To evaluate the effects of anti-glaucoma treatments containing benzalconium chloride (BAC) on the human cornea.
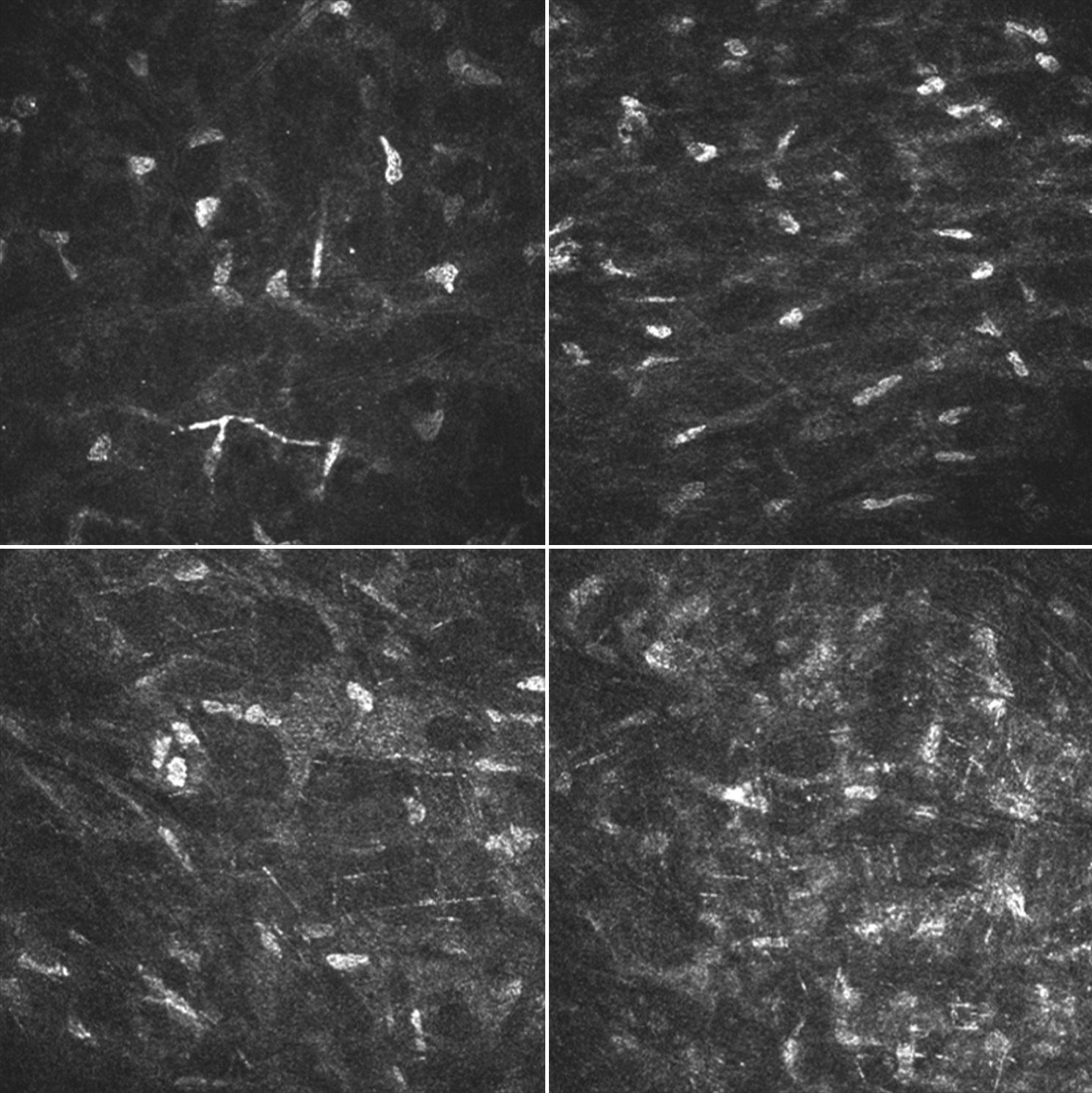
MethodsA prospective single masked cohort study was conducted on the 50 eyes of 50 patients. The inclusion criteria were recently diagnosed glaucoma or ocular hypertension with previous treatment, or ophthalmologist-prescribed anti-glaucoma therapy, and oral consent to participate in the study. The patients were not randomized, as the ophthalmologist decided the best therapy according to clinical criteria. The patients were divided in 2 cohorts: those exposed to BAC (23 patients), and those not exposed (27 patients). The mean follow-up period was 22 weeks (range 18–30). The change in cell density before and after therapy was measured in basal layer epithelium, basal layer of limbal epithelium and endothelium. The change in stromal reflectivity and the number of nerve branches in sub-basal nerve plexus was also measured. BAC exposure was blinded to the main researcher.
ResultsA greater increase in basal layer epithelium cell density was observed in BAC exposed cohort (p<0.05). No significant differences were detected in the endothelium, limbal cell density, stromal reflectivity, or sub-basal nerve plexus. Age, sex, IOP, active ingredient or BAC concentration did not affect the direction or magnitude of the ocular surface alterations found.
ConclusionChronic anti-glaucoma therapy induces changes in the corneal epithelium. Preservative free drops showed less disruption of the ocular surface by confocal microscopy analysis. Further studies should be conducted to evaluate the clinical impact of these histological findings.
Evaluar los efectos sobre la córnea humana de hipotensores oculares con cloruro de benzalconio (BAC).
MétodosEstudio prospectivo de cohortes, simple ciego realizado sobre 50 ojos de 50 pacientes. Los criterios de inclusión fueron: diagnóstico reciente de glaucoma o hipertensión ocular sin tratamiento previo, terapia antiglaucomatosa prescrita por un oftalmólogo y consentimiento para participar en el estudio. Los pacientes no fueron asignados al azar: el oftalmólogo decidió la mejor terapia de acuerdo a los datos clínicos. Se dividieron en dos grupos: uno expuesto a BAC (23 pacientes) y otro no expuesto (27 pacientes). La media de seguimiento fue de 22 semanas (rango 18–30). Se midió el cambio en la densidad celular antes y después de la terapia en: el epitelio basal, la capa basal del epitelio limbal y el endotelio. También se midió el cambio en la reflectividad estromal y el número de ramas del nervio del plexo subasal. La exposición a BAC era desconocida para el investigador principal.
ResultadosUn mayor aumento en la densidad de la capa de células basales del epitelio se observó en la cohorte expuesta BAC (p<0,05). No se detectaron diferencias significativas en la densidad del endotelio, las células del limbo, la reflectividad del estroma ni en el plexo nervioso subbasal. Edad, sexo, PIO, principio activo ni la concentración de BAC afectaron el sentido o la magnitud de las alteraciones encontradas en la superficie ocular.
ConclusiónEl tratamiento crónico antiglaucomatoso induce cambios en el epitelio corneal. Gotas sin conservantes mostraron una menor alteración de la superficie ocular por análisis de microscopia confocal. Los estudios futuros deben evaluar el impacto clínico de estos hallazgos histológicos.