To evaluate the anesthetic block provided by contact topical anesthesia (CTA) in strabismus surgery in adult patients. To analyze postoperative pain and surgical outcome obtained by CTA compared with general anesthesia (GA).
MethodologyProspective longitudinal cohort study of adult patients undergoing strabismus surgery by CTA or GA. The intensity of pain perceived by patients during the course of surgery and in the postoperative period was measured using Numerical Pain Scale. The success of the surgical outcome, considered as a residual ocular deviation <10 prism diopters, was evaluated.
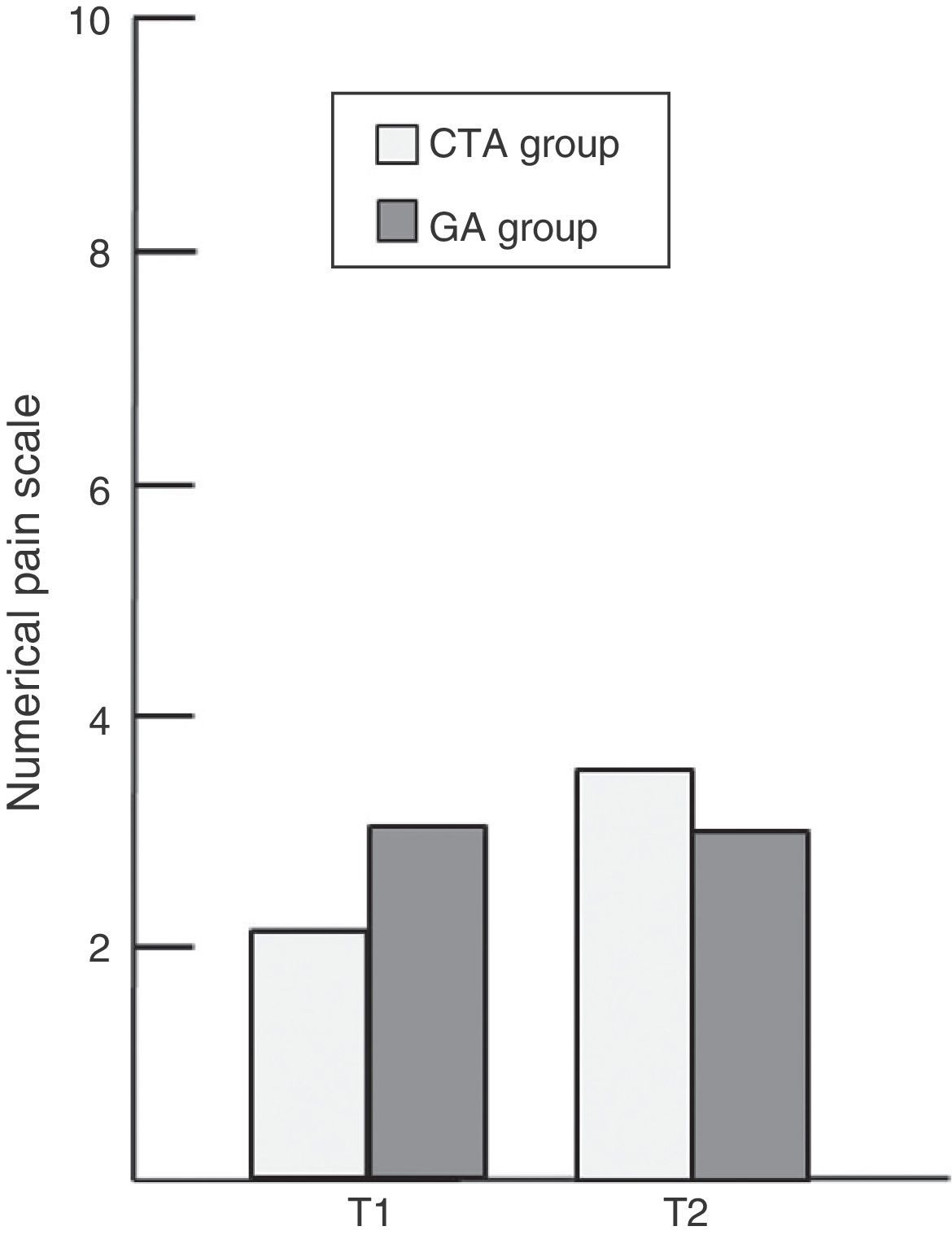
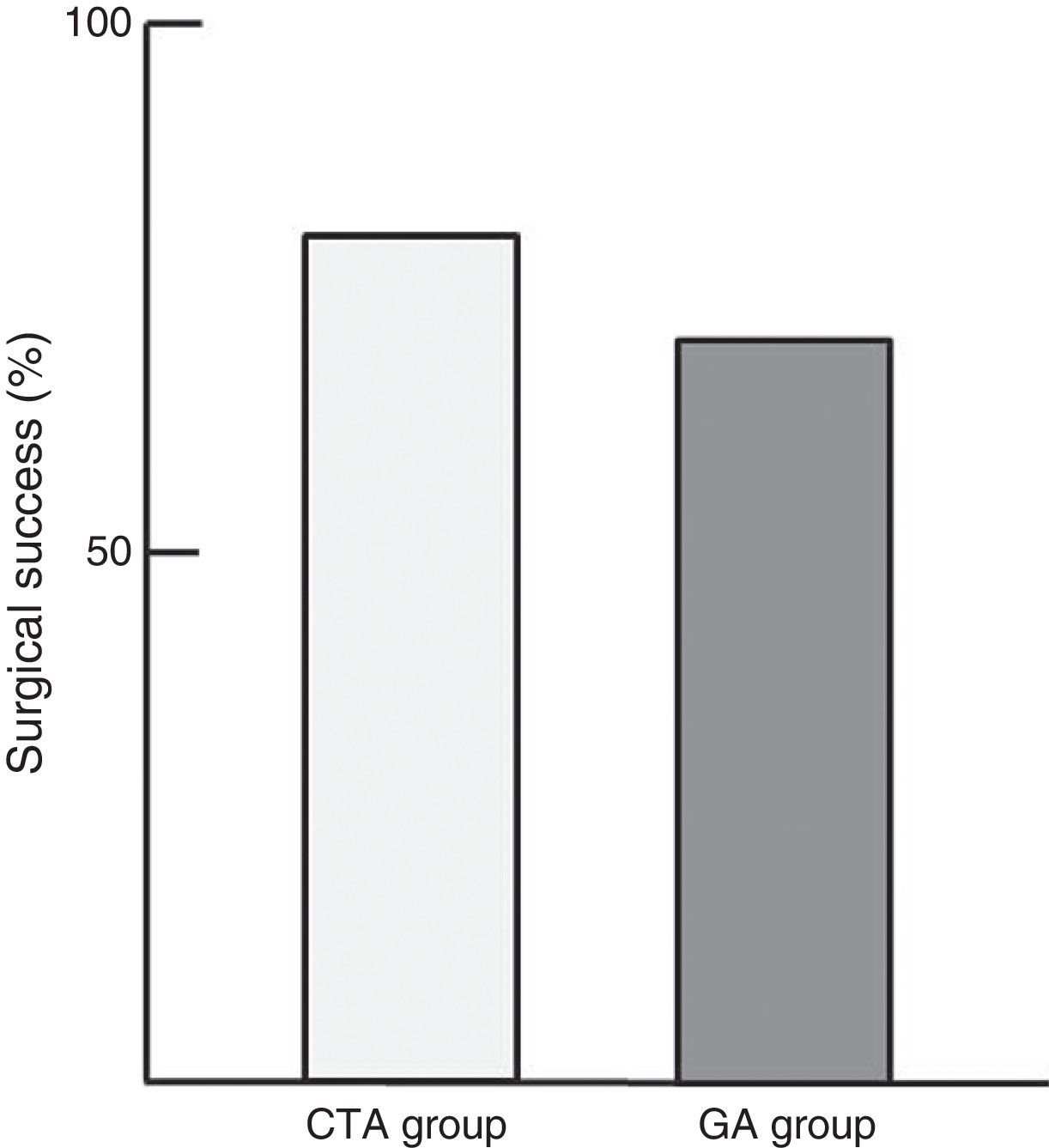
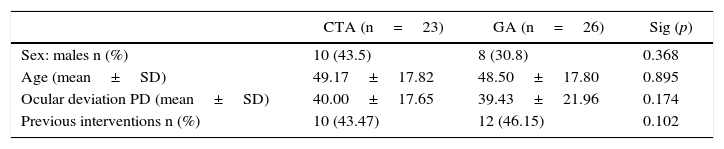
ResultsTwenty-three patients were operated using CTA and 26 using AG. During the course of surgery, pain intensity experienced by patients in ATC group was 3.17±2.44. There were no differences between CTA group and AG group in the intensity of pain in the immediate postoperative period (2.13±2.39 vs. 2.77±2.18, respectively; p=.510) and during the first postoperative day (3.22±2.84 vs. 3.17±2.73; p=.923). Surgical success was significantly higher in the CTA group than in the GA group (78.3% vs. 73.1%; p=.019).
ConclusionsCTA provides adequate sensory block to perform strabismus surgery. The control of postoperative pain is similar to that obtained with AG. Conservation of ocular motility providing CTA enables better surgical outcome.
