To study the costs associated with high myopia (HM) with choroidal neovascularisation (mCNV) or without mCNV.
MethodsObservational, retrospective, cross-sectional, and multicentre study (HM and mCNV) conducted on adult patients. Annualised medical direct cost (MDC) from the perspective of the National Health System, the non-medical direct cost (nMDC) from the patient perspective, and productivity losses were calculated.
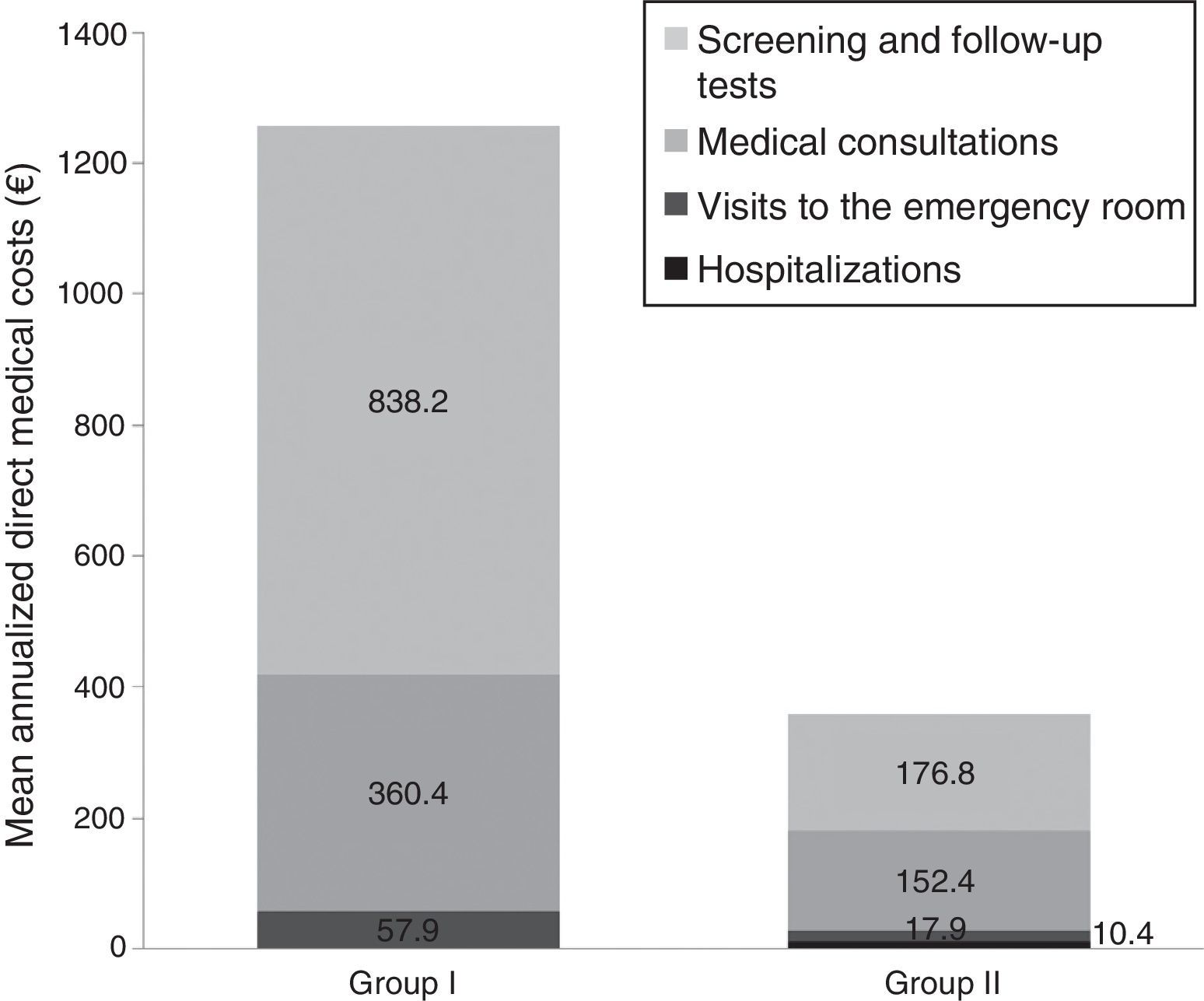
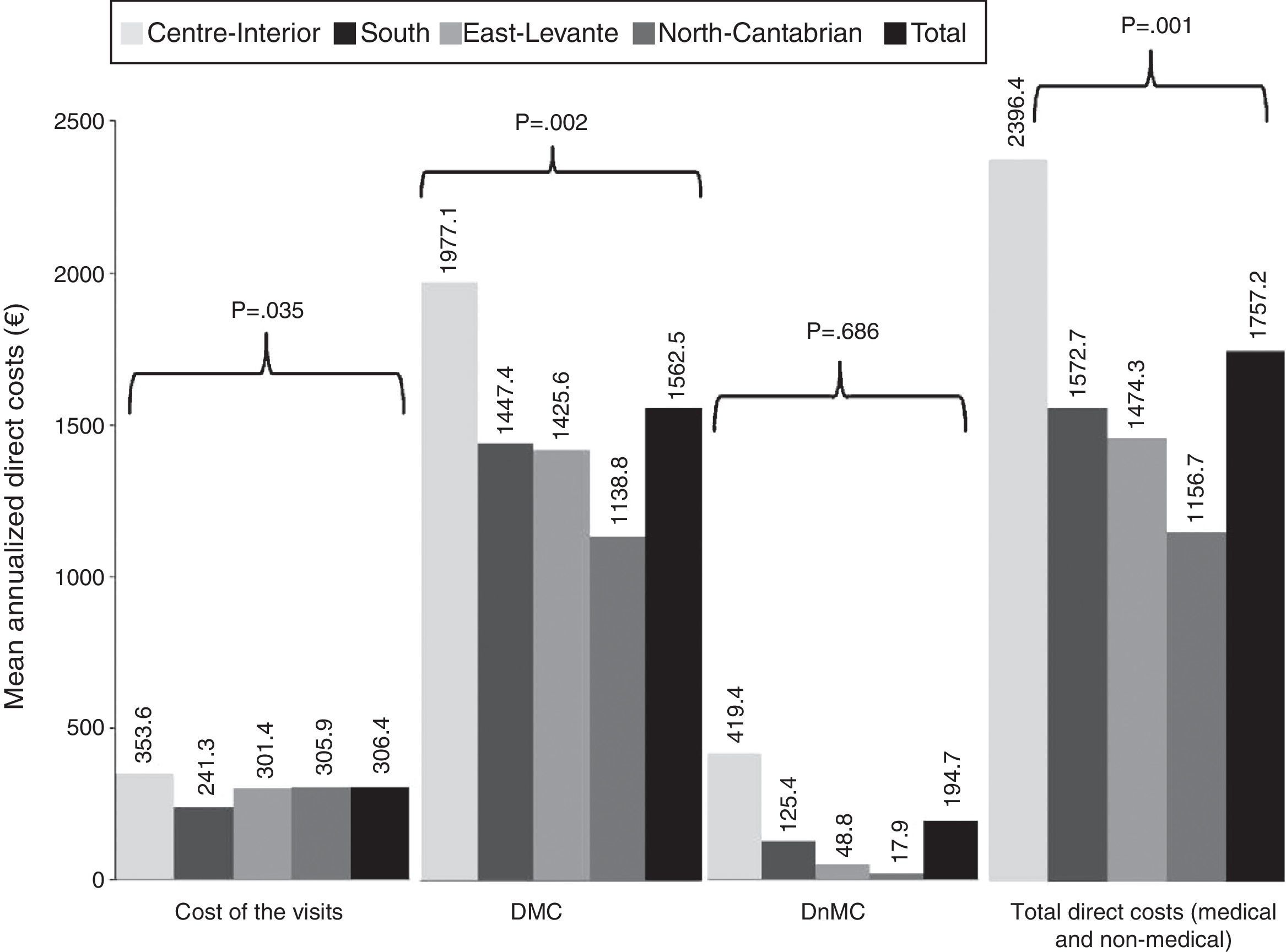
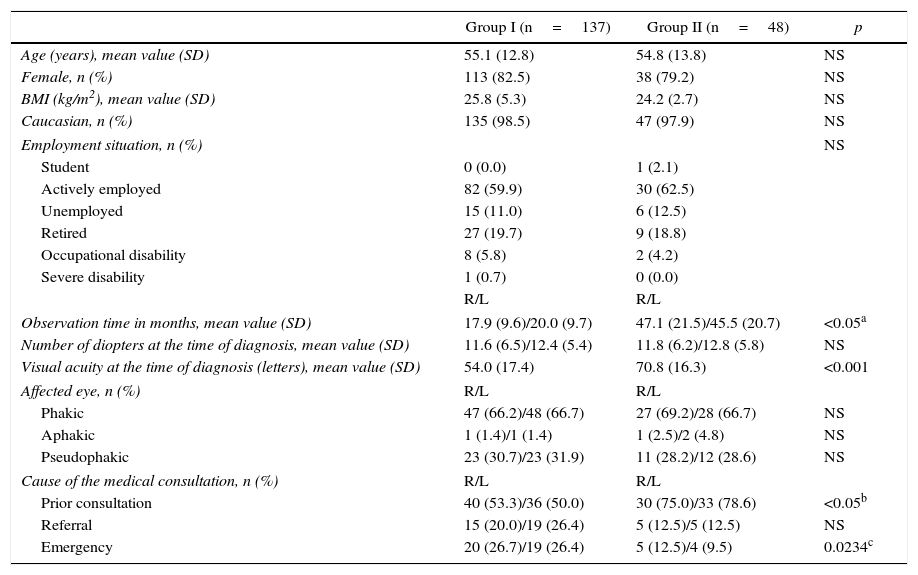
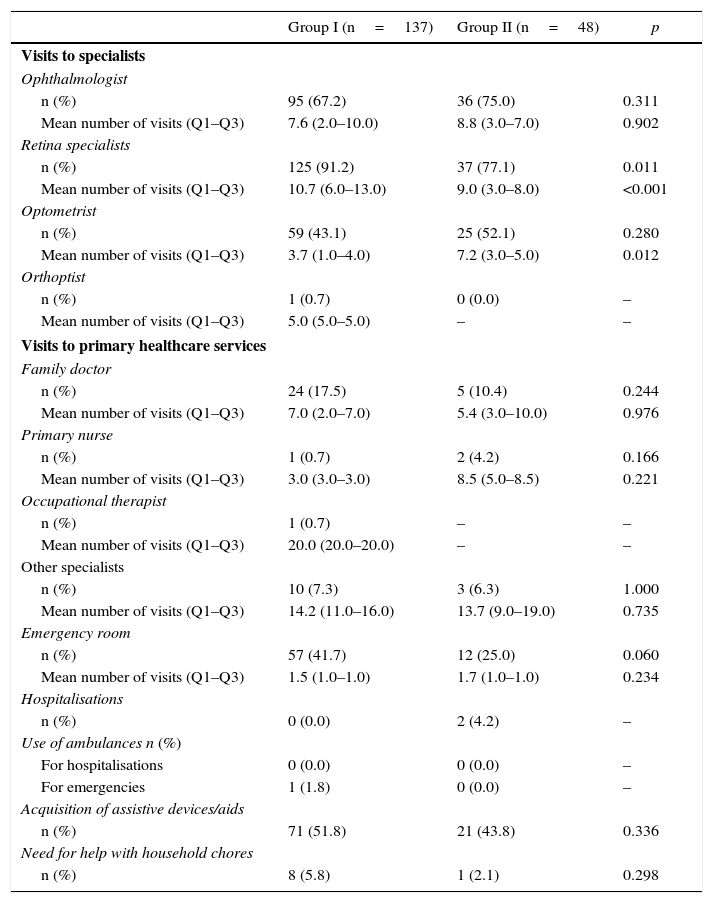
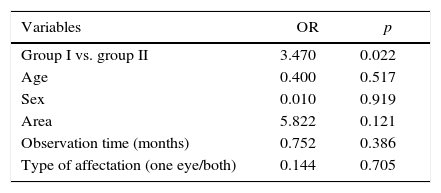
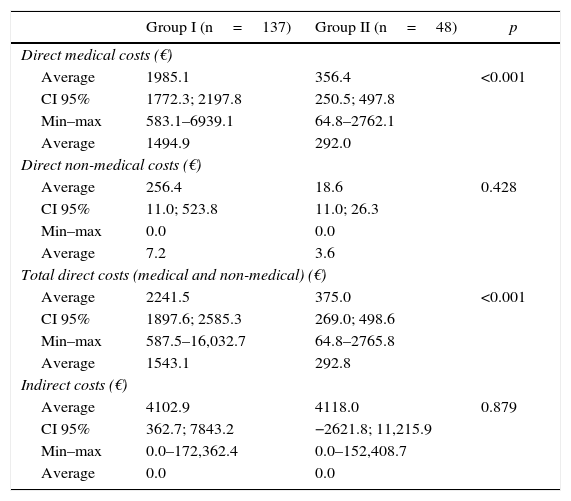
ResultsA total of 137mCNV and 48 HM patients were included (mean age [SD]: 55.1 [2.8] vs. 54.7 [13.8]; p=0.2), with 80% women in both groups. The observation time (months) ranged from 17.9 (9.6) right eye (RE) and 20.0 (9.7), left eye (LE) in mCNV and 47.1 (21.5) RE/45.5 (20.7) LE in MM. A higher percentage of emergency room visits was observed in mCNV vs. HM patients (41.7 vs. 25%; p=0.06) and retinal specialists (91.2 vs. 77.1%; p=0.01). The MDC was higher in mCNV: € 1985 (95% CI: 1772–2198) vs. € 356 (251–480) HM, p<0.001. The nMDC was also higher in mCNV: € 256 (11–524) vs. € 19 (11–26) HM, p>0.4. The number of affected eyes, the follow-up time, and the mCNV were factors associated with direct costs. The impact on work productivity was higher in mCNV (quite/very concerned): 27.7 vs. 10.4% HM. The mCNV showed a significant association with activity impairment (OR: 3.47, 95% CI: 10.101–1.195).
ConclusionsmCNV involves higher medical costs than HM. In addition, mCNV patients have a greater need of care and assistive devices, and greater impact of the disease in their work productivity.
Estudiar los costes asociados a la enfermedad en pacientes miopes magnos (MM) con neovascularización coroidea miópica (NVCm) y sin NVCm.
MétodosEstudio observacional, retrospectivo, transversal, multicéntrico de pacientes MM adultos con y sin NVCm. Se calcularon anualizados el coste directo médico (CDM) desde la perspectiva del Sistema Nacional de Salud, el coste directo no médico (CDnM) desde la perspectiva del paciente y los costes derivados de la pérdida de productividad laboral.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 137 NVCm y a 48 MM pacientes (edad media [DE]: 55,1 [2,8] vs. 54,7 [13,8]; p=0,2). El 80% fueron mujeres en ambos grupos. El tiempo de observación (meses) osciló entre 17,9 (9,6) en el ojo derecho (OD) y 20,0 (9,7) en el ojo izquierdo (OI) en NVCm y 47,1 (21,5) OD y 45,5 (20,7) OI en MM. Se observó un mayor porcentaje de visitas a urgencias en pacientes NVCm vs. MM (41,7 vs. 25%; p=0,06) y a especialistas de retina (91,2 vs. 77,1%; p=0,01). El CDM fue mayor en NVCm: 1.985€ (IC 95%: 1.772-2.198) vs. 356€ (251-480) MM; p<0,001. El CDnM también fue más alto en NVCm: 256€ (11-524) vs. 19€ (11-26) MM; p>0,4. El número de ojos afectos, tiempo de seguimiento y NVCm se asociaron con los costes directos. El impacto en la actividad laboral fue mayor en NVCm (bastante/muy afectados): 27,7 vs. 10,4% en MM. La NVCm mostró una asociación significativa con la afectación laboral (OR: 3,47; IC 95%: 10,101-1,195).
ConclusionesLa NVCm implica un coste médico más elevado que la MM. Los pacientes con NVCm presentan una mayor necesidad de cuidados y de dispositivos de ayuda, así como un mayor impacto de la enfermedad en su vida profesional.