To assess the characteristics of patients with wet AMD and low intake of lutein and zeaxanthin in our population.
MethodsA prospective, observational, cross-sectional study was conducted on patients with active wet AMD. A full blood count, a lipid and liver profile, a dietary interview (24-h recall), and an anthropometric study were performed. Lutein–zeaxanthin (LZ) intake results split the patents in two groups.
Group 1 (“sufficient” intake): patients with ≥1400mg/day intake in women and 1700mg/day in men (2/3 of the average daily intake in a normal population).
Group 2: patients with daily intakes below that of group 1. A descriptive and comparative statistical study was performed.
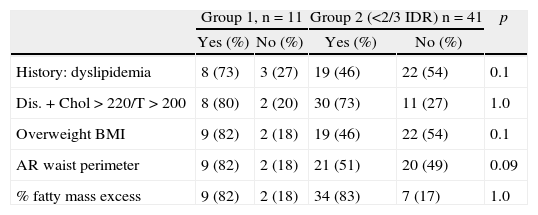
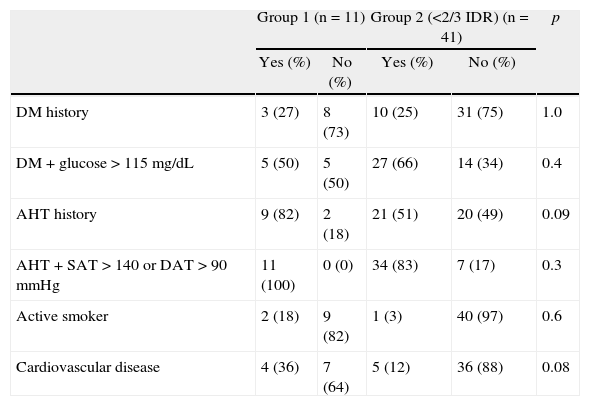
ResultsFifty-two patients with a mean age of 78.9 years. Group 1: eleven patients (21% of the sample). Group 2: forty-one patients. The subjects with adequate intake of LZ had higher a body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference. Between 70 and 80% of patients in group 1 had inadequate intake of vitamins A, C, E and zinc.
ConclusionsSeventy-nine percent of the patients with wet AMD have a deficient daily intake in LZ. The population with adequate intake is associated with an increased BMI and waist circumference, and in addition, most of them have an insufficient intake of vitamins A, C, E and zinc.
Averiguar las características de los pacientes con DMAE húmeda que ingieren suficiente luteína y zeaxantina en nuestra población.
MétodosEstudio protocolizado, prospectivo, observacional, transversal, en pacientes diagnosticados de DMAE húmeda activa. Se efectúa hemograma, perfil lipídico, y perfil hepático; una entrevista dietética sobre los hábitos alimentarios a partir de la realización de un recordatorio de 24 h y estudio antropométrico. Se dividen en dos grupos en función de la ingesta de luteína-zeaxantina (L-Z).
Grupo 1 (ingesta «suficiente»): pacientes con ingesta diaria ≥1.400 mg/día en mujeres y 1.700 mg/día en hombres (2/3 de la ingesta media diaria en población normal).
Grupo 2: pacientes con ingesta diaria inferior a las del grupo 1. Se efectúa un estudio estadístico descriptivo y comparativo entre ambos grupos.
ResultadoUn total de 52 pacientes, con una edad media de 78,9 años. Grupo 1: 11 pacientes (21% de la muestra). Grupo 2: 41. Los pacientes con ingesta suficiente de L-Z tienen mayor índice de masa corporal y perímetro de cintura. El 70-80% de los pacientes del grupo 1 presentan ingesta insuficiente de vitaminas A, C y E, y zinc.
ConclusionesEl 79% de los pacientes tienen ingesta diaria de L-Z baja. Los pacientes con aporte suficiente tienen un aumento en el índice de masa corporal y perímetro de cintura, y además la mayoría tienen una ingesta insuficiente de vitaminas A, C y E, y zinc.