When a phacoemulsification, a filtration surgery or a combined surgery are necessary, questions about the convenience of continuing certain antiglaucomatous drugs could appear. The aim of this review article is to unify criteria that will guide daily clinical practice and including the developing algorithms of action in the preoperative and postoperative periods of filtration surgery and/or cataract surgery.
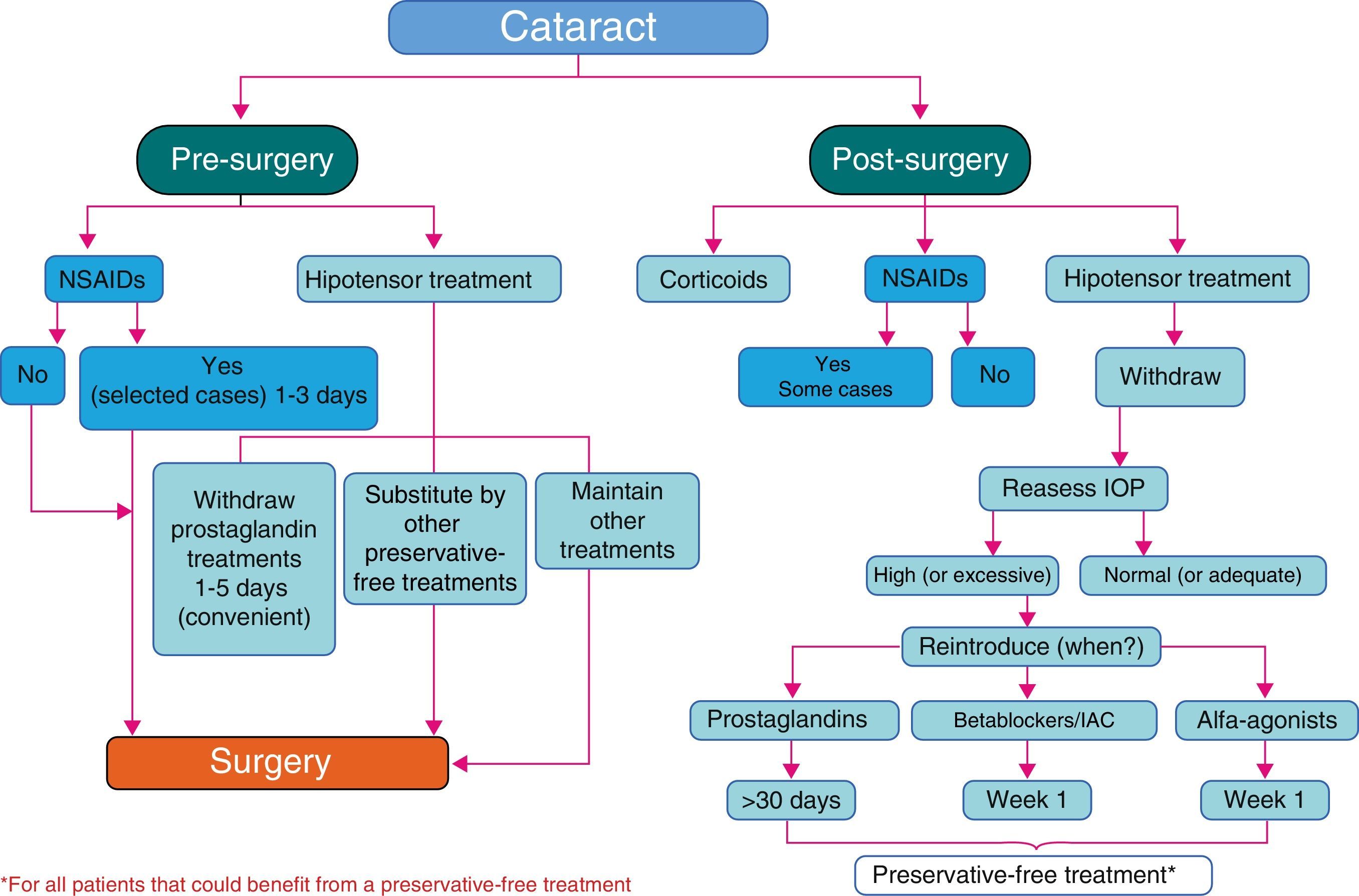
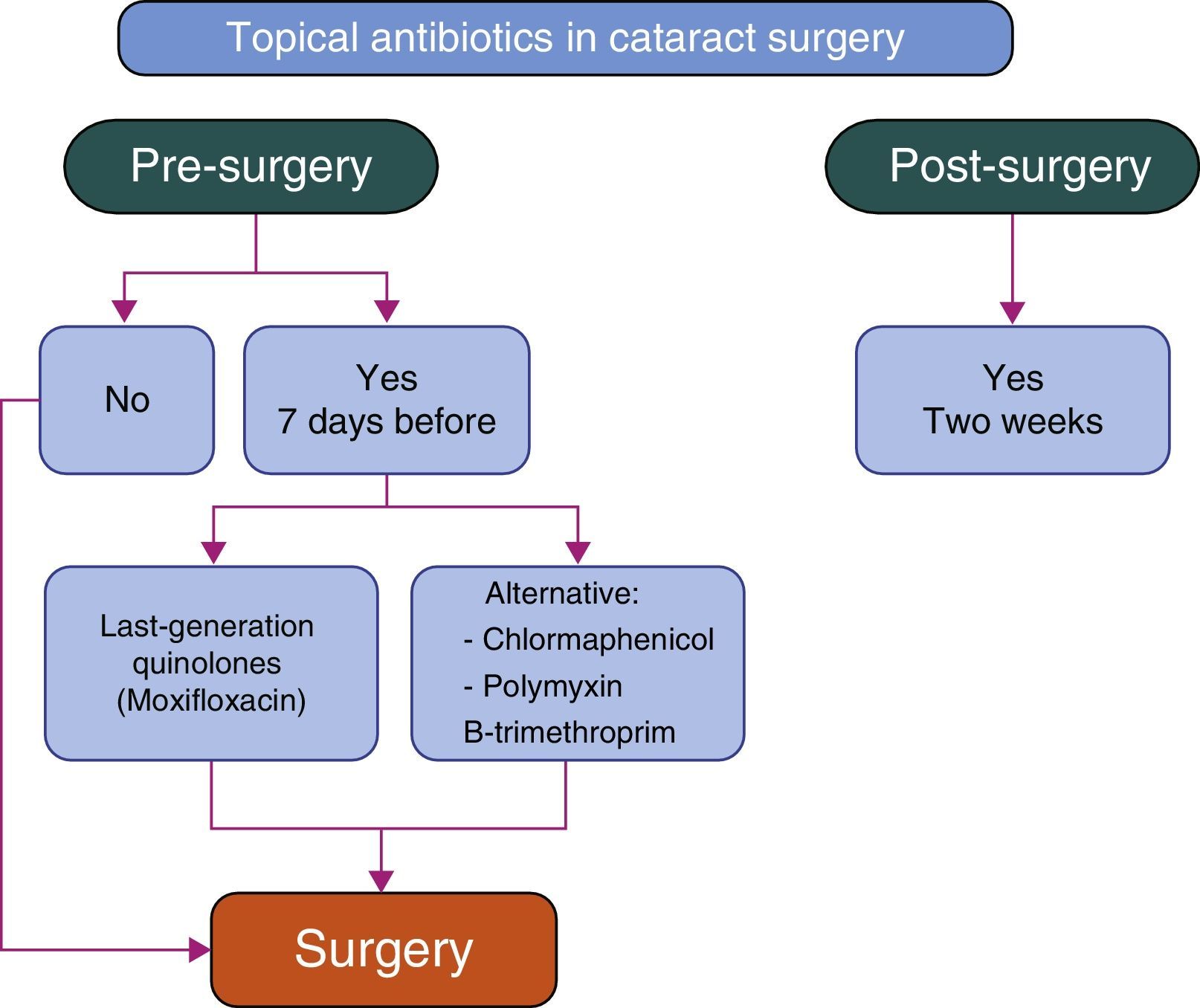
Proposed protocolsIn the preoperative period of cataract surgery, the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is at the discretion of the surgeon, with the monodose presentation being recommended. The suspension of prostaglandines a fewdays before the surgery should be considered. Preservative-free drugs ensure a better recovery of the ocular surface (OS) after cataract surgery. Once all modifying factors of the intraocular pressure (IOP) have been removed, baseline IOP should be evaluated again, choosing preservative-free antiglaucomatous drugs when needed.
