To study the structures of the iridocorneal angle using anterior segment optical coherence tomography (OCT) defining their tomographic characteristics and quantifying their identification frequency.
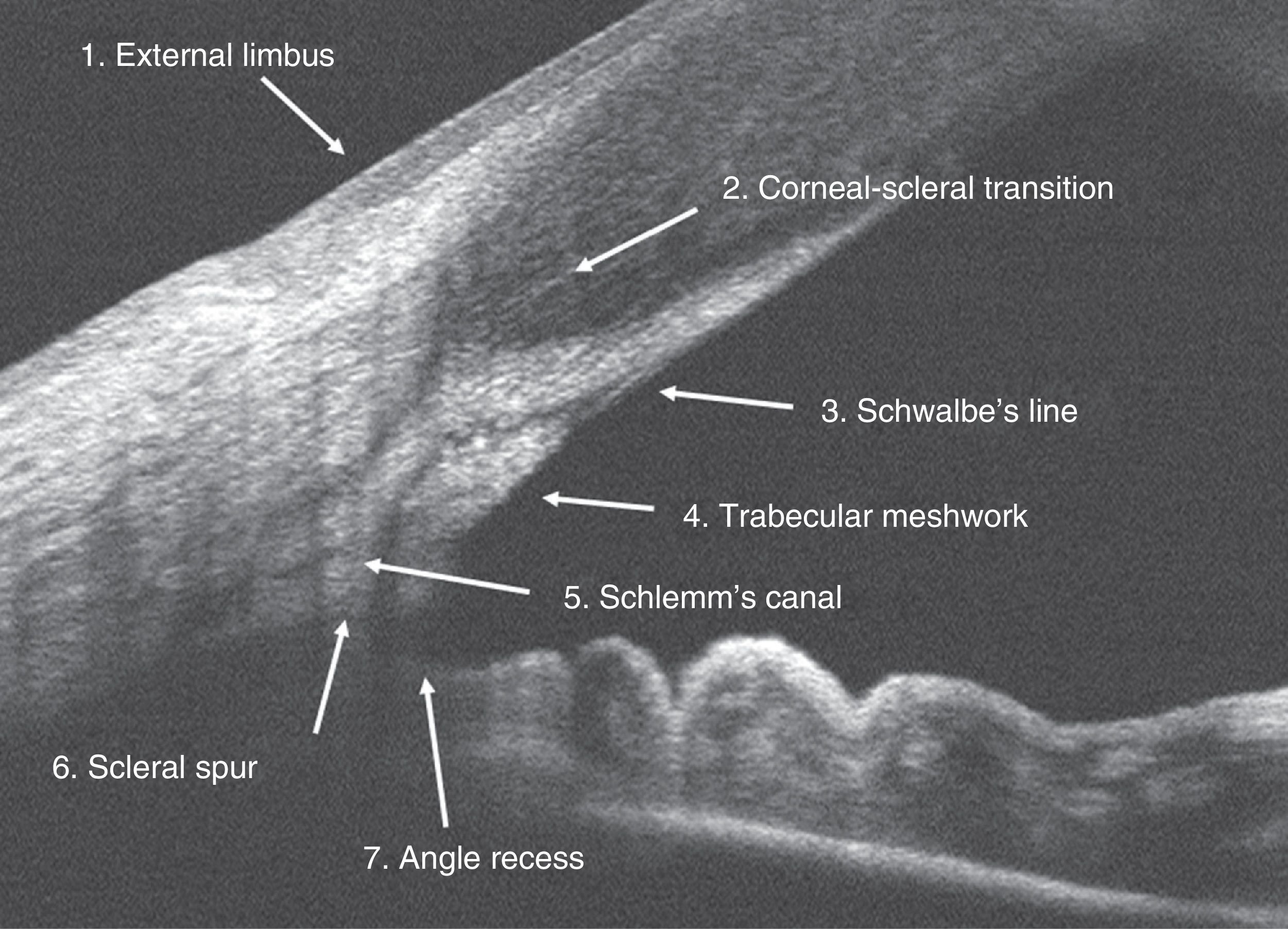
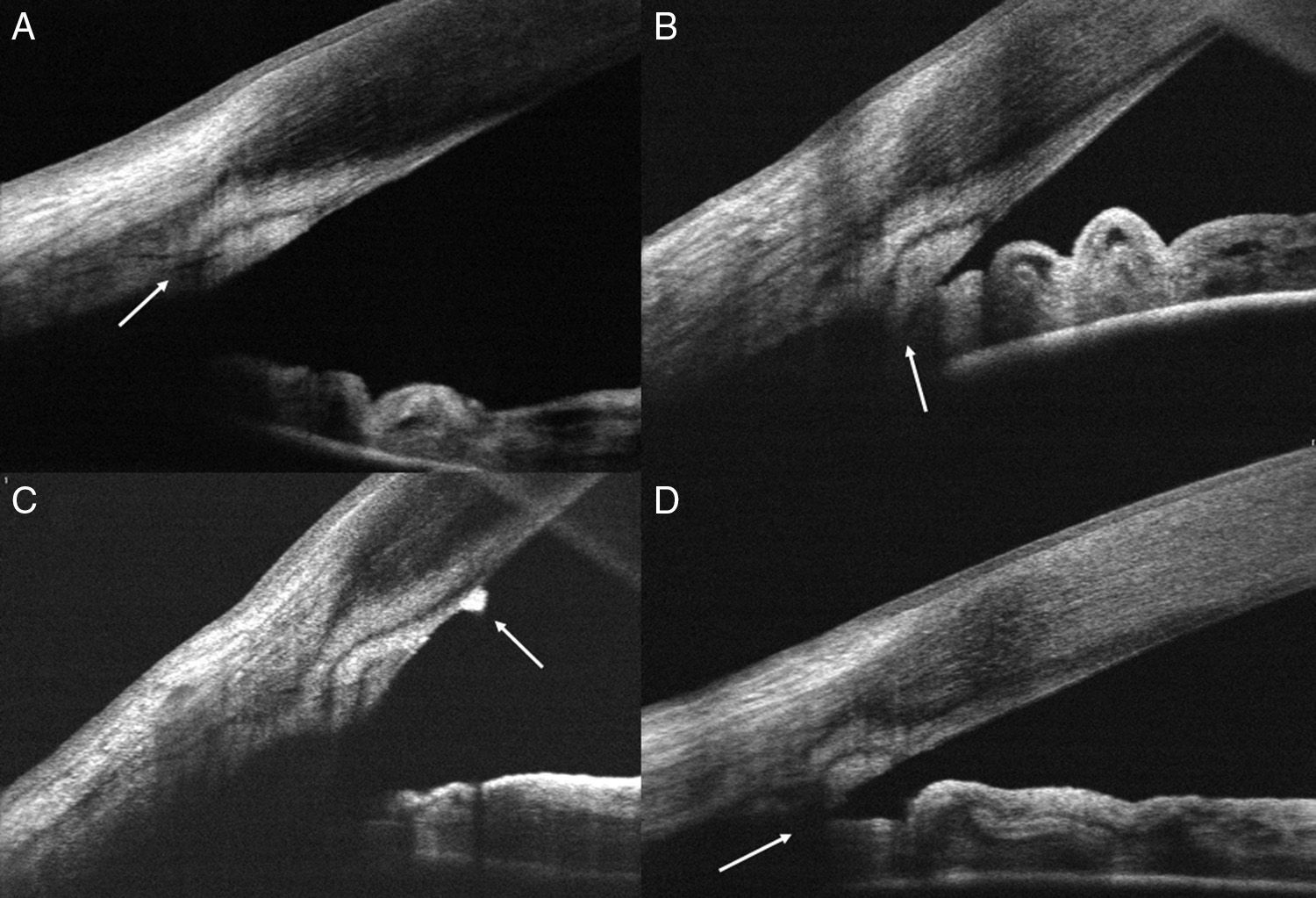
Material and methodsA cross-sectional study was performed on 267 right eyes of 267 consecutive healthy patients. Fourier domain OCT RTVue (Optovue Inc, CA, EE. UU.) was used to examine the iridocorneal angle in the nasal and temporal sectors. The structures evaluated were: sclerocorneal limbus, sclerocorneal transition, Schwalbe's line, trabecular meshwork, Schlemm's canal, scleral spur, and angular recess. Within and between agreements to identify structures were calculated using Cohen's kappa coefficient.
