Abstracts of the 2022 Annual Meeting of the ALEH
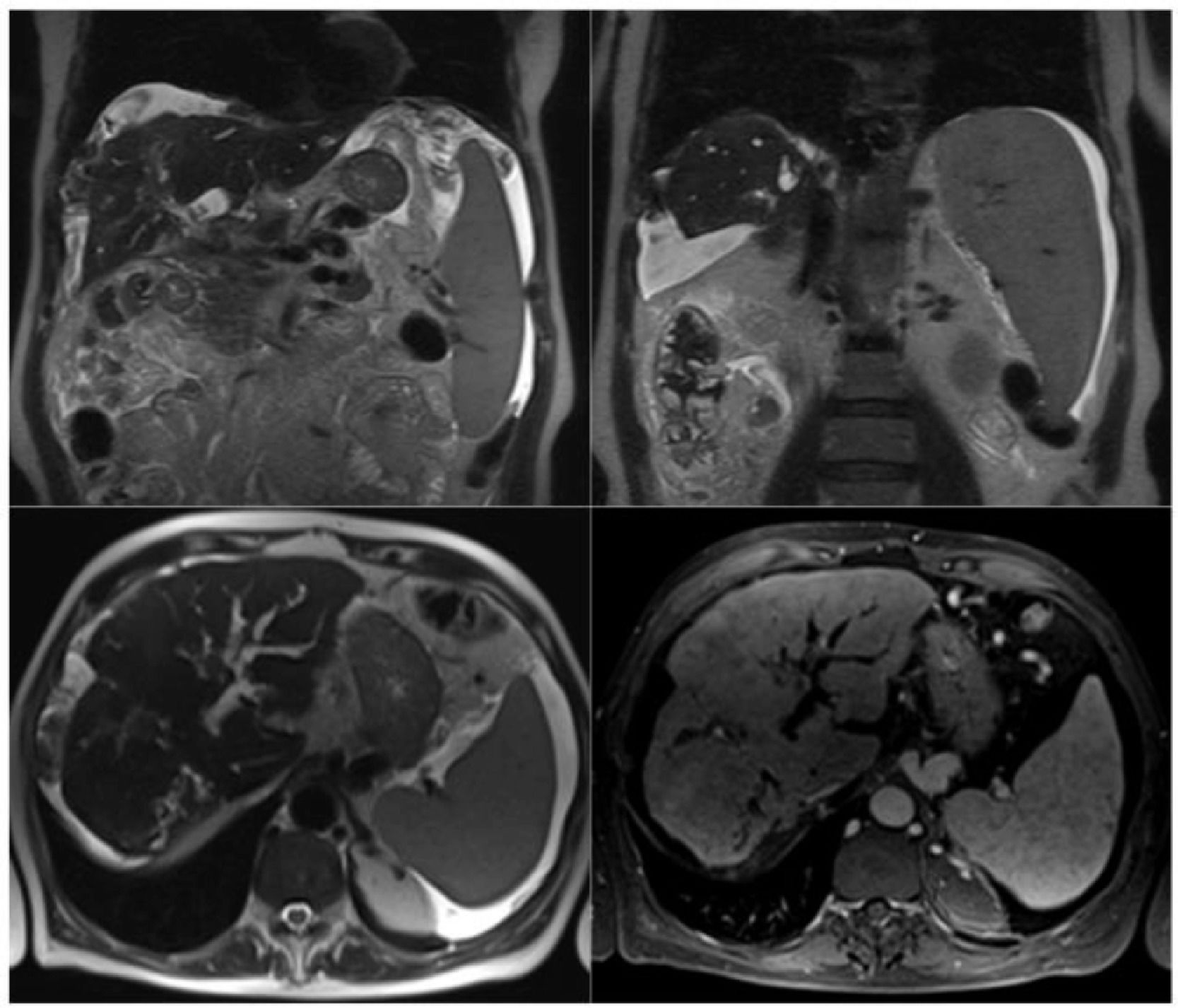
More infoPrimary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a progressive cholestatic liver disease leading to infectious complications, biliary cirrhosis, portal hypertension and the development of cholangiocarcinoma. Imaging is essential for diagnosis. MRI risk scoring systems, called Anali without/with gadolinium, are suggested to predict disease progression. This study aimed to evaluate the usefulness of Anali scores determined by MRI of the abdomen and cholangioMR to predict the prognosis of patients with PSC.
- Analyze interobserver variability of Anali scores.
Materials and MethodsCohort retrospective study of patients diagnosed with PSC, with baseline and follow-up MRIs (2009 to 2020). The study was approved by the institution's Ethics Committee.
MRIs were reviewed by two radiologists and Anali scores were calculated: without gadolinium= (0-2 x intrahepatic bile duct dilatation) + (2 x hepatic dysmorphism) + (1 x portal hypertension) with a possible score of 0 to 5; with gadolinium = (1 x hepatic dysmorphism) + (1 x heterogeneity of hepatic parenchymal enhancement) with a possible score of 0 to 2.
Clinical endpoints included liver transplantation, cirrhotic decompensation, or death.
ResultsTwenty-nine patients were included, of whom 12 presented a clinical event on follow-up. We recorded seven liver transplants and five cirrhotic decompensations. The median time between the clinical event and MRI was 30.5 months.
Patients with a clinical event had a median Anali score without gadolinium 4 and with gadolinium 2, while in those without clinical events, the Anali score was 1 in both modalities.
The Kappa index for interobserver agreement with respect to the Anali score was 0.87 (95% CI). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis comparing event-free time according to the Anali scale was 59 months for scales 0-2 and 32 months for scales 3-5.
ConclusionsMRI Anali scores correlate with the occurrence of clinical events in PSC, with a high degree of interobserver agreement. They should be considered a useful prognostic tool in evaluating these patients.