Evaluar el bloqueo anestésico proporcionado por la anestesia tópica de contacto (ATC) en cirugía de estrabismo en pacientes adultos. Analizar el dolor postoperatorio y el resultado quirúrgico obtenido mediante ATC y compararlo con la anestesia general (AG).
MetodologíaEstudio de cohortes longitudinal prospectivo en pacientes adultos intervenidos de estrabismo mediante ATC o AG. Se midió la intensidad del dolor percibido por los pacientes durante el desarrollo de la intervención y en el periodo postoperatorio mediante la Escala Numérica del Dolor (END). Se evaluó el éxito del resultado quirúrgico, considerado como una desviación ocular residual <10 dioptrías prismáticas.
ResultadosSe intervino a un total de 23 pacientes con ATC y a 26 con AG. Durante el desarrollo de la intervención quirúrgica, la intensidad del dolor padecido por los pacientes del grupo ATC fue de 3,17±2,44. No hubo diferencias entre el grupo ATC y el grupo AG en la intensidad de dolor en el postoperatorio inmediato (2,13±2,39 vs. 2,77±2,18 respectivamente; p=0,510) ni durante el primer día postoperatorio (3,22±2,84 vs. 3,17±2,73; p=0,923). El éxito quirúrgico fue significativamente mayor en el grupo ATC que en el grupo AG (78,3 vs. 73,1%; p=0,019).
ConclusionesLa ATC proporciona un adecuado bloqueo sensitivo para poder llevar a cabo la cirugía de estrabismo, logrando un control del dolor postoperatorio similar al obtenido con la AG. La conservación de la motilidad ocular que proporciona la ATC permite obtener un mejor resultado quirúrgico.