Background. The D-MELD score was designed to prevent donor-recipient matches with a high risk of unfavorable outcome. The main objective of the present study was to assess the predictive value of the D-MELD score for 1-month and 3-month post-transplant mortality in a cohort of patients who underwent deceased-donor liver transplantation in Southern Brazil.
Material and methods. A cohort study was conducted. Receiver operating characteristic c-statistics were used to determine the ability of the D-MELD score to predict mortality. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to analyze survival as a function of time regarding D-MELD scores, and the Cox model was employed to assess the association between D-MELD and mortality.
Results. Most recipients were male, with a mean age of 54.3 ± 9.6 years (n = 233 transplants). Mean donor age was 44.9 ± 16.8 years (19.3% of donors were aged ≥ 60 years). Mean MELD and D-MELD scores were 16.3 ± 7.1 and 733.1 ± 437.8 respectively. Overall survival at 1 and 3 months was 83.6%. The c-statistic value for 1- and 3-month mortality was < 0.5 for the D-MELD. Analysis of Kaplan-Meier curves for groups with D-MELD scores < 1,600 and ≥ 1,600 did not show statistically significant differences in survival (p = 0.722).
Conclusion. D-mElD scores were unable to predict survival in this cohort of Brazilian liver transplant recipients.
The disparity between the number of candidates for liver transplantation and the number of potential donors is a worldwide issue. A current strategy that attempts to address this issue is the use of donor grafts that, up to approximately 15 years ago, would have been considered unfit for transplantation.1–3 There are no universally accepted criteria to define these grafts, formerly known as “marginal” and now as “expanded-criteria” grafts,2 but they include those obtained from elderly donors, donation after cardiac death (DCD), donors with active bacterial infection, those with previous exposure to the hepatitis B or C viruses, fatty grafts (> 30% steatosis), and split-liver grafts.1,4 According to different previously published series, expanded-criteria donor grafts are associated with a greater risk of early dysfunction and, consequently, increased recipient morbidity and mortality.1,2,4,5
In Brazil, the current graft allocation system adopted by the National Transplant System (NTS) prioritizes the most seriously ill patients, with disease severity estimated by means of the Model for End-stage Liver Disease (MELD) scoring system.6 Each transplant center is responsible for developing and adopting protocols to accept these grafts and ascertain which patients should receive them.
The importance of the match between graft quality and recipient disease severity as a determining factor of post-liver transplantation outcomes has been the object of increasing study in recent years.7–11
In 2006, the concept of a donor risk index (DRI) was introduced.12 The research underlying the DRI included over 20,000 liver transplants performed in the United States between January 1998 and December 2002 and recorded in the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) database. Of the several donor variables assessed, nine were significantly associated with graft failure: age (> 40 and particularly over 60), DCD, split or partial grafts, less height, African-American race, cerebrovascular accident as cause of death, death not associated with trauma or anoxia, regional organ sharing, and cold ischemia time. Of these, donor age was the strongest predictor of graft failure after liver transplantation. The importance of donor age to post-liver transplant outcomes has been repeatedly demonstrated in several investigations12–19 including a large study (n = 5,273) conducted in Europe.20 Grafts from elderly donors are believed to be more susceptible to the effects of ischemia and reperfusion injury, with higher liver enzyme levels in the post-transplantation period, greater endothelial injury, and greater risk of inflammation, thrombosis, and rejection.21,22
A study published by Halldorson, et al.23 in 2008 introduced the concept of D-MELD, a score corresponding to the product of donor age and recipient MELD (as calculated on the basis laboratory tests obtained on the day of transplantation), with a maximum value of 40. The Halldorson study included 17,942 liver transplants performed in the U.S. between January 2003 and December 2006. The investigators found that recipients with a D-MELD score above 1,600 exhibited worse outcomes, and considered the D-MELD a good predictor of survival after liver transplantation. Its use could therefore prevent donor-recipient matches with a high risk of unfavorable outcomes, which, in turn, would lead to better utilization of available resources.
The main objective of the present study was to assess the predictive value of the D-MELD score for 1-month and 3-month post-transplant mortality in a cohort of patients who underwent deceased-donor liver transplantation in Southern Brazil.
Material and MethodsThis was a retrospective cohort study. All patients who underwent liver transplantation with donation-after-brain death grafts at a tertiary care center (Irmandade da Santa Casa de Misericórdia de Porto Alegre, Brazil) between 18 July 2006 and 18 June 2011 were eligible for inclusion. Data were recorded prospectively and collected by database mining. Patients who received combined liver-kidney transplantation, those transplanted for fulminant hepatic failure, and those whose records were incomplete were excluded from analysis. In patients who underwent liver retransplantation, only the first transplant was taken into account for analysis; all procedures pertaining to retransplantation were excluded.
