To propose guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of facial dystonia prepared by a group of experts in orbit and oculoplastics from the Iberoamerican Oculoplastic Society.
Material and methodsAn interactive discussion between the expert panel and those attending the 6th Iberoamerican Society of Oculoplastics Congress, which took place at the Hospital Nuestra Señora de la Luz in Mexico City on 22 October 2018, providing their personal experience based on evidence for diagnosis and treatment of facial dystonia. Around 200 ophthalmologists specialized in oculoplastics from North, Central and South America, Spain, and Portugal were involved. Discussion was focused on the following themes: pathophysiology, diagnosis, medical management, and surgical management.
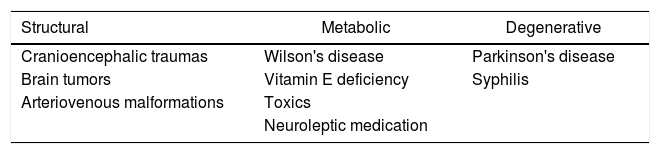
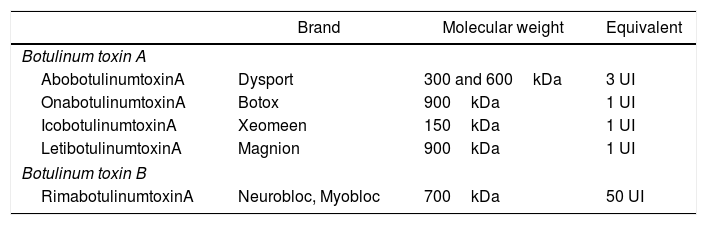
ConclusionsFacial dystonia diagnosis is clinical; therefore, image studies are rarely needed. The ophthalmologist is generally the first physician to be consulted, and is able to be the treating physician, with the exception of specific cases of hemifacial spasm where management with neurosurgery may be beneficial. Botulinum toxin is the treatment of choice. Treatment with oral neuroleptics and myectomy of the orbicularis oculi muscle are reserved for refractory cases, since these do not have an adequate clinical response as first choice treatments. Persistent use of botulinum toxin does not modify the natural course of the disease.
Proponer una guía para el diagnóstico y el manejo de pacientes con distonías faciales por parte de un grupo de expertos en órbita y oculoplástica miembros de la Sociedad Iberoamericana de Oculoplástica.
Material y métodosSe realizó una discusión dirigida interactiva entre el panel de expertos y los asistentes al VI Congreso de la Sociedad Iberoamericana de Oculoplástica realizado en las instalaciones del Hospital Nuestra Señora de la Luz en la Ciudad de México el 22 de octubre de 2018, presentando la experiencia basada en la evidencia y la experiencia personal para el diagnóstico y el tratamiento de distonías faciales. Al encuentro asistieron alrededor de 200 médicos oftalmólogos especialistas en oculoplástica originarios de Norte, Centro y Sudamérica, así como de España y Portugal. La discusión se centró en los siguientes sub-temas: fisiopatología, diagnóstico, manejo médico y manejo quirúrgico.
ConclusionesEl diagnostico de las distonías faciales es clínico y rara vez requiere estudios complementarios de imagen. El oftalmólogo es generalmente el médico de primer contacto y está capacitado para ser el médico tratante salvo casos muy específicos de espasmo hemifacial, donde el manejo en conjunto con neurocirugía puede resultar beneficioso. El tratamiento de primera elección es la toxina botulínica. La terapia con neurolépticos orales y la miectomía del músculo orbicular se reservan para casos refractarios, ya que no presentan buena respuesta clínica como terapias de primera elección. El uso crónico de toxina botulínica no modifica el curso natural de la enfermedad.