To evaluate patients 24 months after deep sclerectomy (DE) with supraciliary implant, and identify any predictive success factors by examination with ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM).
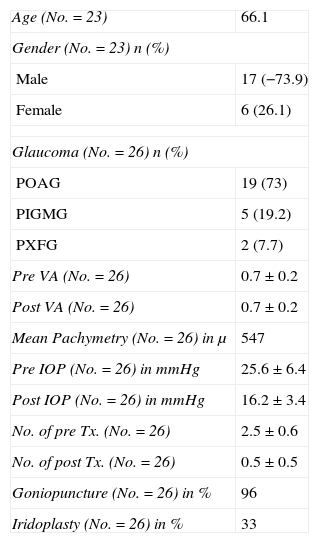
Materials and methodsThis study included 26 eyes of 23 patients evaluated by UBM 24 months after a deep sclerectomy with a supraciliary hema implant.
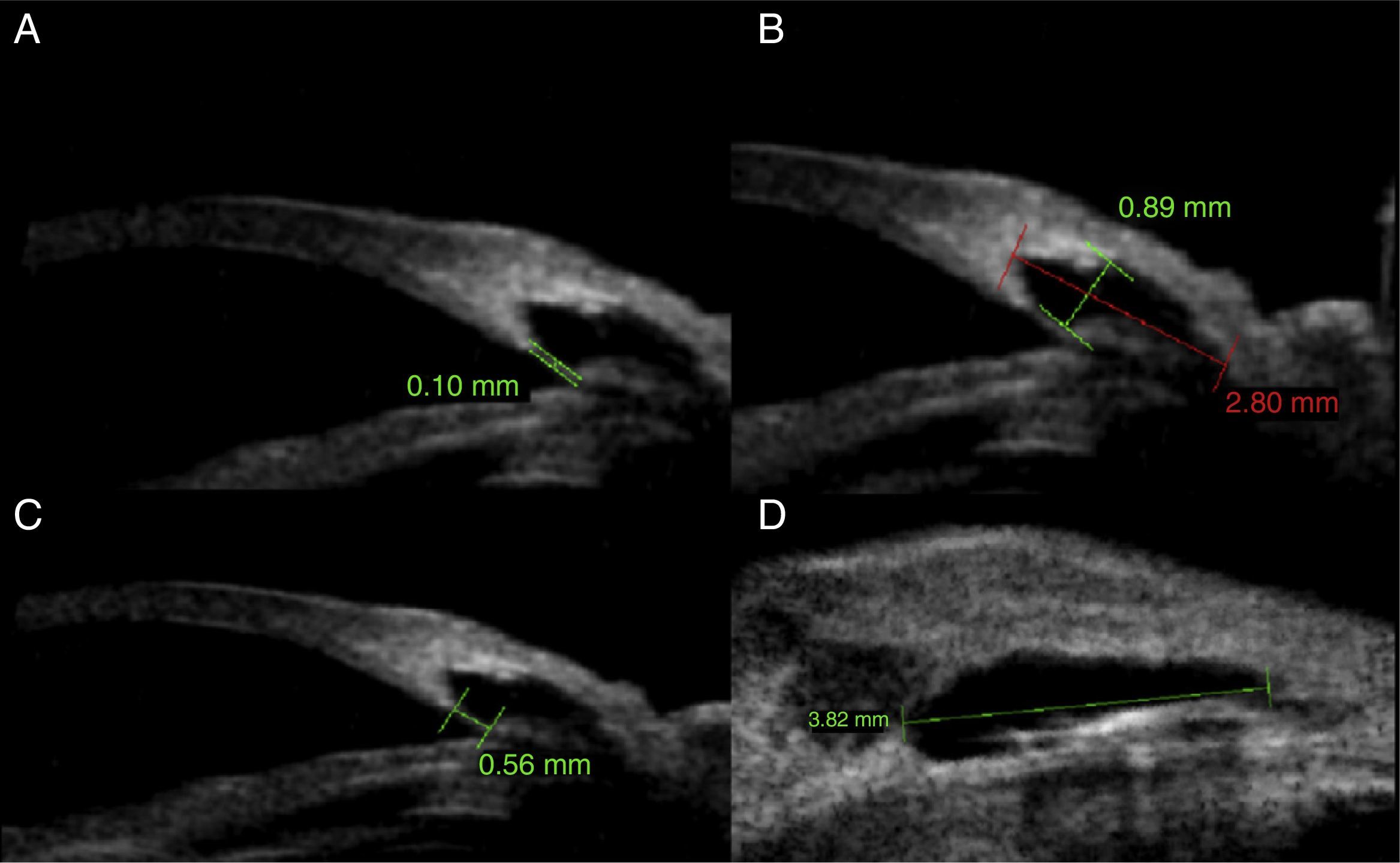
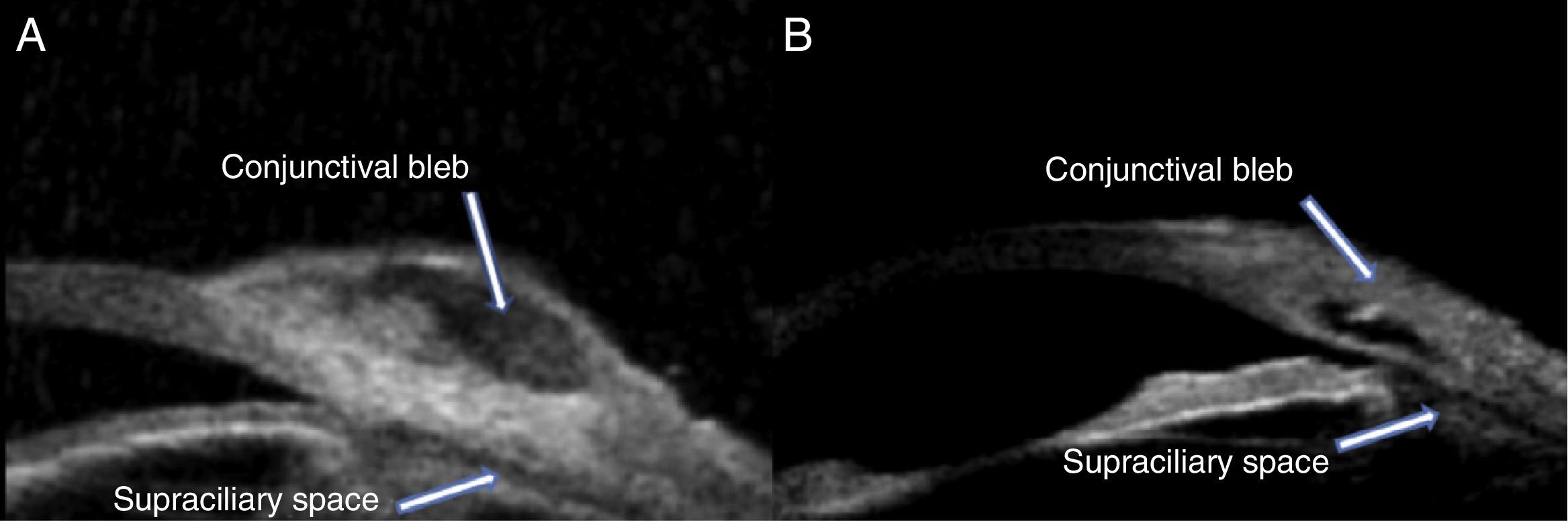
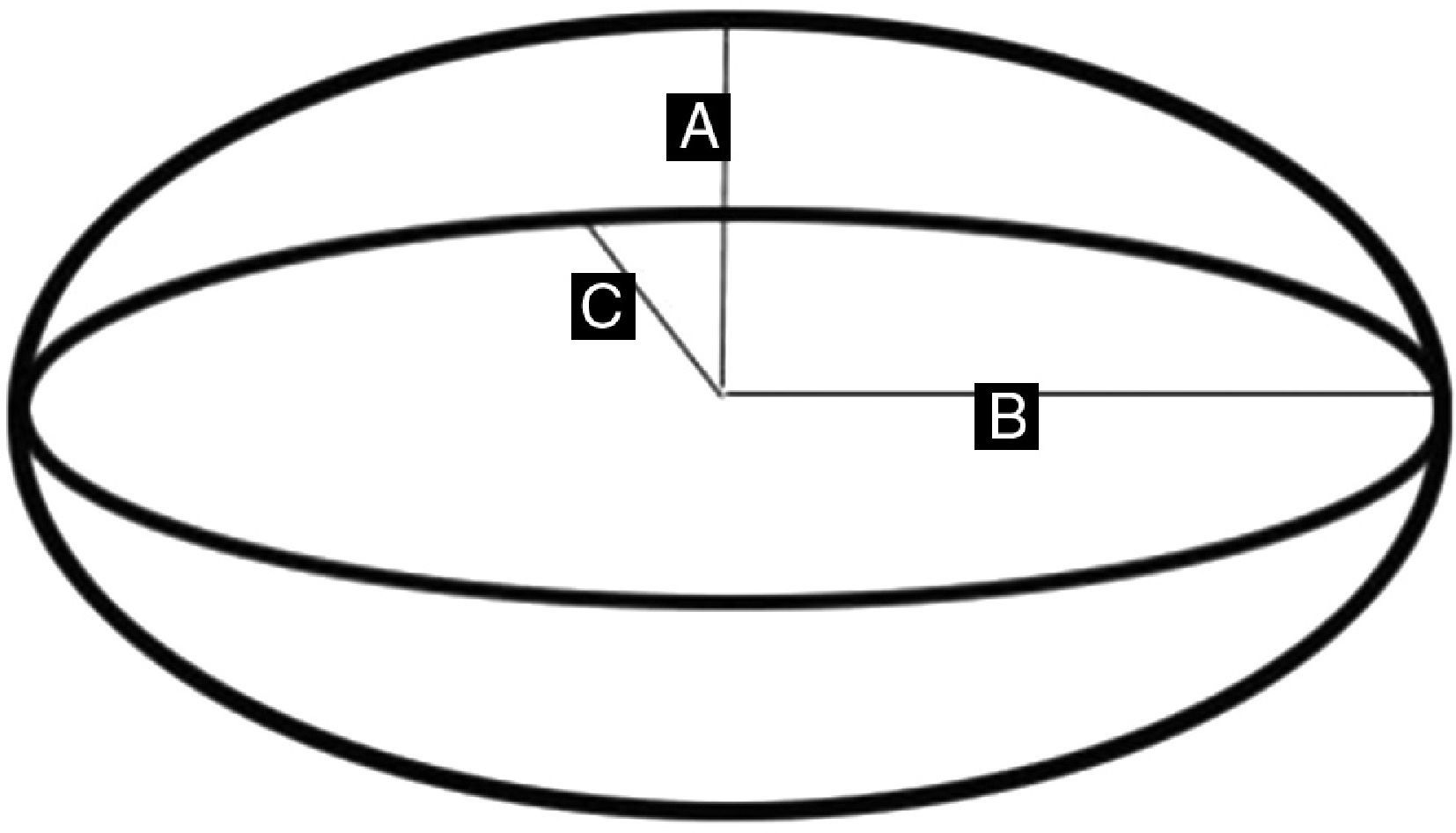
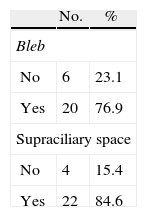
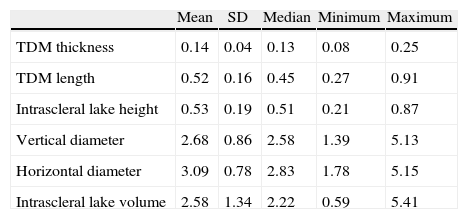
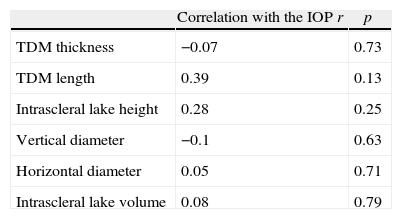
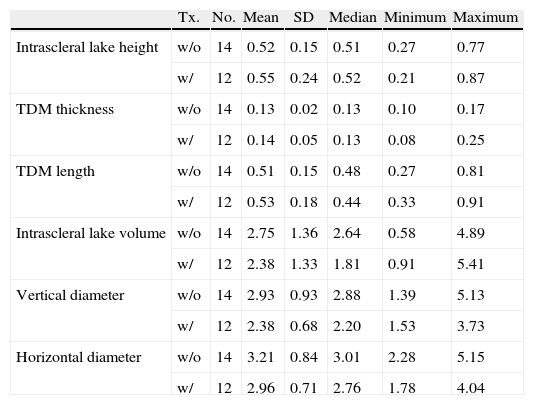