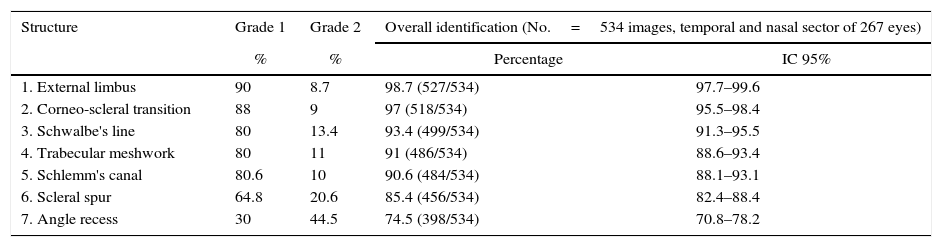
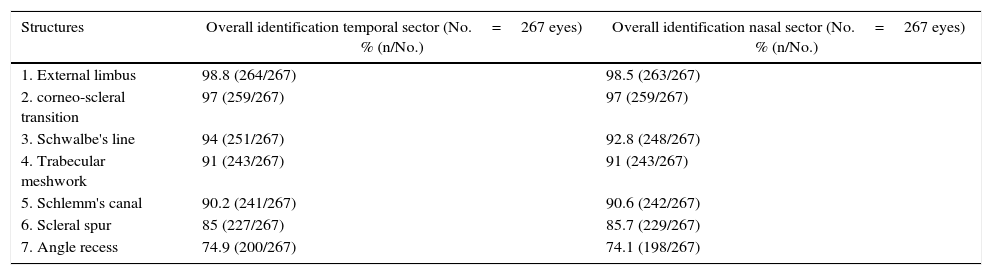
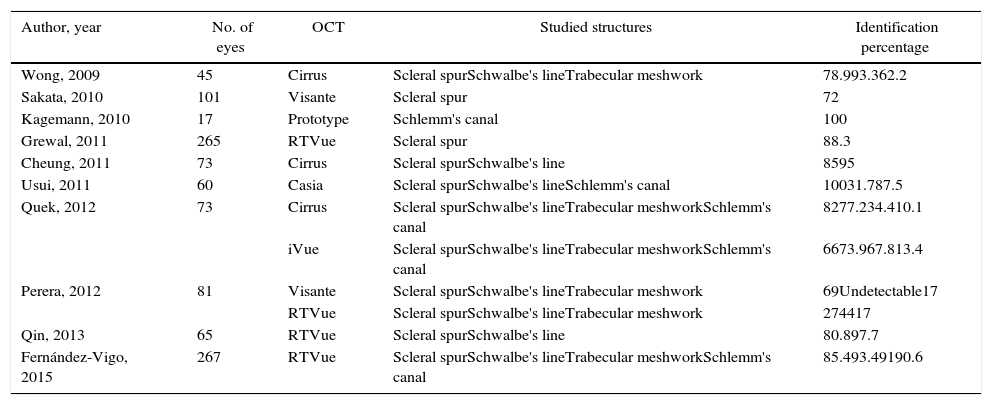
ResultsThe mean age was 41.3±14.3 years (range 20–80), with 57% being women. The sclerocorneal limbus, sclerocorneal transition, and Schwalbe's line were identified by 98.7, 97 and 93.4% of the images, respectively, with the trabecular meshwork and Schlemm's canal being identified in 91% of cases. The scleral spur could be identified in 85.4%, and the angular recess in 74.5%. There was no difference in the identification between the temporal and nasal sectors. Within and between agreement was k=0.92 and k=0.88, respectively, in the identification of the structures of the total images studied.
ConclusionsFourier domain OCT is a reliable technique for the identification of the structures of the iridocorneal angle, among which can be highlighted are, the trabecular meshwork, Schlemm's canal, scleral spur, and Schwalbe's line.
Estudiar las estructuras que conforman el ángulo iridocorneal mediante tomografía de coherencia óptica (OCT) de segmento anterior, definiendo sus características tomográficas y cuantificando su frecuencia de identificación.
Material y métodosEstudio transversal realizado en 267 ojos derechos de 267 pacientes consecutivos sanos. Se empleó una OCT de dominio Fourier RTVue (Optovue Inc, CA, EE. UU.) para explorar el ángulo iridocorneal en los sectores nasal y temporal. Las estructuras evaluadas fueron: el limbo externo, transición corneoescleral, línea de Schwalbe, malla trabecular, canal de Schlemm, espolón escleral y receso angular. Se calculó la concordancia intra- e interobservador para la identificación de las estructuras mediante el coeficiente kappa.
ResultadosLa edad media fue 41,3±14,3 años (rango 20-80); el 57% eran mujeres. El limbo externo, la transición córneo-escleral y la línea de Schwalbe se identificaron en un 98,7; 97 y 93,4%, respectivamente de las imágenes. La malla trabecular y el canal de Schlemm se identificaron en el 91% de los casos. El espolón escleral pudo ser identificado en un 85,4% y el receso angular en un 74,5%. No existió diferencia en la identificación entre el sector temporal y nasal. La concordancia intra- e interobservador fue de k=0,92 y k=0,88 respectivamente, en la identificación de las estructuras para el total de las imágenes estudiadas.
ConclusionesLa OCT de dominio Fourier es una técnica eficaz para la identificación de las estructuras que conforman el ángulo iridocorneal, entre las que destacan la malla trabecular, el canal de Schlemm, el espolón escleral y la línea de Schwalbe.