To evaluate the usefulness of a semiautomatic measuring system of arteriovenous relation (RAV) from retinographic images of hypertensive patients in assessing their cardiovascular risk and silent brain ischemia (ICS) detection.
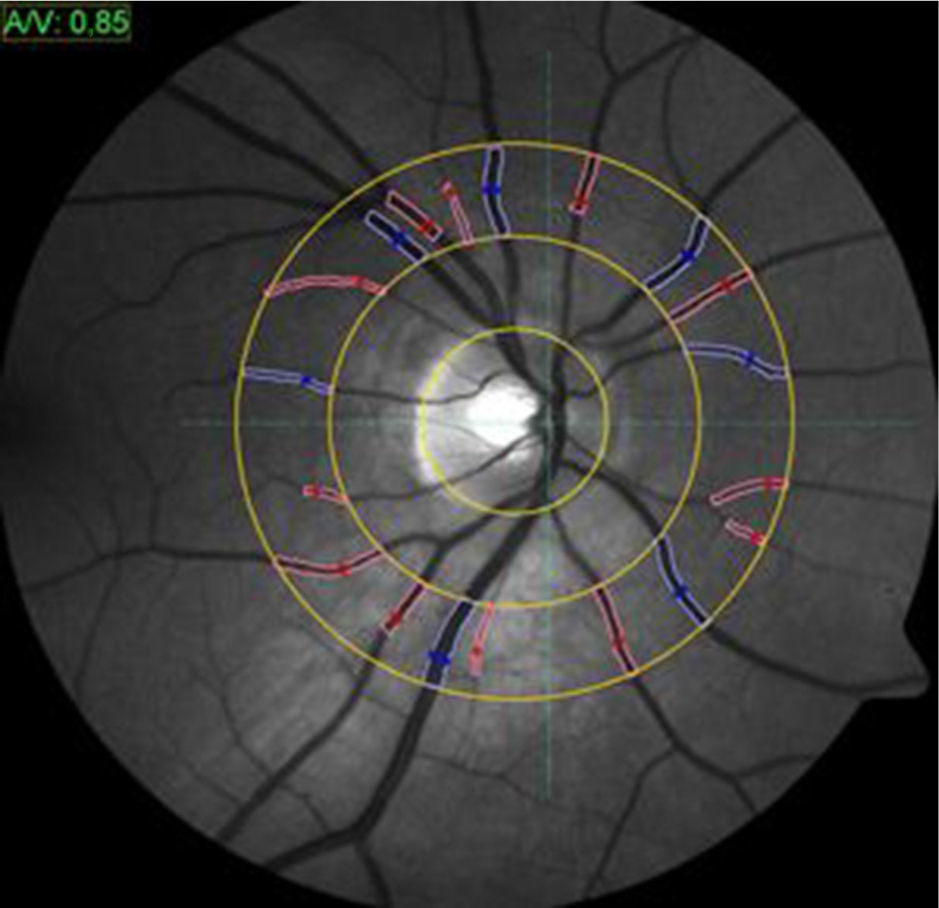
MethodsSemi-automatic measurement of arterial and venous width were performed with the aid of Imedos software and conventional fundus examination from the analysis of retinal images belonging to the 976 patients integrated in the cohort Investigating Silent Strokes in Hypertensives: a magnetic resonance imaging study (ISSYS), group of hypertensive patients. All patients have been subjected to a cranial magnetic resonance imaging (RMN) to assess the presence or absence of brain silent infarct.
