To determine the effectiveness of a botulinum toxin type A injection in both medial rectus muscles in patients with partially accommodative esotropia. Residual deviation and stability of strabismus were evaluated at 18 months follow up.
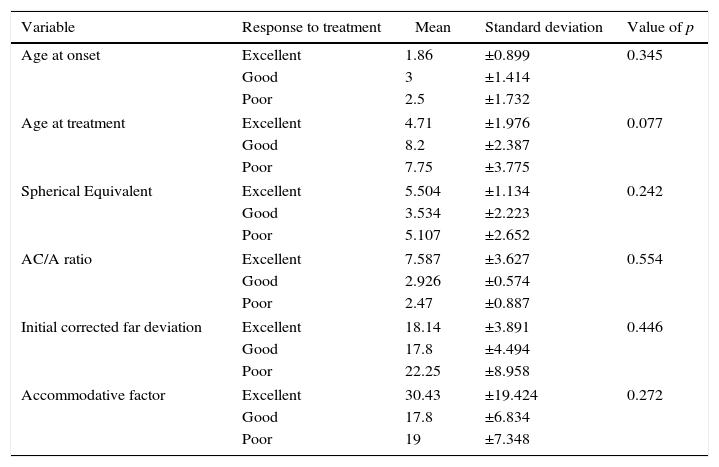
MethodA prospective, analytical, quasi-experimental study was conducted on a cohort of 21 patients who underwent total cycloplegic refraction and with a residual deviation of at least 14 DP. A botulinum toxin type A dose of 5IU was injected into each medial rectus muscle for a residual deviation greater than 18 DP, with a dose of 2.5IU being used for a deviation between 14 and 18 DP. Multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed to relate residual deviation to variables recorded as potential predictors.
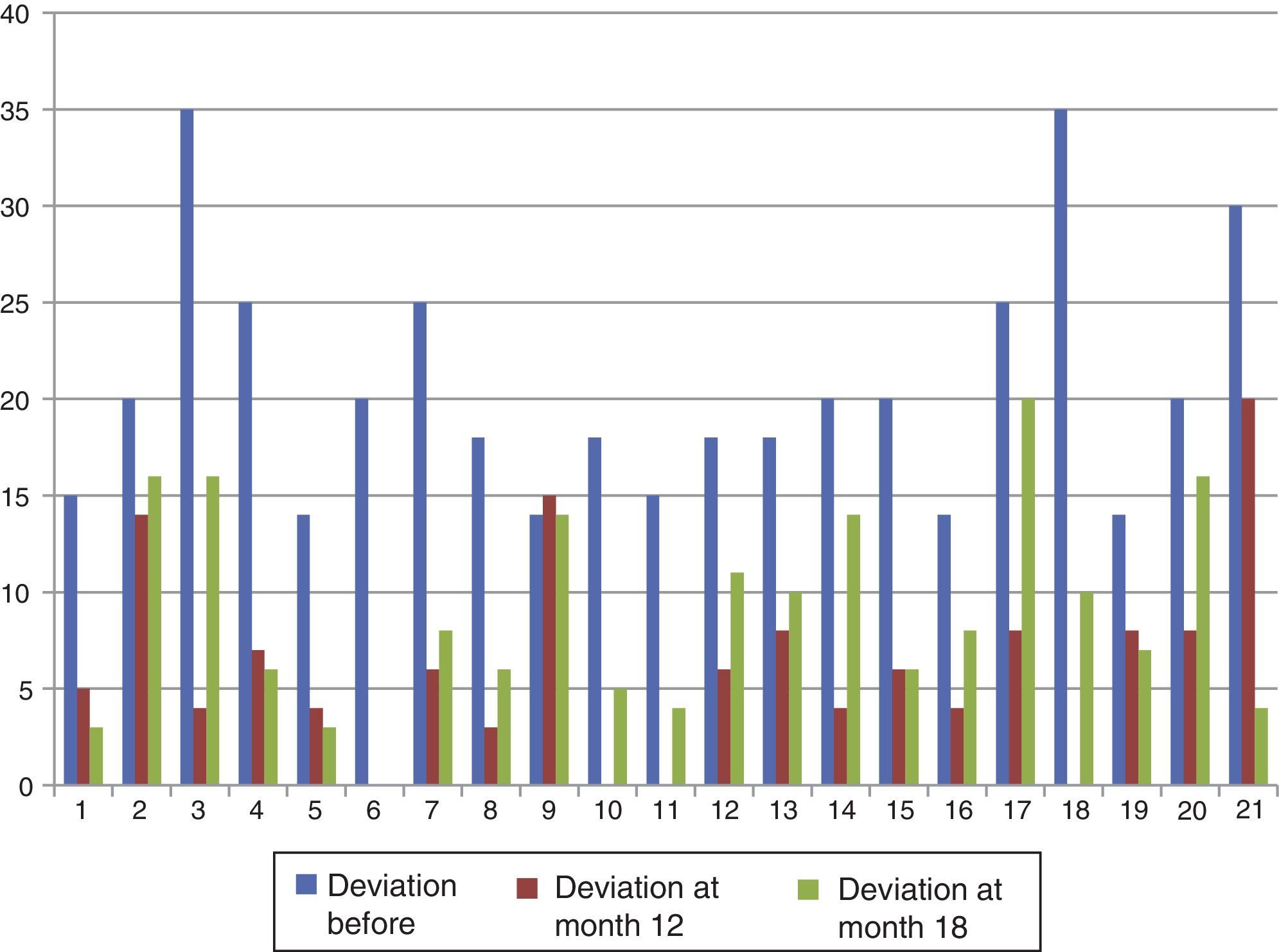
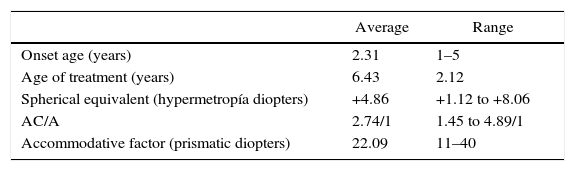
ResultsA total of 21 patients were included, 33.3% (n=7) males and 66.6% (n=14) females. Mean visual acuity was –0.28±0.25 logMAR for right eye (range 0 to –1) and –0.42±0.31 logMAR for left eye (range 0 to –1.3). Mean angle of residual deviation before application of botulinum toxin was 40.95±8.6 DP without spectacles correction, and 22.3±7.99 DP with full cycloplegic refraction. Adverse effects were ptosis in 14.2% (n=3), diplopia 23.8% (n=5), and vertical deviation in 33% (n=7). One patient had a poor outcome, therefore required surgical treatment.
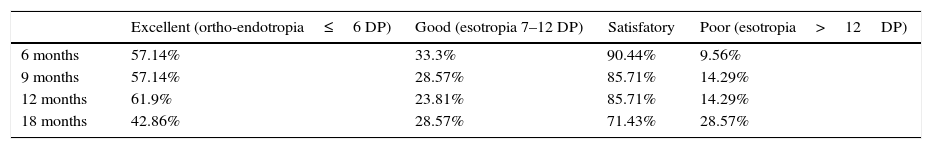
At one year follow up, 85.71% of patients showed good results with esotropia of 12 DP or less, dropping to 71.43% at 18 months of follow up.