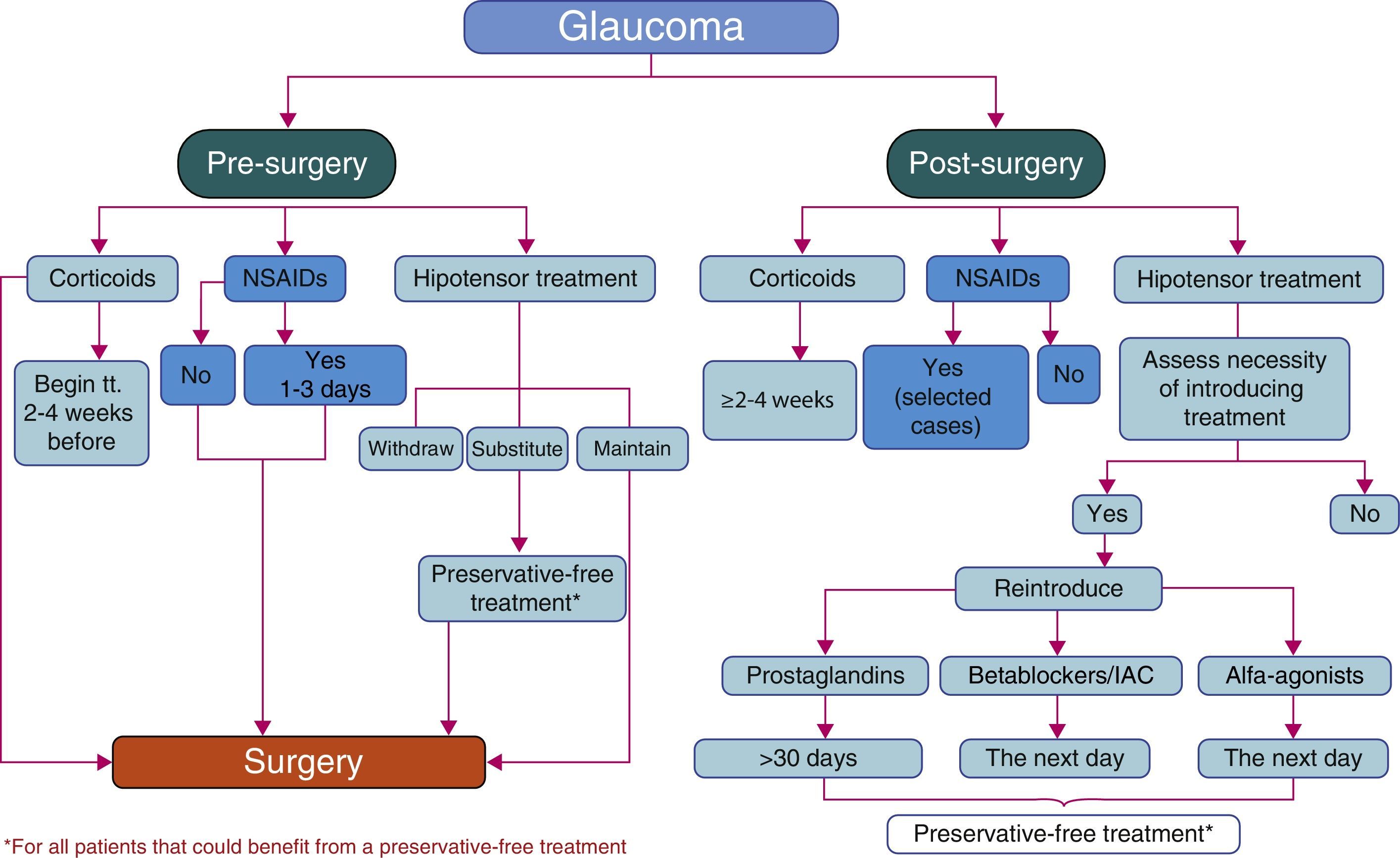
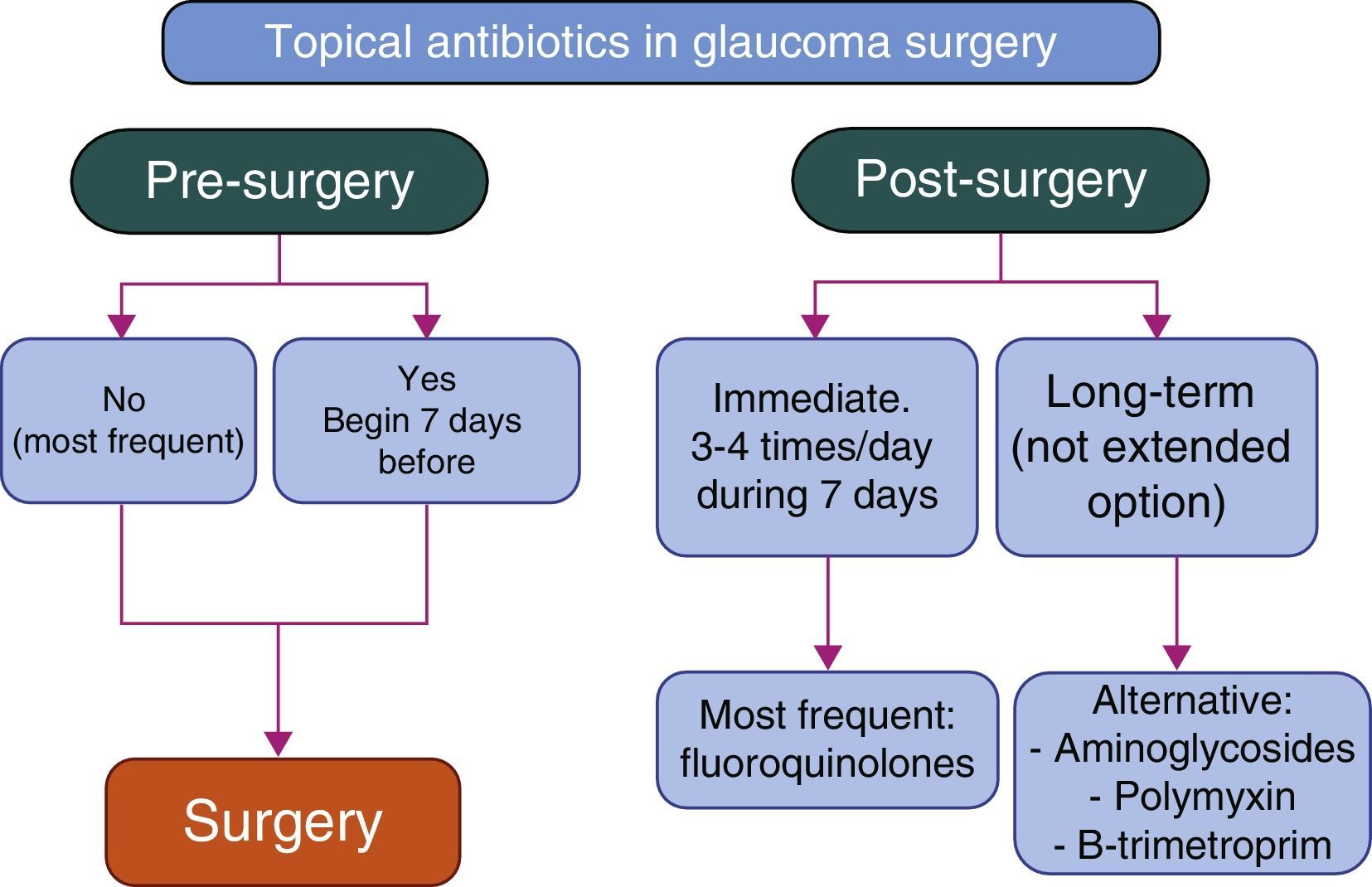
The use of preservative-free ocular antihypertensive drugs and steroids in the preoperative period of glaucoma surgery reduces the risk of surgical failure. The interruption of prostaglandines is recommended. In the postoperative period of glaucoma surgery, steroids are the anti-inflammatory treatment of choice, the preservative-free ones being preferred. When reintroducing antiglaucomatous treatment, preservatives should be avoided to prevent scarring. The appropriate perioperative management of patients with glaucoma is essential to obtain a correct control of IOP, improve the situation of the OS, prevent complications and improve the result of the filtration surgery and cataract surgery.
ConclusionsThis protocol aims to unify the different lines of action in order to decrease the incidence of adverse events and maximize the surgical outcome.
Ante la necesidad de realizar una facoemulsificación, una cirugía filtrante o la combinación de ambas, pueden plantearse dudas sobre la conveniencia de mantener determinados fármacos antiglaucomatosos. El objetivo del presente trabajo es unificar criterios que puedan orientar la práctica clínica diaria y que permitan desarrollar algoritmos de actuación en el preoperatorio y el postoperatorio de la cirugía filtrante o de catarata.
Protocolos propuestosEn el preoperatorio de la cirugía de catarata, el uso de antiinflamatorios no esteroideos queda a criterio del cirujano, recomendándose el formato de monodosis. Se plantea la suspensión de las prostaglandinas unos días antes de la cirugía. Los fármacos sin conservantes favorecen la mejor recuperación de la superficie ocular (SO) tras la cirugía de catarata. Una vez eliminados todos los aspectos modificadores de la presión intraocular (PIO), se debe reevaluar la PIO basal, prefiriendo los fármacos hipotensores sin conservantes, en caso de necesitarlos.
La utilización de hipotensores oculares y corticoides libres de conservantes en el preoperatorio de la cirugía de glaucoma reduce el riesgo de fracaso quirúrgico. Se recomienda interrumpir las prostaglandinas. En el postoperatorio de la cirugía de glaucoma los corticoides constituyen el tratamiento antiinflamatorio de elección, siendo preferibles aquellos libres de conservantes. Al reintroducir un tratamiento antiglaucomatoso, se deben evitar los conservantes para no potenciar la cicatrización.
Conclusionesel presente protocolo de consenso persigue la unificación de las pautas de actuación con el fin de disminuir la incidencia de acontecimientos adversos y maximizar el resultado quirúrgico.