To study the ocular surface in filtering blebs using impression cytology, comparing the bleb side and areas outside the bleb edges.
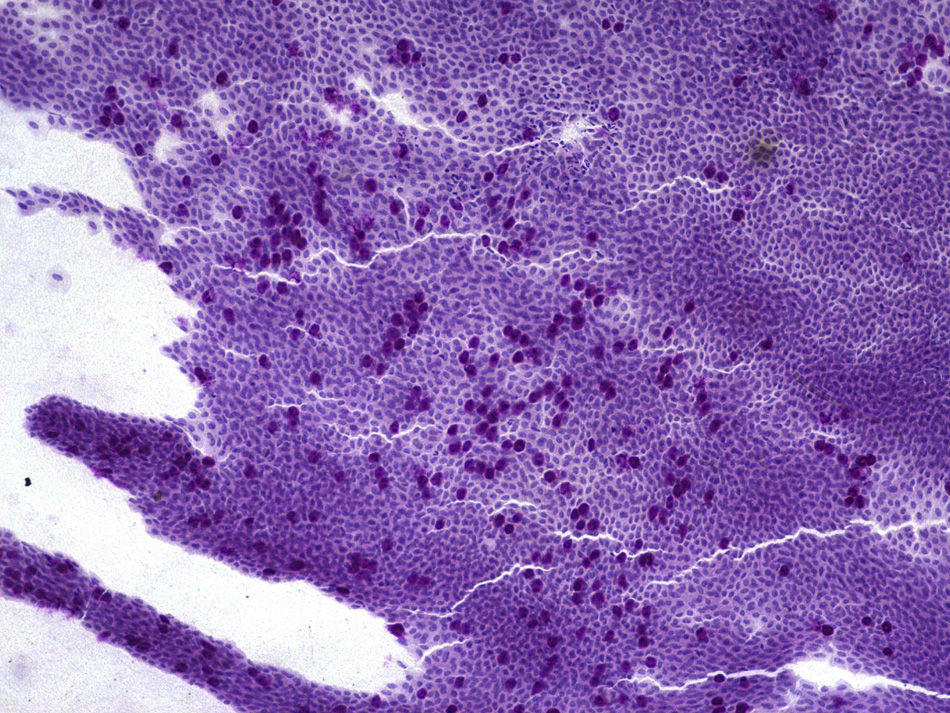
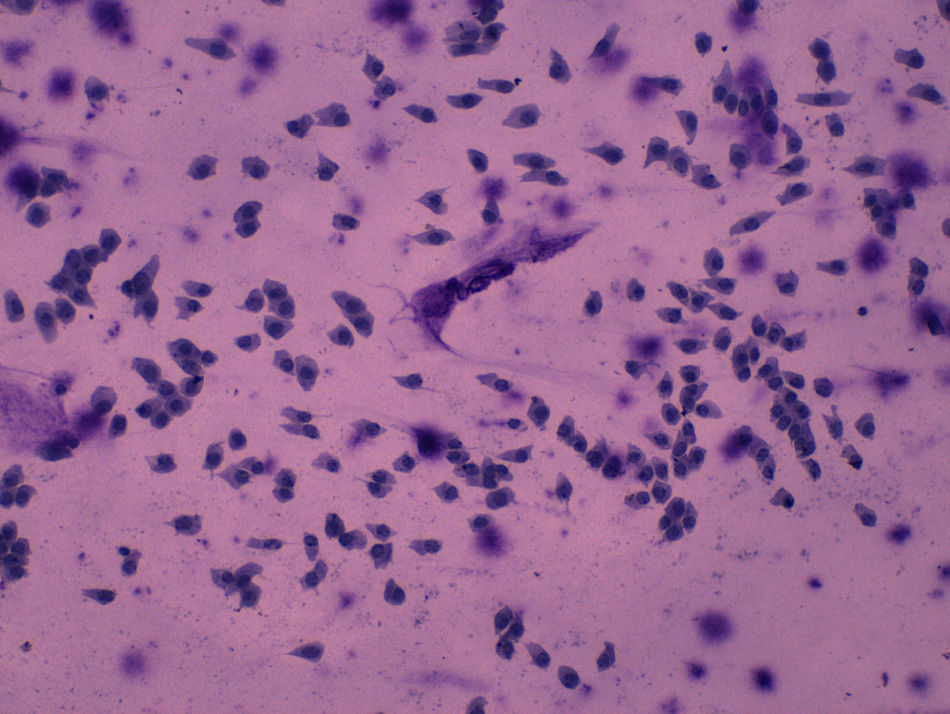
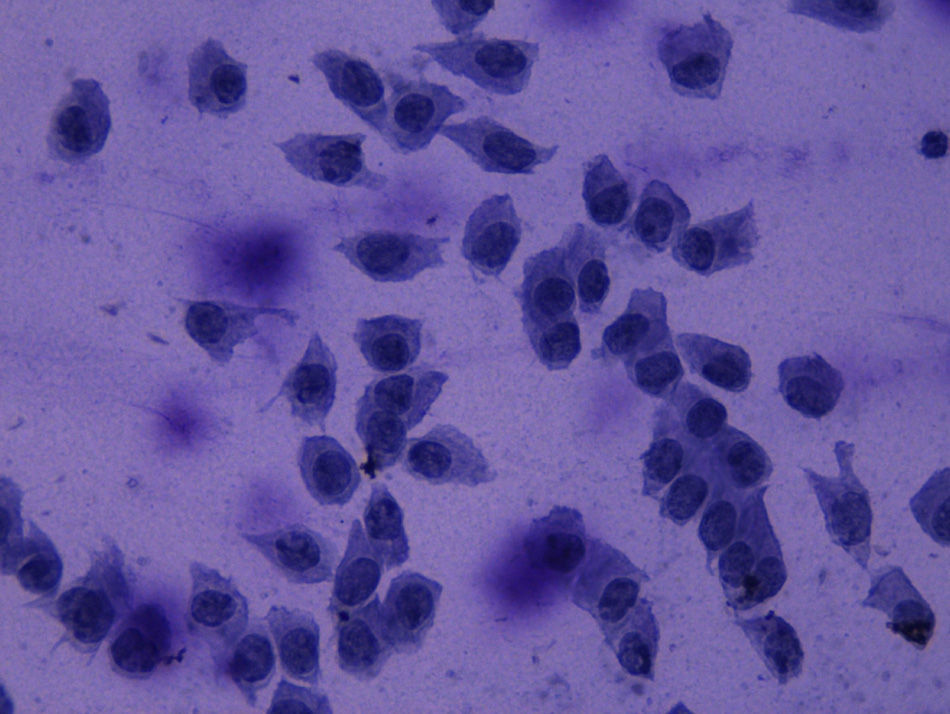
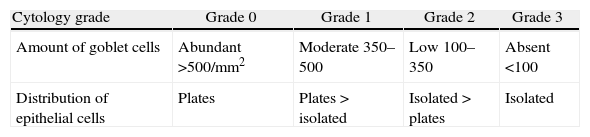
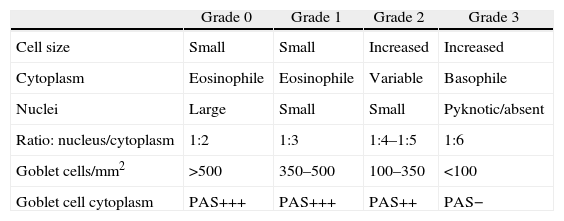
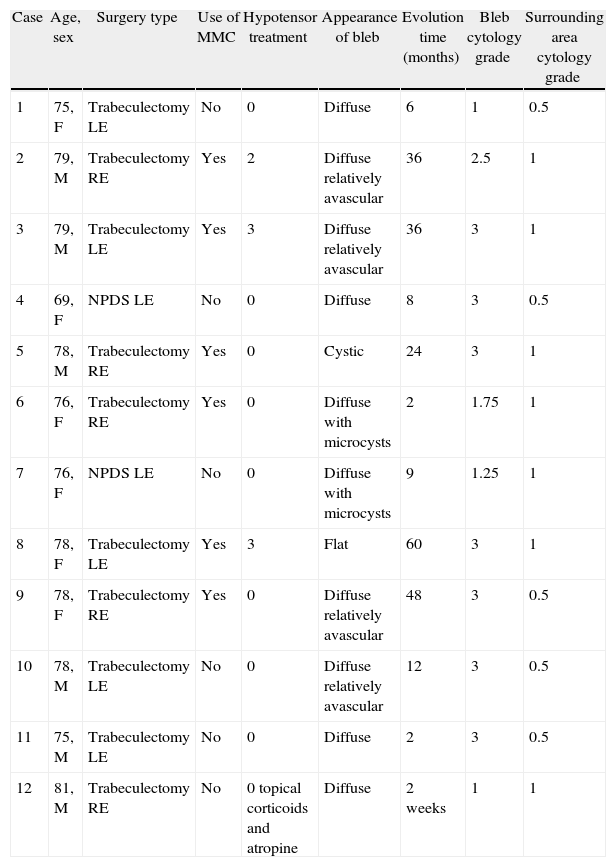
MethodsTwelve filtering blebs of 8 patients were included: 4 cases of trabeculectomy without mitomycin C (MMC), 6 cases of trabeculectomy with MMC, and 2 cases of non-penetrating glaucoma surgery. Impression cytology specimens were taken from filtering blebs as well as outside the bleb area. A classification scale from 0 to 3 was used to describe the distribution of epithelial cells and the density of goblet cells. Grade 0 indicated cohesive epithelial cells and abundant goblet cells; and the grade 3 indicated loss of epithelial cohesion and absence of goblet cells.
ResultsThe mean grade of cytology in filtering blebs was 2.4±0.9, and in the outside bleb area of 0.8±0.3 (p<.001). These differences were independent of the use of MMC (p=.48). The large majority (83%) of filtering blebs showed a decrease in epithelial cohesion and absence of goblet cells. Outside the bleb area, 100% of the cases had cohesive epithelial cells with different grades of goblet cells.
ConclusionThe conjunctival epithelium overlying the filtering blebs showed significant changes that consisted of increased intercellular spaces and loss of goblet cells. These increased intercellular spaces could explain the trans-epithelial pathway of aqueous humor. The least amount of mucin due to loss of goblet cells could contribute to increase the risk of infection in filtering blebs.
Estudiar la superficie conjuntival de ampollas filtrantes mediante citología de impresión y comparar los resultados con el área de conjuntiva circundante.
MétodoSe incluyeron 12 ampollas de 8 pacientes; 4 tras trabeculectomía sin mitomicina C (MMC), 6 tras trabeculectomía con MMC y 2 tras esclerectomía profunda no perforante sin MMC. Se realizaron citologías de impresión conjuntival de las ampollas filtrantes y del área circundante. Se usó una clasificación de 0 a 3 para describir el grado de cohesión de las células epiteliales y la densidad de células caliciformes, siendo el grado 0 indicador de células epiteliales en placas y abundantes células caliciformes y el grado 3, de pérdida de cohesión del epitelio y ausencia de células caliciformes.
ResultadosEl grado medio de la citología de impresión en las ampollas de filtración fue de 2,4±0,9 y en el área circundante de 0,8±0,3 (p<0,001). Estas diferencias fueron independientes del uso de MMC (p=0,48). El 83% de las ampollas presentaban células epiteliales cilíndricas dehiscentes y ausencia de células caliciformes. En la conjuntiva circundante, el 100% de los casos presentaban células epiteliales en placas con distintos grados de células caliciformes.
ConclusiónEl epitelio de las ampollas filtrantes presentó cambios significativos que consistían en aumento de los espacios intercelulares y pérdida de células caliciformes. Estos espacios intercelulares aumentados podrían explicar un paso transcelular del humor acuoso. La pérdida de mucina secundaria a la pérdida de células caliciformes contribuiría al riesgo de infección de las ampollas filtrantes.