To determine the effectiveness and safety of the micropulse transscleral technique in lowering intraocular pressure in patients with glaucoma.
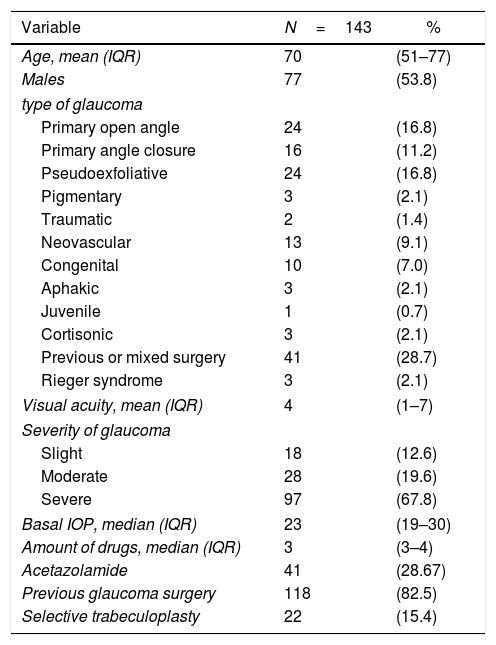
Materials and methodsA retrospective cohort study was conducted on 143 eyes with various glaucoma subtypes between October 2016 and December 2018. Patients were grouped for analysis based on glaucoma subtypes, preoperative demographics, previous surgical procedures, and postoperative results. The data collected was based on intra- and post-operative complications, intraocular pressure, visual acuity, the need of micropulse re-treatment, incisional glaucoma surgery, and increasing the dose/quantity of medications.
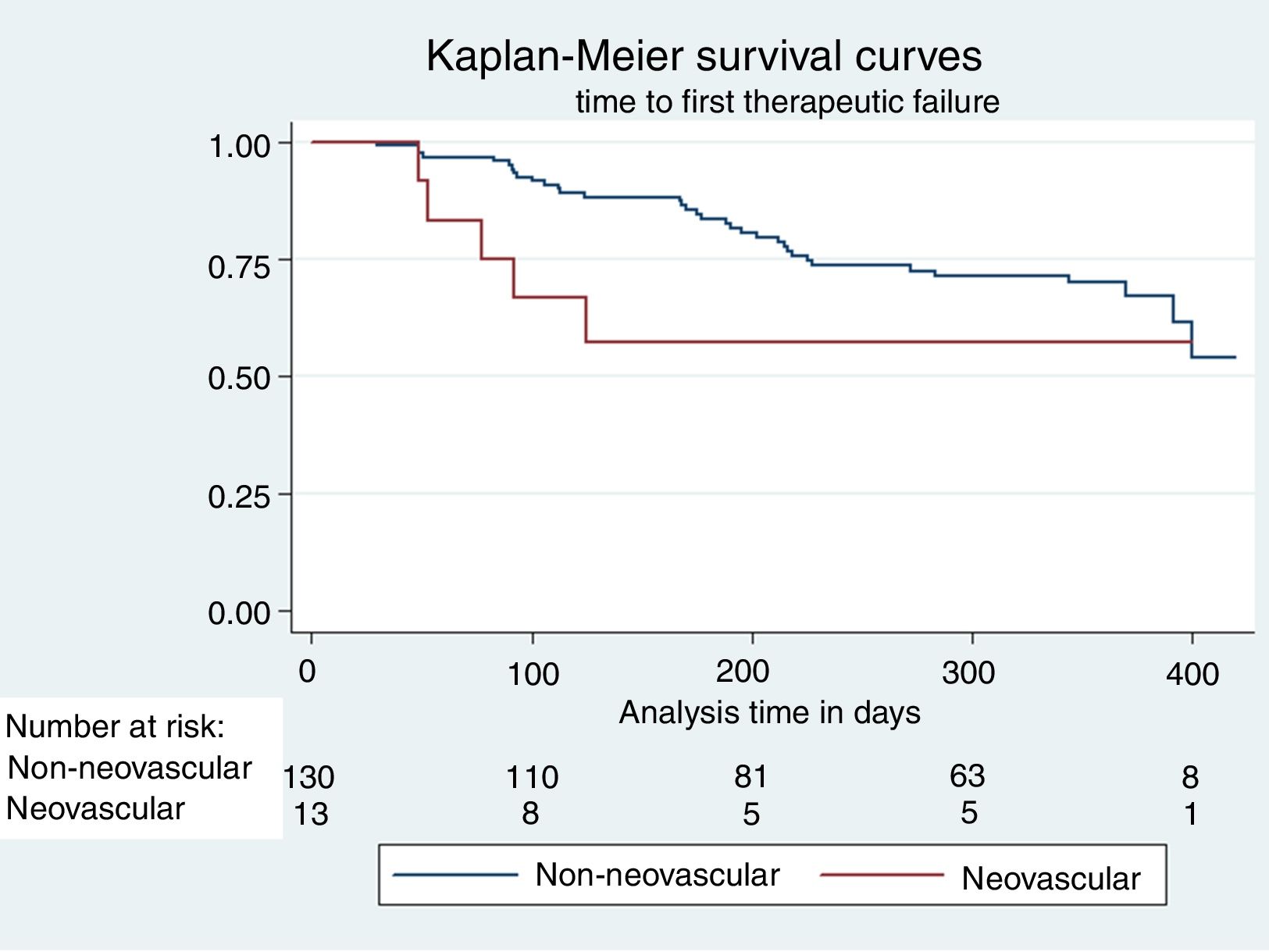
A logistic and Cox regression model was performed to determine predictors of therapeutic failure, in addition to building Kaplan–Meier curves.
