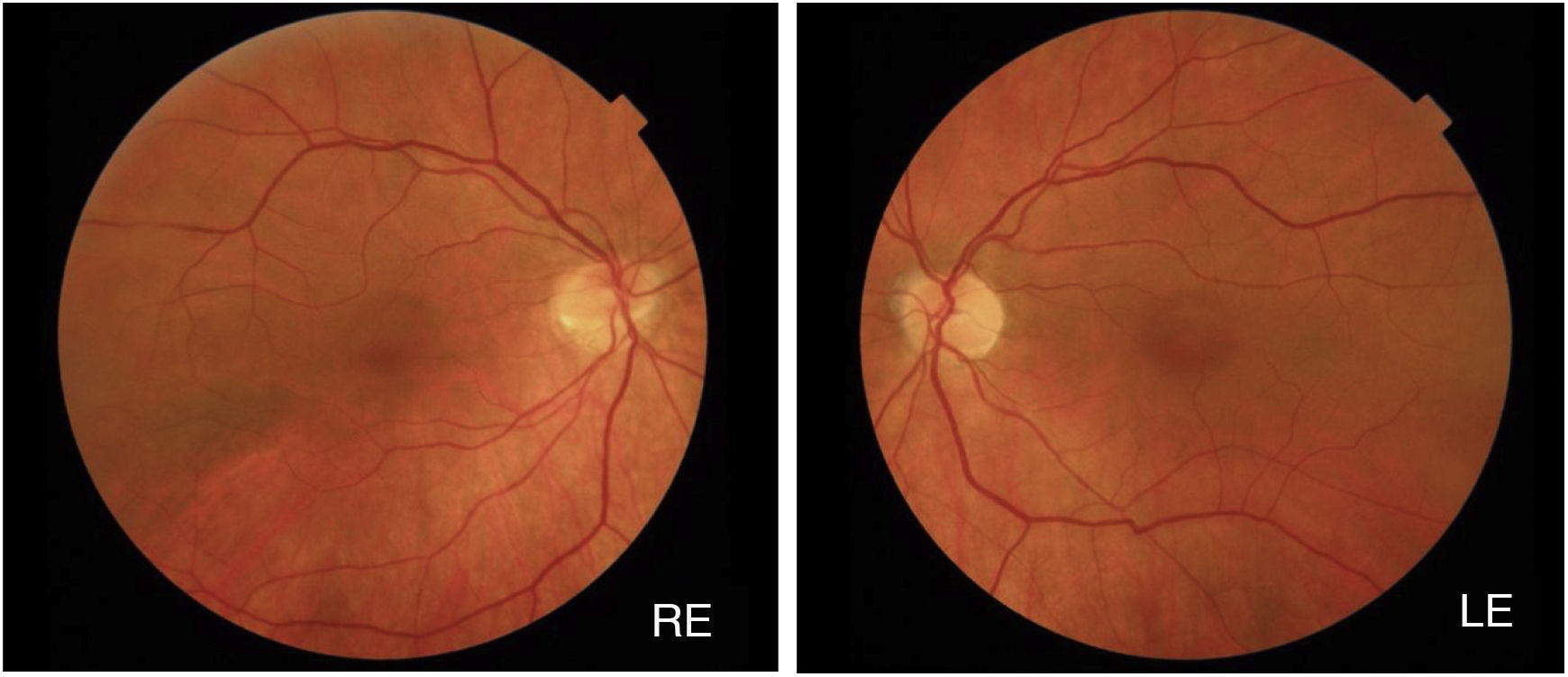
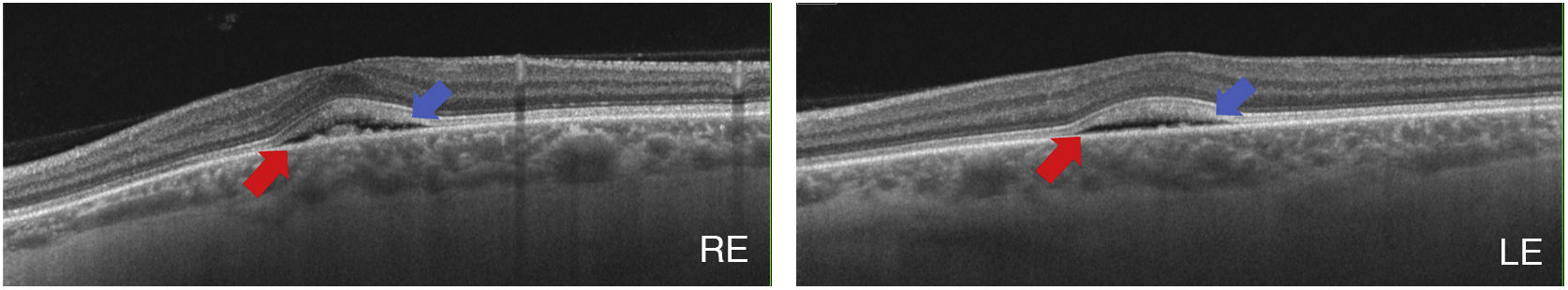
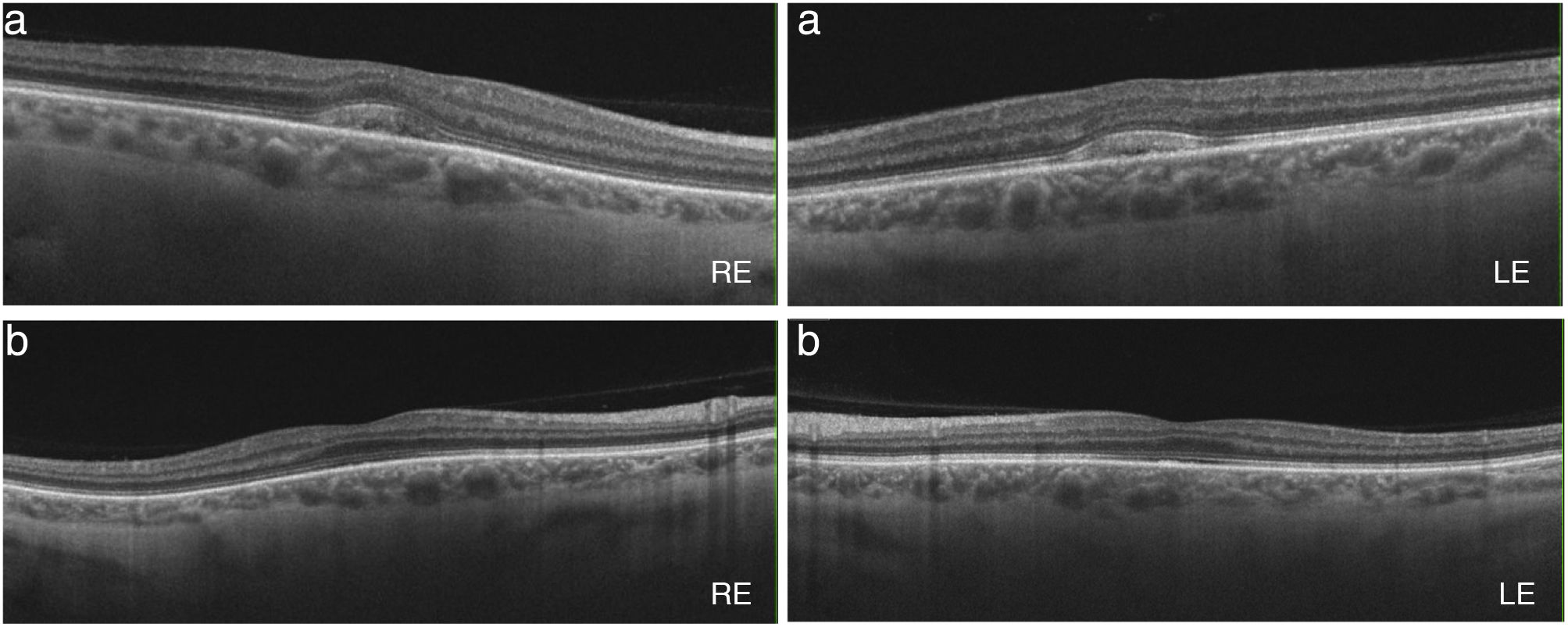
Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) inhibitors have significantly improved the prognosis of various types of cancer such as metastatic melanoma. However, their use is usually associated with ocular side effects. A retinopathy associated with these agents (MEKAR) has been described, consisting of the development of neurosensory detachments, generally bilateral and multiple, similar to those that appear in the central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC). Generally, optical coherence tomography allows us to differentiate the two conditions. We present the case of a 55-year-old woman in treatment with a MEK inhibitor, who developed bilateral neurosensory detachments and blurred vision, which resolved with the discontinuance of the treatment due to tumour progression.
Los inhibidores de la proteína quinasa de activación mitogénica (MEK) son fármacos utilizados para el tratamiento de neoplasias tales como el melanoma metastásico. Su introducción ha mejorado el pronóstico de estas enfermedades, pero su uso no está exento de complicaciones oculares. Se ha descrito una retinopatía asociada a estos fármacos (MEKAR) consistente en la aparición de desprendimientos neurosensoriales (DNS), generalmente bilaterales y múltiples similares a los que aparecen en la coriorretinopatía serosa central (CSC). En la mayoría de casos la tomografía de coherencia óptica es suficiente para diferenciar esta entidad de una CSC. Presentamos el caso de una paciente de 55 años que, en este contexto, desarrolló DNS bilaterales que asociaron disminución de agudeza visual, y que se resolvieron cuando se suspendió la terapia por progresión tumoral.