Abstracts of the 2022 Annual Meeting of the ALEH
More infoThe diagnostic work-up of chronic liver disease includes less invasive procedures such as transient elastography (TE), abdominal ultrasonography, esophagogastroduodenoscopy, and more invasive procedures, mainly portal gradient pressure measurement and liver biopsy. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) recently included shear-wave elastography (tissue elasticity), defined as the elastic modulus by measuring shear-wave velocity. This study aimed to evaluate EUS shear-wave of the liver to predict liver cirrhosis.
Materials and Methodsa single-center, diagnostic cohort study. Consecutive patients with a history of chronic liver disease were evaluated with an EUS shear-wave elastography of the right and left hepatic lobes. Patients without any medical condition history despite subepithelial lesions were included as a control. A TE was performed to study and control patients to correlate with elastography. We calculated the overall accuracy of EUS shear-wave elastography of the liver in the prediction of liver cirrhosis.
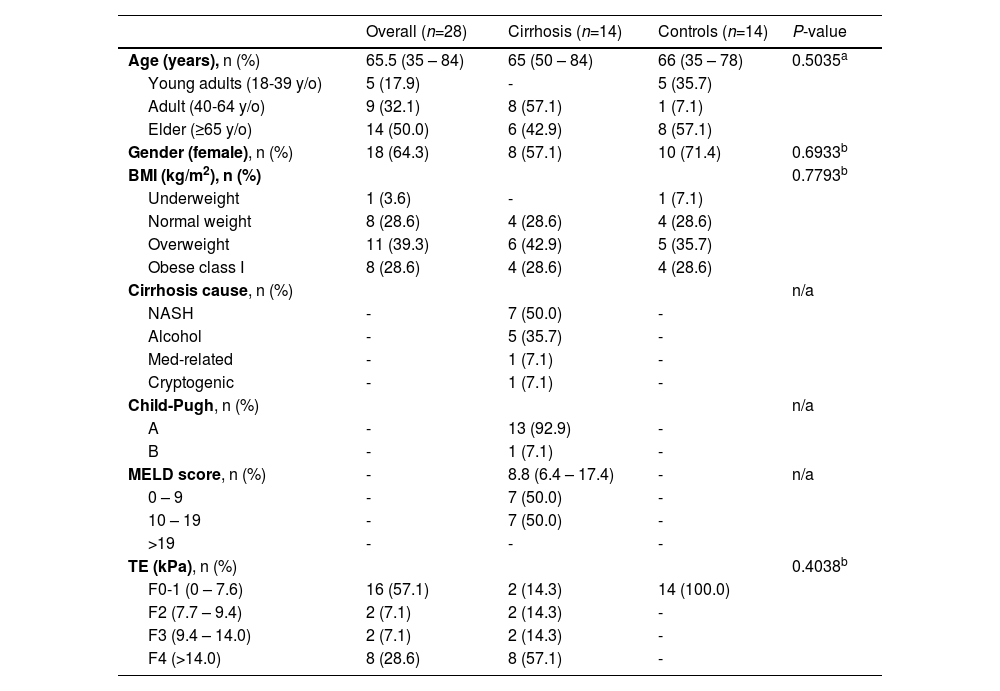
ResultsAmong the 28 patients included, 14 had liver cirrhosis. Baseline data is described in table 1. EUS shear-wave elastography of the right hepatic lobe has a direct, proportional and significant correlation (r=0.693 [95% CI 0.431 – 0.847; P<0.001]) as well as left hepatic lobe (r=0.460 [95% CI 0.105 – 0.711; P =0.014]). EUS shear-wave of the right and left hepatic lobe reached an area under the receiver operating characteristics curve (AUROC) of 0.98 and 0.96, respectively. For identifying patients with cirrhosis, EUS shear-wave elastography of the right hepatic lobe with a cut-off value of ≥10.7 kPa had a sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of 100%, 93%, 93%, 100%, respectively. In the left hepatic lobe using a cut-off value of ≥14.0 kPa, EUS shear-wave had a sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of 93%, 93%, 93%, and 93%, respectively.
ConclusionsEUS shear-wave of the liver accurately diagnoses patients with liver cirrhosis. EUS shear-wave of the right and left hepatic lobe correlates with TE measurements of the liver.
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the patients included in the study.
BMI, body mass index; y/o, years old; AST, aspartate transaminase; ALT: alanine transaminase, MELD, Model for End-Stage Liver Disease; n/a, not available; TE, Transient elastography. a. Mann-Whitney U test. b. Pearson's Chi-squared test.