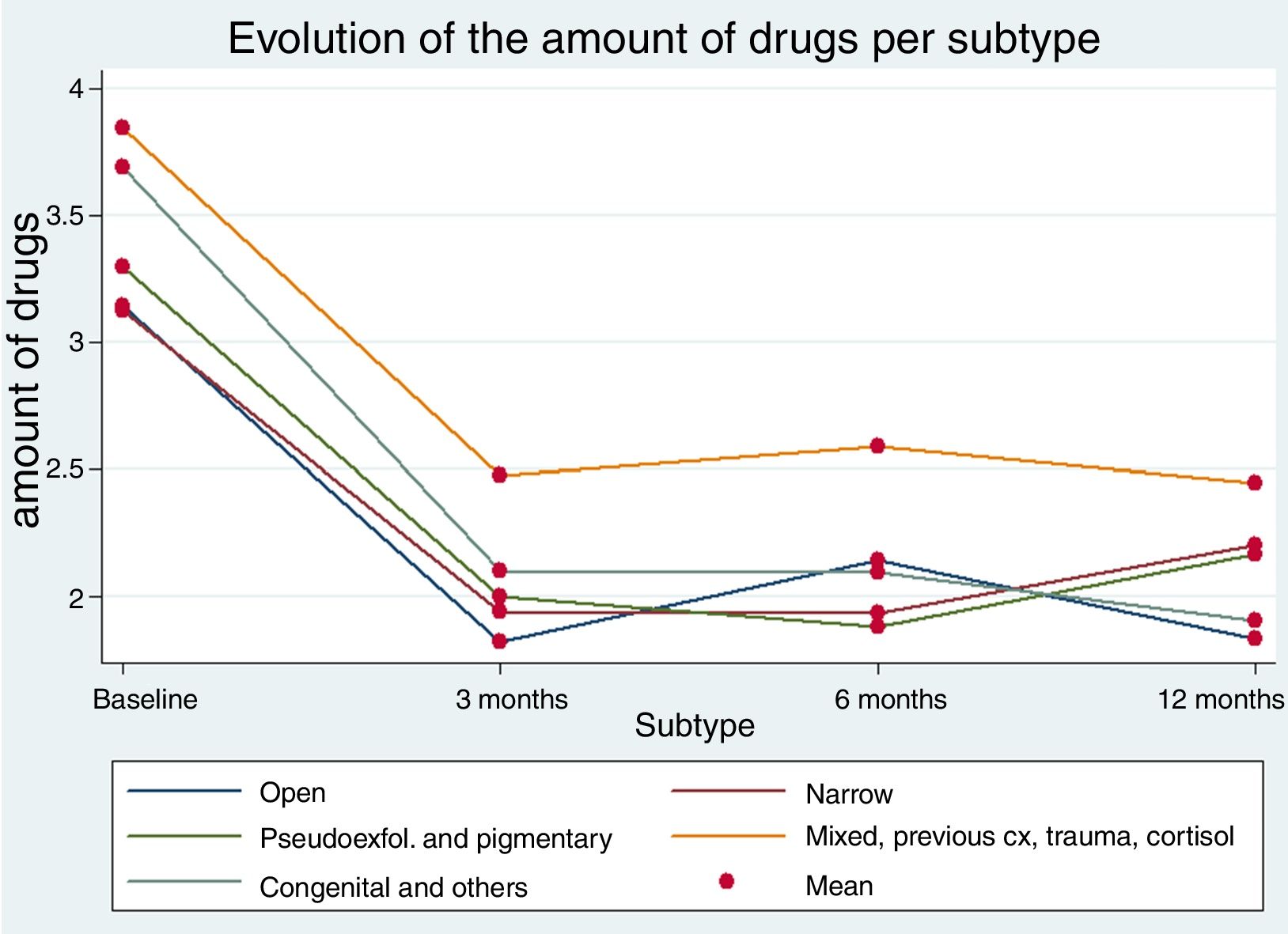
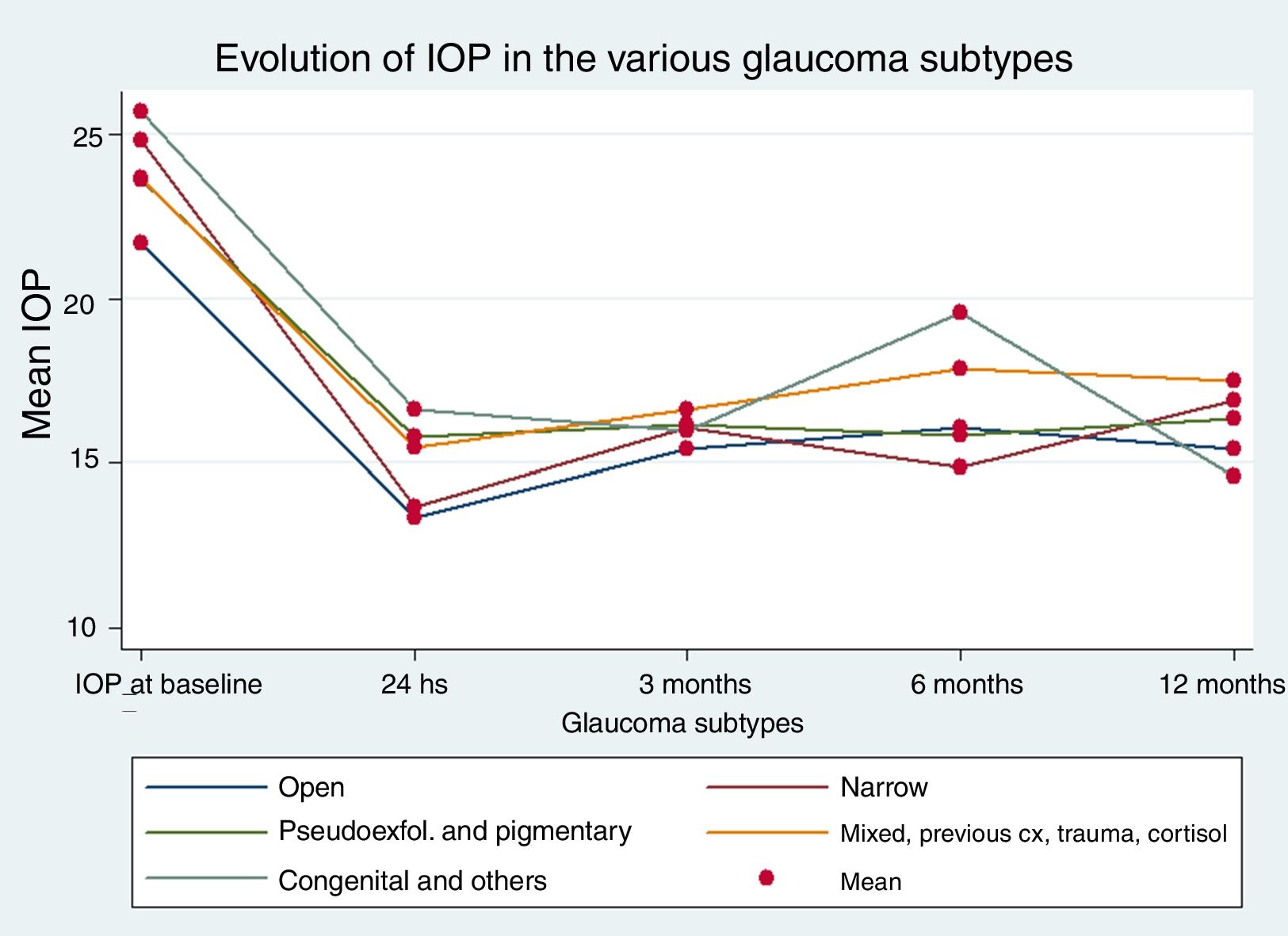
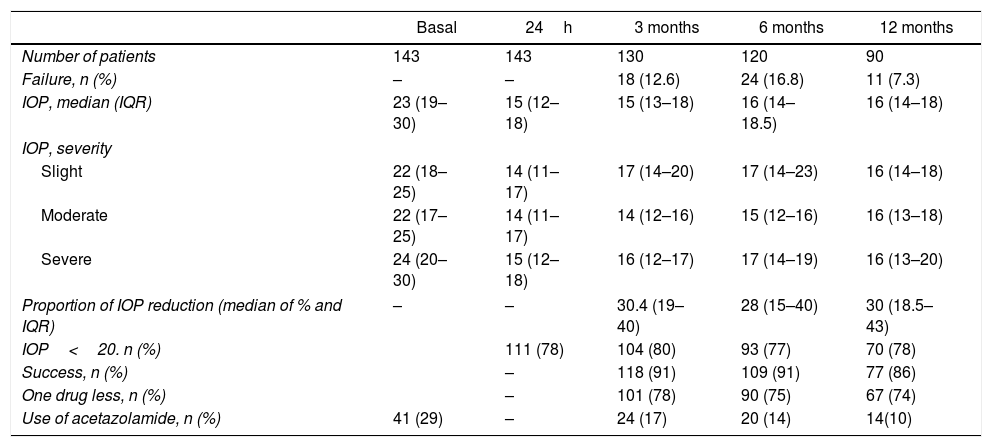
ResultsThe mean follow-up was 268 days, and 63% of the patients completed one year. The micropulse procedure achieved a mean intraocular pressure decline of 7.3mmHg (excluding neovascular glaucoma), independent of the glaucoma subtype. The percentage of patients who achieved intraocular pressure less than 20mmHg at 24h was 78%, with 80% at 3 months, 77% at 6 months, and 78% at 12 months. During the follow-up, 29.6% of the patients required additional treatment or a dose increase. Only 2 patients presented with minimal postoperative complications.
ConclusionThe treatment with transscleral micropulse is a safe and efficient technique for use in glaucoma, attaining a reduction in intraocular pressure and decrease in need of antihypertensive medications within the first year following the procedure.