ResultsThere was a significant reduction in intraocular pressure (IOP), changing from a preoperative mean of 25.6±6.4mmHg to a postoperative mean of 16.2±3.4mmHg (p<0.001). The number of preoperative glaucoma medications also decreased from 2.5±0.6 drugs per patient to 0.5±0.5 (p<0.001). No change was observed in the best-corrected visual acuity. The anatomical characteristics of the surgical area and its relationship with IOP were examined using UBM. There was no correlation between the level of IOP at the time of UBM and the horizontal (r=−0.05: p=0.71) and vertical diameter (r=−0.1; p=0.63), the height (r=0.28; p=0.25) and the volume of intrascleral space (r=−0.08; p=0.79), the thickness (r=−0.07; p=0.73) and the length (r=0.39; p=0.13) of trabeculo-Descemet's membrane (TDM), the presence of filtering bleb (p=0.30) and the hypoechoic area in the supraciliary space (p=0.24).
ConclusionsThe insertion of a hema implant in the supraciliary space is an effective and safe surgery for patients with open angle glaucoma (OAG). No predictive success factors for supraciliary implant were found using the UBM study.
Evaluar a pacientes 24 meses después de ser intervenidos mediante esclerectomía profunda no perforante (EPNP) con implante supraciliar y determinar la existencia de factores predictivos de la eficacia de la técnica mediante la exploración biomicroscópica (BMU).
Material y métodosSe incluyen 26 ojos de 23 pacientes explorados con UBM 24 meses después de ser intervenidos mediante EPNP con implante de hema supraciliar.
ResultadosSe ha encontrado un descenso significativo de la presión intraocular (PIO) de 25,6±6,4mmHg a 16,2±3,4mmHg y en el número de medicaciones antiglaucomatosas de 2,5±0,6 por paciente a 0,5±0,5 (p<0,001). No se evidenciaron cambios significativos en la agudeza visual. Mediante BMU no se ha podido correlacionar la PIO con el diámetro horizontal (r=−0,05; p=0,71) ni vertical (r=−0,1; p=0,63) del lago intraescleral, su altura (r=0,28; p=0,25) ni volumen (r=−0,08; p=0,79), el grosor de la MBTD (r=−0,07; p=0,73) ni su longitud (r=0,39; p=0,13), la presencia de ampolla filtrante (p=0,3) ni de un área hipogénica en el espacio supracoroideo (p=0,2).
ConclusionesLa inserción del implante de hema en el espacio supraciliar durante la cirugía no perforante del glaucoma es segura y efectiva en el glaucoma de ángulo abierto (GAA) pero no hemos podido establecer factores.