 eyes from 13 patients with a mean age of 72.64 years and a mean follow-up of 80.5 weeks. Intraretinal fluid was observed in 6 eyes (42.9%), while subretinal fluid was shown in 8 eyes (57.1%), with high density in 4 eyes (28.5%), and low density in 4 eyes (28.5%). Snellen best-corrected visual acuity improved from 0.37 at baseline to 0.56 at the final visit (P=0.002). Central subfield thickness (microns) significantly decreased (P<0.001) from 291.0 at baseline to 228.9 at the final visit. Eight eyes received ranibizumab, 5eyes received bevacizumab, and one case received triamcinolone.
ConclusionsCases of atrophic AMD may present with subretinal or intraretinal fluid in the absence Neovascularisation. Further studies are required to analyze the value of this finding as a risk factor of developing advanced forms of AMD, as well as the efficacy of intravitreal therapies.
Evaluar la eficacia de las terapias intravítreas en casos de degeneración macular asociada a la edad (DMAE) atrófica con fluido intra- o subretiniano.
MétodosRevisamos, de forma retrospectiva, las características de pacientes diagnosticados de DMAE atrófica con fluido intra- o subretiniano. Examinamos las retinografías y las imágenes de tomografía de coherencia óptica de dominio espectral analizando en ellas la presencia de fluido y su densidad. Descartamos la existencia de neovascularización coroidea mediante angiografía con fluoresceína o con verde de indocianina.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 14 ojos de 13 pacientes con una edad media de 72,64 años y un seguimiento medio de 80,5 semanas. Se observó fluido intrarretiniano en 6 ojos (42,9%) y fluido subretiniano en 8 ojos (57,1%). Este fluido era de alta densidad en 4 de ellos (28,5%) y de baja densidad en los otros 4 ojos (28,5%). La mejor agudeza visual corregida evaluada mediante la escala de Snellen mejoró de 0,37 inicialmente a 0,56 en la visita final (p=0,002). El grosor macular central (en micras) disminuyó de forma significativa de 291,0 μm al inicio a 228,9μm en la visita final (p≤0,001). Del total, 8 ojos recibieron ranibizumab, 5 ojos recibieron bevacizumab y un ojo recibió triamcinolona intravítrea.
ConclusionesLa DMAE atrófica puede presentarse con fluido intra- o subretiniano en ausencia de neovascularización coroidea. Son necesarios estudios adicionales para analizar el valor de estos hallazgos como factor de riesgo en el desarrollo de formas avanzadas de DMAE, así como la eficacia de las terapias intravítreas.