The following recipient variables were assessed: age, sex, indication for liver transplantation, postoperative death, need for retransplantation, and length of follow-up. MELD scores6 were calculated using the pre-transplant test results (serum creatinine, total serum bilirubin, and INR) with a maximum score of 40. D-MELD scores were calculated as the product of donor age and recipient MELD score.23 In those patients who underwent liver transplantation with supplementary MELD points, such as those with 20 points because of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) within the Milan criteria, the MELD score was calculated based on immediate pretransplant laboratory results.
Patients were followed for at least 3 months to determine the primary endpoint (death). Patient survival was established from the day of transplantation until the date of death, retransplantation, or until the end of the study, according to patient status at follow-up. The post-transplant observational period ended on 18 December 2011.
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Irmandade Santa Casa de Misericórdia de Porto Alegre, which is accredited by the Office of Human Research Protection. Terms and conditions for collection and proper use of institutional data, including confidentiality, were completed and signed by the authors for all patients included in the study sample.
Statistical analysisQuantitative data were expressed as mean (standard deviation) and median (range). D-MELD scores were expressed as median (interquartile range). Categorical data were expressed as absolute and relative counts.
Patients were stratified into four groups by D-MELD score:
- •
G1: D-MELD score below first quartile (84-405).
- •
G2: D-MELD score between first and second quartiles (408-648).
- •
G3: D-MELD between second and third quartiles (650-986).
- •
G4: D-MELD score above third quartile (988-2,701).
Patient survival as a function of time after transplantation was evaluated according to the D-MELD score categories described above, using the KaplanMeier method, and compared using the log-rank test.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to present the accuracy of the D-MELD score in predicting overall mortality at two different time periods after liver transplantation (1 month and 3 months), represented by area under the curve (AUC). AUC < 0.5 was indicative of no discriminating power, values in the range of 0.7-0.8 were considered clinically useful, and values over 0.8 were considered to indicate excellent discriminating power.24 In addition, a Cox proportional hazards model yielded hazard ratios (HR), with their respective 95% confidence intervals and significance values (P), to express the association between D-MELD quartiles and mortality.
All data were processed and analyzed in SPSS 18.0.
ResultsBetween 18 July 2006 and 18 June 2011, a total of 281 liver transplants were performed at Irmandade Santa Casa de Misericórdia de Porto Alegre. Overall, 48 transplants performed on 47 patients (one patient underwent retransplantation twice) were excluded from analysis: 15 retransplantation procedures (5.3%), 13 combined liver-kidney transplants (4.6%), 11 transplants performed for acute liver failure (3.9%), and 9 cases in which donor age was not recorded (3.2%).
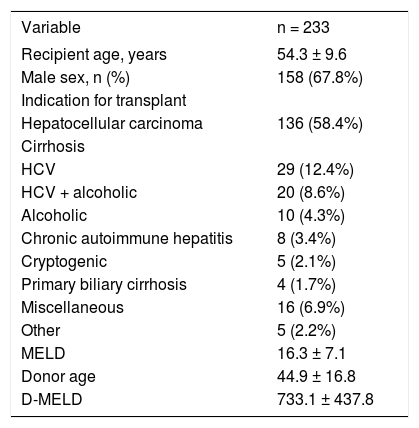
The overall characteristics of the 233 patients included in analysis are listed in table 1. Mean recipient age was 54.3 ± 9.6 years, and 67.8% of recipients were male. The leading indications for liver transplantation were HCC (58.4% of recipients, 79.4% of whom were infected with the hepatitis C virus [HCV]) and HCV-related cirrhosis (12.4%). The mean MELD score was 16.3 ± 7.1. Donor age ranged from 7 to 82 years (mean, 44.9 ± 16.8 years). Only 45 (19.3%) donors were aged ≥ 60 years. Two patients (0.86%) were on hemodialysis before liver transplantation. The median and mean D-MELD scores were 650 and 733.1 ± 437.8 respectively (range, 84-2,701). Eleven patients (4.7%) had a D-MELD score of ≥ 1,600. The small number of patients with a D-MELD score ≥ 1,600 prevented a proper comparison with patients with a D-MELD score < 1,600. However, in order to assess the impact of the D-MELD score on post-liver transplant outcomes (length of hospital stay, percentage of patients who developed primary graft dysfunction, and survival at 1 and 3 months), we compared the occurrence of outcomes between the different D-MELD categories (quartiles). There was no correlation between the occurrence of the outcomes assessed and the different D-MELD categories.