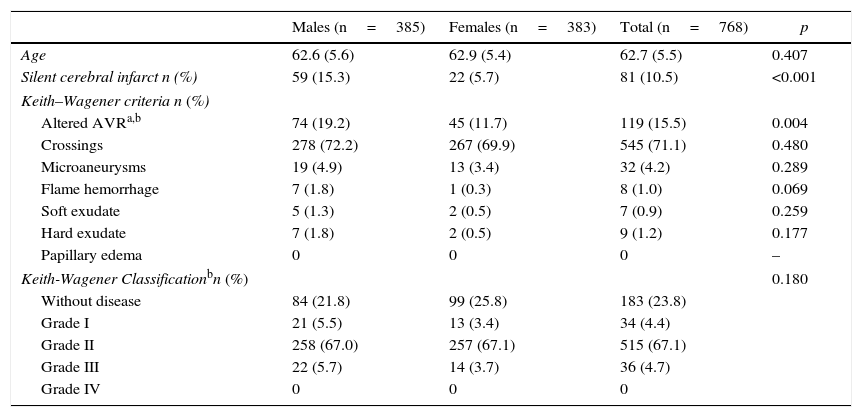
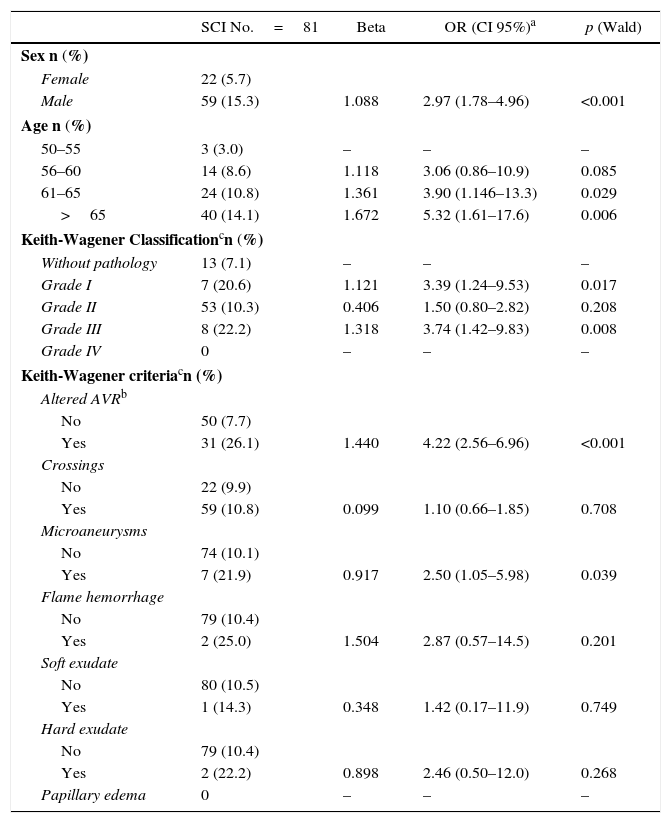
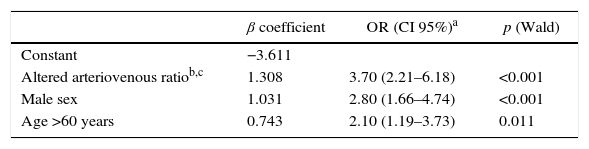
ResultsRetinal images of 768 patients were studied. Among the clinical findings observed, association with ICS was only detected in patients with microaneurysms (OR 2.50; 95% CI: 1.05–5.98) or altered RAV (<0.666) (OR: 4.22; 95% CI: 2.56–6.96). In multivariate logistic regression analysis adjusted by age and sex, only altered RAV continued demonstrating as a risk factor (OR: 3.70; 95% CI: 2.21–6.18).
ConclusionsThe results show that the semiautomatic analysis of the retinal vasculature from retinal images has the potential to be considered as an important vascular risk factor in hypertensive population.
Evaluar la utilidad de un sistema semiautomático de medición de relación arteriovenosa (RAV) retiniana sobre imágenes retinográficas de pacientes hipertensos en la valoración del riesgo cardiovascular y la detección de isquemia cerebral silente (ICS).
MétodoUn total de 976 pacientes de la cohorte Investigating Silent Strokes in Hypertensives: a magnetic resonance imaging study (ISSYS) estudiados mediante resonancia magnética craneal para valorar la presencia o no de ICS fueron invitados a realizar una retinografía para un examen convencional de fondo de ojo y una medición semitautomática del promedio de los calibers vasculares para el cálculo de la relación arteriovenosa (RAV).
ResultadosSe analizaron las retinografías de 768 pacientes. Entre las lesiones observadas, solamente se encontró una asociación con la detección de ICS en aquellos pacientes con microaneurismas (OR: 2,50; IC 95%: 1,05–5,98) o una RAV alterada (<0,666) (OR: 4,22; IC 95%: 2,56–6,96). En el análisis de regresión logística multivariante ajustado por edad y sexo, solamente la RAV alterada continuó manifestándose como un factor de riesgo (OR: 3,70; IC 95%: 2,21-6,18).
ConclusionesLos resultados muestran que el análisis semiautomático de la vasculatura retiniana a partir de retinografías tiene el potencial de ser considerado como un factor de riesgo vascular importante en la población hipertensa.