ConclusionBotulinum toxin type A is an effective long-term treatment with a good response in 71.43% of patients. No predictors of good response were demonstrated.
Determinar la efectividad de la toxina botulínica (TB) tipo A aplicada en ambos rectos mediales en pacientes con endotropía parcialmente acomodativa (ETPA). Se evaluó la desviación residual y su estabilidad a 18 meses de seguimiento.
MétodoEstudio analítico prospectivo, cuasi experimental. Se estudió una cohorte de 21 pacientes con uso de refracción ciclopléjica total con desviación residual igual o mayor a 14 DP. Se realizó aplicación de TB en ambos rectos mediales, 5U de TB para desviaciones residuales mayores de 18 DP y 2,5U para desviaciones residuales menores. El análisis incluyó regresión logística entre variables para considerar factores predictivos.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 21 pacientes, 33,3% pacientes (n=7) del género masculino y 66,6% (n=14) del género femenino. La capacidad visual promedio fue de –0,28±0,25 logMAR ojo derecho (rango 0 a –1) y –0,2±0,31 logMAR ojo izquierdo (rango 0 a –1,3). El ángulo de endodesviación promedio previo a la aplicación de TB se encontró de 40,95±8,6 DP sin corrección y de 22,3±7,99 DP con corrección. Los principales efectos secundarios fueron: ptosis 14,2% (n=3), diplopía 23,8% (n=5) y desviaciones verticales 33% (n=7).
Al año de seguimiento el 85,71% de pacientes tuvieron un resultado bueno con endotropía menor a 12DP. Estos porcentajes disminuyeron a los 18 meses de seguimiento al 71,43%.
ConclusionesEl uso de TB tipo A permite obtener un resultado motor bueno a 18 meses en la mayoría de los pacientes. No se demostraron factores predictivos para el pronóstico.