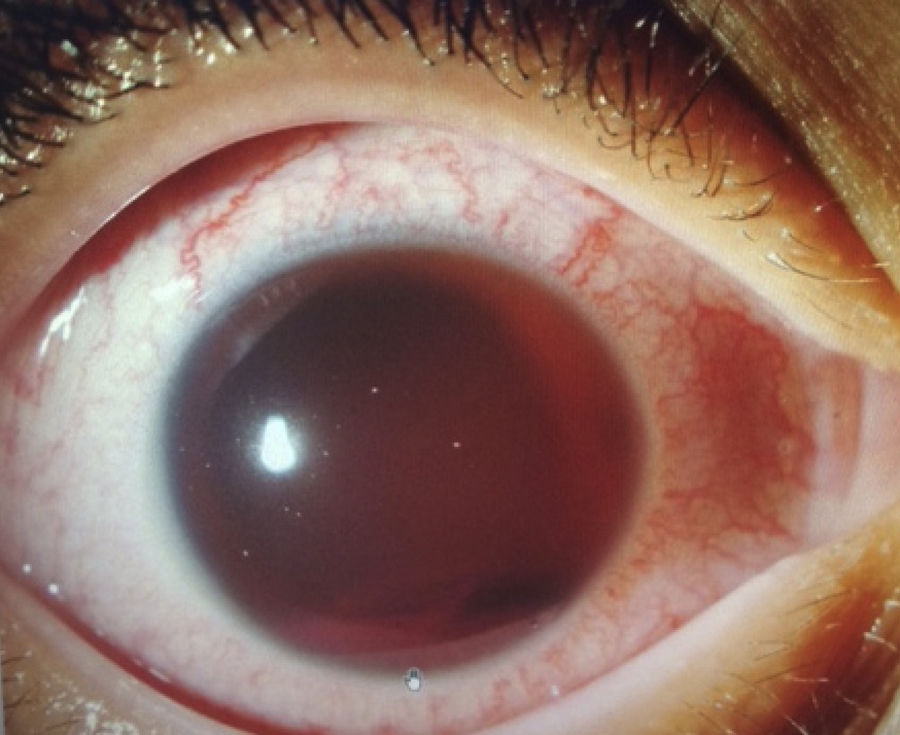
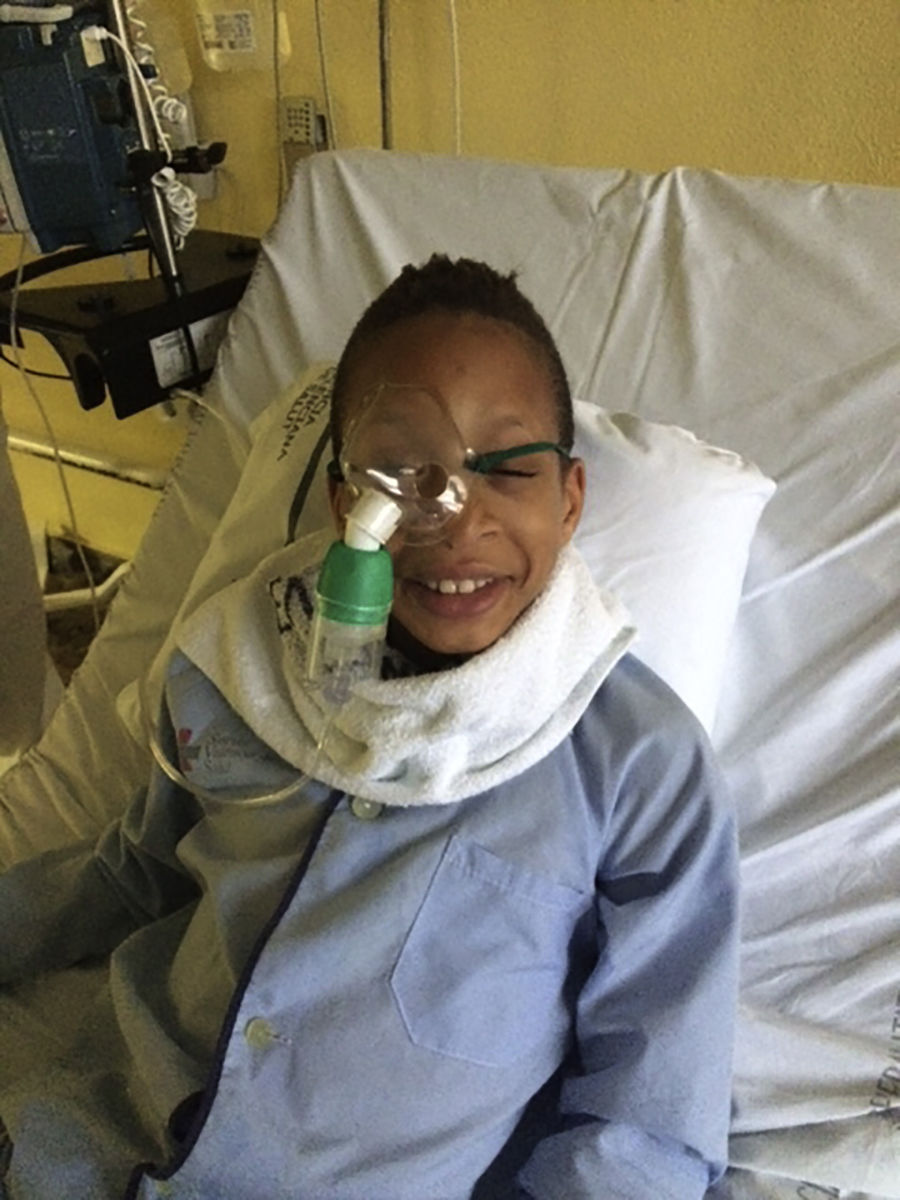
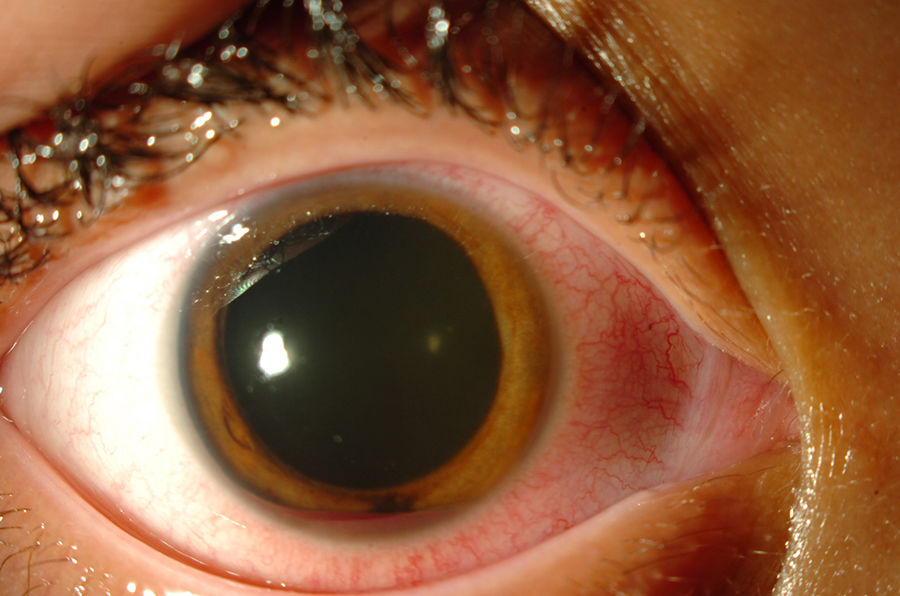
The case concerns a 10-year-old boy of African origin, who suffered a mild ocular trauma to the left eye. Upon examination, the best visual acuity was 0.2 using the Snellen scale, with a 1mm height hyphema, intraocular pressure (IOP) of 12mmHg on left eye, with an increase up to 20mmHg within 72h. With a positive test for sickle cell disease, it was decided to treat medically with transcorneal oxygen therapy. Clearing of the anterior chamber was achieved, with an improvement in the best visual acuity to 0.8, and lowering of IOP to 8mmHg.
DiscussionIn the context of patients with persistent hyphema with sickle cell trait, transcorneal oxygen therapy is an effective alternative therapy. Achieving immediate and favorable results by lowering the IOP and improving the clearing of the anterior chamber.
Paciente varón de 10 años, de raza negra, con antecedente de traumatismo leve en ojo izquierdo; presenta agudeza visual corregida de 0,2 en escala de Snellen, hifema con altura de 1mm, presión intraocular (PIO) de 12mmHg en ese ojo, con incremento de PIO a 20mmHg a las 72h. Con el resultado positivo del estudio de drepanocitos, se decide tratamiento médico con oxigenoterapia transcorneal. Se logra el aclaramiento de la cámara anterior, con agudeza visual corregida de 0,8 y la reducción de la PIO a 8mmHg.
DiscusiónEn los pacientes con hifema persitente en el contexto de una drepanocitosis, la oxigenoterapia transcorneal es una buena alternativa terapéutica. Se obtienen resultados satisfactorios inmediatos con la disminución de la PIO y el aclaramiento de la cámara anterior.