To investigate the factors associated with persistent serous retinal detachment in highly myopic eyes with inferior posterior staphyloma.
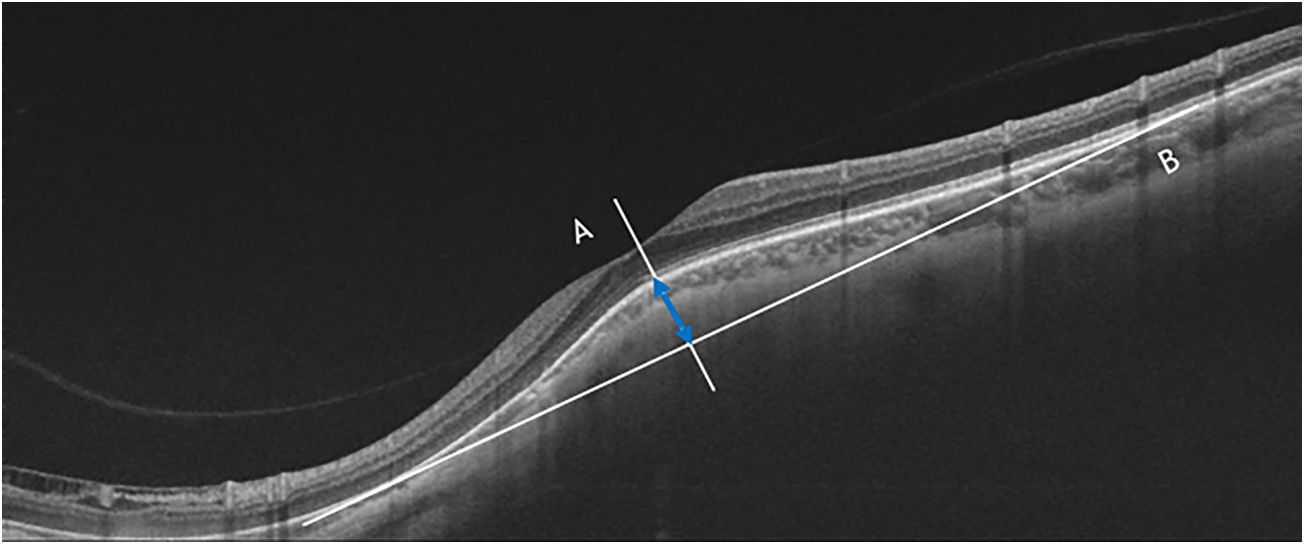
MethodsA total of 27 highly myopic patients (44 eyes) with an inferior posterior staphyloma were recruited. Serous retinal detachment was investigated; 13 eyes had persistent sub-macular fluid (study group), and 31 eyes lacked sub-macular fluid (control group). All patients underwent complete ophthalmologic examinations, including axial length measurement and fluorescein angiography (FA). Triton Deep Range Imaging (DRI) optical coherence tomography (OCT) (Topcon Corp., Tokyo, Japan) scans through the fovea measured choroidal thicknesses, macular bend height, and vitreoretinal interface factors.
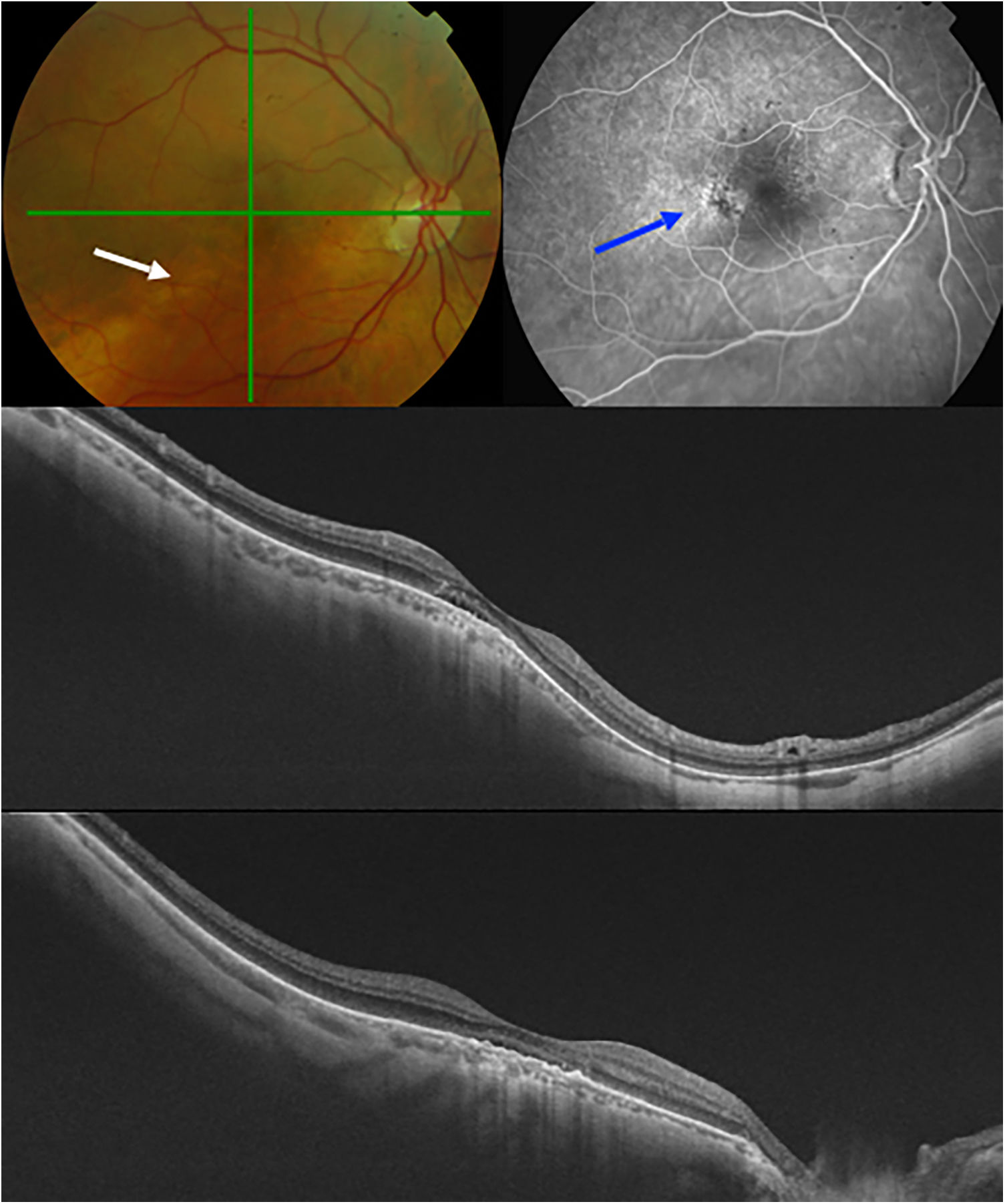
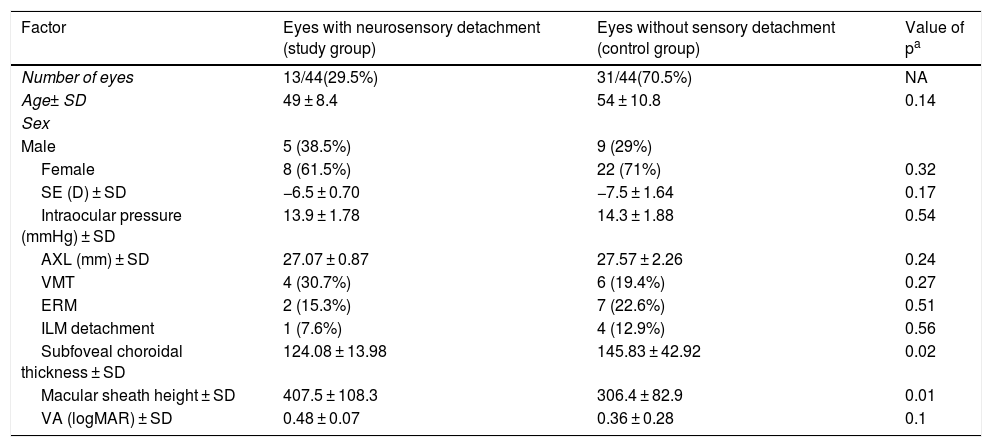
ResultsOf the 44 eyes, 13 had neurosensory retinal detachment and 31 did not. No significant differences were found in any of the studied variables (age, gender, spherical equivalence, axial length, vitreomacular traction, epiretinal membrane, internal limiting membrane detachment), except a higher macular bend height (P = .01), and a reduced macular choroidal thickness (P = .02), which were associated with the risk of serous retinal detachment. No statistically significant differences in best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) were observed between the study and control groups. Serous retinal detachment always occurred at the bisected retinal pigment epithelium of the macula corresponding to the upper edge of the staphyloma, and was characterised by multiple hyperfluorescent granular patches on fluorescein angiography.
