Abstracts of the 2024 Annual Meeting of the ALEH
More infoNo
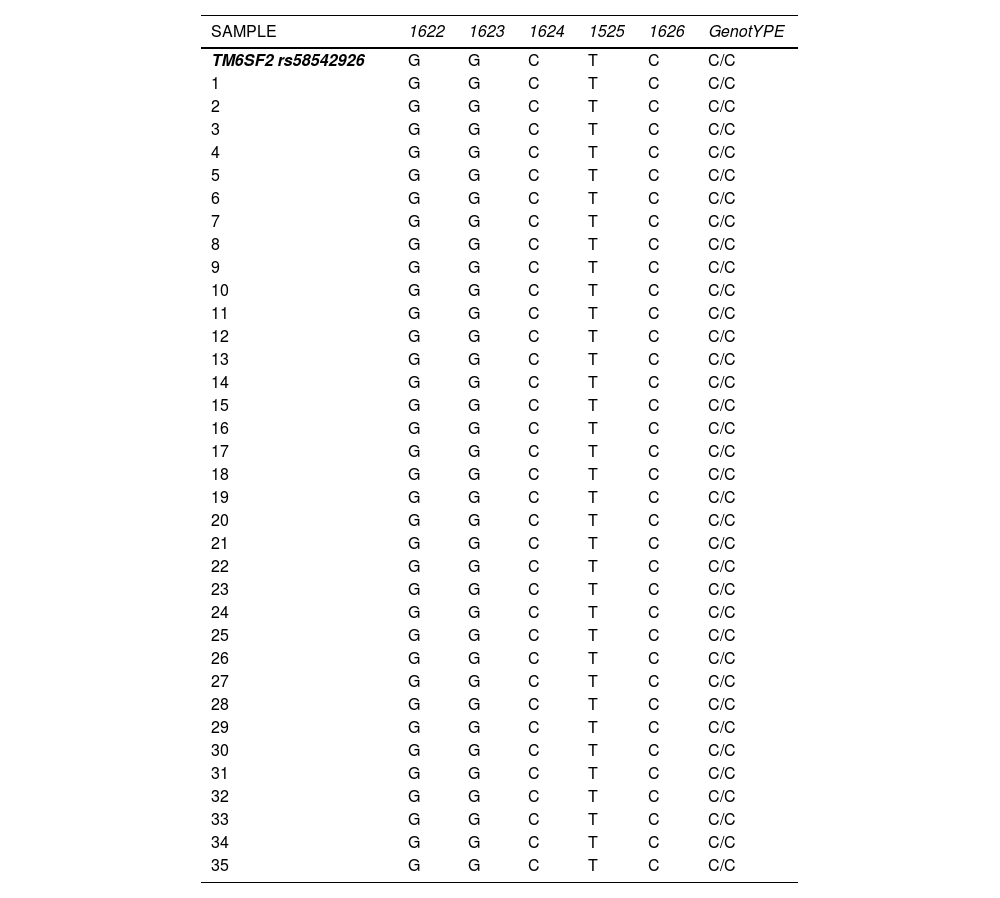
Introduction and ObjectivesGenes that influence lipids have led to the discovery of a non-synonymous variant (rs58542926) located in the TM6SF2 gene (transmembrane 6 member of superfamily 2) that is associated not only with the serum lipid levels, including serum total cholesterol, low-density cholesterol (LDL-C), and triglycerides, but also the risk of cardiovascular disease. The Dallas Heart Study reported that rs58542926 is associated with hepatic fatty infiltration. Objective: To establish the frequency of the C> T polymorphism in the TM6SF2 gene (rs58542926).
Patients / Materials and MethodsA multistage random sample was drawn from an inpatient population between 40 and 70 years of age.
We analyzed the DNA of thirty-five (35) patients. Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood leukocytes. For genotyping of SNP rs58542926, the following pair of primers was used: forward = 5′- GGT CTT GGC ACA AAT CCG GT-3′ and reverse = 5′- AAG AGA AAT TGG CAG CTG GA-3′.
Results and DiscussionThe frequency of the minor allele T (KK) was 0.000 and the frequency of the ancestral allele C (EE) was 1.0000; These frequencies were similar to those observed in a frequency report from the 1000 genomes project (http://browser.1000genomes.org/). The association with fatty liver infiltration may be due to the founder effect, genetic drift, or possibly population inbreeding. In addition, it could be a selective disadvantage compared to other pathologies such as fatty liver.
ConclusionsThe results for the C/C and C/T genotypes studied are like those of other previous studies. The presence of the ancestral C allele (EE) in 100% of the patients suggests a probable genetic deviation or founder effect, probably increasing the frequency of this allele over the other existing alleles.
Results: TMG polymorphisms