Determinar la eficacia y seguridad de la técnica de micropulso transescleral para disminuir la presión intraocular en pacientes con glaucoma.
Materiales y métodosSe realizó, entre octubre de 2016 y diciembre de 2018, un estudio de cohorte retrospectiva en pacientes con diferentes subtipos de glaucoma. Se analizaron datos sobre las características demográficas preoperatorias, los procedimientos quirúrgicos previos y los resultados postoperatorios. Se recolectó información sobre complicaciones intra- y postoperatorias, presión intraocular, agudeza visual, necesidad de retratamiento con micropulso, de cirugía incisional de glaucoma o de incrementar la medicación.
Se aplicó un modelo de regresión logística y de Cox para determinar los predictores de fracaso terapéutico, además de construir curvas de Kaplan-Meier.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 143 ojos, con una media de seguimiento de 268 días, de los cuales 90 (63%) completaron un año de seguimiento. El procedimiento micropulsado logró un descenso medio de la presión intraocular para cualquier tipo de glaucoma de 7,3mmHg (excluyendo glaucoma neovascular). El porcentaje de pacientes que alcanzó una presión intraocular menor de 20mmHg a las 24h fue el 78%, el 80% a los 3 meses, el 77% a los 6 meses y el 78% a los 12 meses. Durante el seguimiento, un 29,6% de los pacientes requirió un tratamiento adicional o un incremento de la medicación. Solo 2 pacientes presentaron mínimas complicaciones postoperatorias.
ConclusiónLa técnica micropulsada es un tratamiento seguro y eficaz para el glaucoma porque logra una reducción de la presión intraocular o una menor necesidad de medicamentos antihipertensivos a un año de seguimiento.