ConclusionsA higher macular bend height and a reduced macular choroidal thickness may be important factors in the development of serous retinal detachment in patients with inferior posterior staphyloma.
Investigar los factores clínicos asociados con el desprendimiento neurosensorial macular en ojos de pacientes miopes magnos con estafiloma inferior.
Material y métodoEstudio transversal de 27 pacientes miopes magnos (44 ojos) con estafiloma inferior. Todos los pacientes fueron sometidos a un examen oftalmológico completo, incluyendo angiografía fluoresceína. El grosor coroideo, la interfaz vitreorretiniana y la altura del envainamiento macular se analizaron mediante el dispositivo DRI OCT Triton Swept-Source (Topcon Corp., Tokio, Japan).
ResultadosDe los 44 ojos, 13 presentaron un desprendimiento de la retina neurosensorial y 31 carecían del mismo. No observamos diferencias estadísticamente significativas en ninguna de las variables estudiadas (edad, sexo, equivalente esférico, longitud axial, agudeza visual, tracción vitreomacular, membrana epirretiniana o desprendimiento de membrana limitante interna). Los ojos con desprendimiento de la retina neurosensorial presentaron una mayor altura del envainamiento macular (p = 0.01) y una reducción del espesor coroideo (p = 0.02). El desprendimiento neurosensorial macular siempre se produjo en el borde superior del estafiloma inferior y se caracterizó por una hiperfluorescencia granular en la angiografía fluoresceínica.
ConclusionesUna mayor altura del envainamiento macular y un menor grosor coroideo podrían ser factores importantes en el desarrollo del desprendimiento neurosensorial macular en pacientes miopes magnos con estafiloma inferior.