Background and aim: ACLF is a dynamic syndrome. It may improve, follow a steady course or worsen during hospitalization. Although there is considerable variability between patients, some broad principles regarding the course of the condition can be put forward. ACLF in cirrhosis frequently develops in the setting of an acute event that acts as a precipitating factor. The aim was to describe the main characteristics of hospitalized cirrhotic patients who met acute on chronic liver failure (ACLF) criteria.
Material and methods: Study design. Observational, descriptive, transversal study. A case series. Procedure: The clinical data of hospitalized cirrhotic patients, from October 2019 to February 2020, who met criteria for ACLF, were collected. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize the main characteristics of the series of patients.
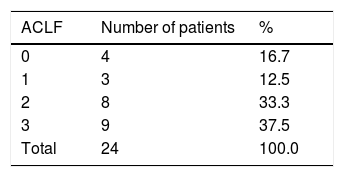
Results: A total of 24 admissions of cirrhotic patients who met criteria of ACLF were registered in the study period, 20 (83.3%) were men, mean age 52.2±13.3 years, the most common cause of liver disease was heavy alcohol intake in 19 (79.2%) cases, followed by 3 (12.5%) with NASH, 1 (4.2%) autoimmune hepatitis, and 1 (4.2%) cryptogenic origin. Mean MELD-Na was 30.2±6,7. The most important cause of acute decompensation was gastro-intestinal bleeding 13 (54.2%), followed by hepatic encephalopathy 4 (16.7%), recent in-crease on alcohol intake 3 (12.5%), bacterial infections 2 (8.4%), ascites 1 (4.2%), development of jaundice 1 (4.2%). The distribution according to the ACLF category is shown on Table 1.
Conclusions: Alcohol intake remains as an important cause of chronic liver disease in México. Gastrointestinal bleeding is the most important cause of acute decompensation in our cirrhotic patients.
Conflicts of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.