Overall profile of liver transplant recipients (n = 233) and donor age.
| Variable | n = 233 |
|---|---|
| Recipient age, years | 54.3 ± 9.6 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 158 (67.8%) |
| Indication for transplant | |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | 136 (58.4%) |
| Cirrhosis | |
| HCV | 29 (12.4%) |
| HCV + alcoholic | 20 (8.6%) |
| Alcoholic | 10 (4.3%) |
| Chronic autoimmune hepatitis | 8 (3.4%) |
| Cryptogenic | 5 (2.1%) |
| Primary biliary cirrhosis | 4 (1.7%) |
| Miscellaneous | 16 (6.9%) |
| Other | 5 (2.2%) |
| MELD | 16.3 ± 7.1 |
| Donor age | 44.9 ± 16.8 |
| D-MELD | 733.1 ± 437.8 |
Data expressed as mean ± standard deviation or absolute and relative counts as appropriate. HCV: hepatitis C virus. MELD: Model for End-stage Liver Disease. D-MELD: Donor Model for End-stage Liver Disease.
The median length of follow-up was 39 months.
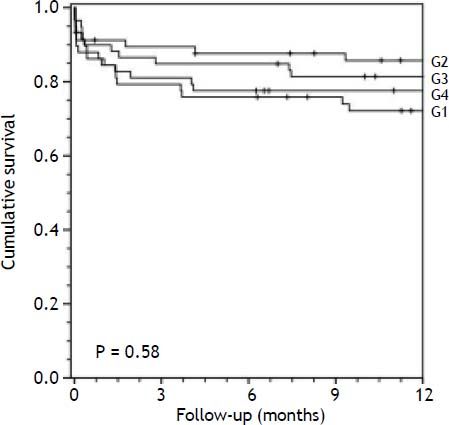
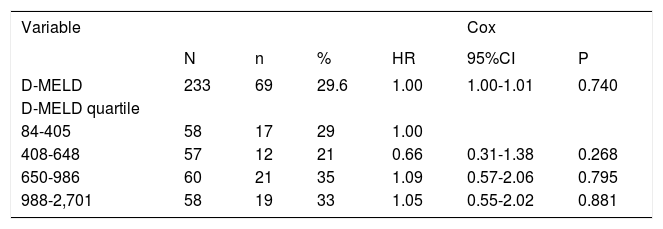
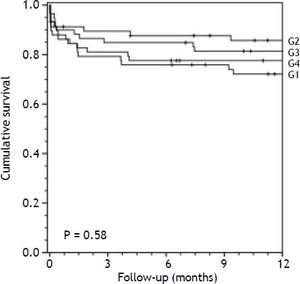
Survival analysisThe overall mortality rate during the follow-up period was 29.6%. Overall survival at 1 and 3 months was 83.6%. Associations between D-MELD scores (evaluated as a continuous variable or stratified into quartiles) and death, using a simple Cox proportional hazards model, are shown in table 2. There were no statistically significant associations. Survival curves for patients categorized into each D-MELD quartile are shown in figure 1. There were no statistically significant differences between D-MELD quartiles (p = 0.58) or between patients with a D-MELD score < 1,600 and a D-MELD score ≥ 1,600 (p = 0.722). Assessment of the accuracy of the D-MELD score as a predictor of patient survival by ROC curve analysis revealed AUC values of 0.49 (95%CI 0.38-0.60) for both 1- and 3-month survival, which indicate that the D-MELD score was not able to predict post-transplantation survival at any of the time points of analysis. The stratification of the MELD score into quartiles to verify whether the D-MELD score would play a more important role in some subgroup of patients showed that AUC values increased as MELD scores increased, but always within the range of values without clinical significance (AUC of 0.30 for patients with a MELD score of 6-11, and AUC of 0.57 for patients with a MELD score ≥ 20).
Association between D-MELD scores (evaluated as a continuous variable and stratified into quartiles) and mortality in liver transplant recipients.
| Variable | Cox | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | n | % | HR | 95%CI | P | |
| D-MELD | 233 | 69 | 29.6 | 1.00 | 1.00-1.01 | 0.740 |
| D-MELD quartile | ||||||
| 84-405 | 58 | 17 | 29 | 1.00 | ||
| 408-648 | 57 | 12 | 21 | 0.66 | 0.31-1.38 | 0.268 |
| 650-986 | 60 | 21 | 35 | 1.09 | 0.57-2.06 | 0.795 |
| 988-2,701 | 58 | 19 | 33 | 1.05 | 0.55-2.02 | 0.881 |
D-MELD: Donor Model for End-stage Liver Disease. n: absolute number of deaths in each group. %: percent mortality in each group. HR: hazard ratio. 95%CI: 95% confidence interval. P: statistical significance level.
Survival of liver transplant recipients in the sample by D-MELD score quartile (Kaplan-Meier curve). G1, D-MELD score below first quartile (84-405); G2, D-MELD score between first and second quartiles (408-648); G3, D-MELD between second and third quartiles (650-986); G4, D-MELD score above third quartile (988-2,701).
The disparity between the number of transplant candidates and organ donors and the widespread, worldwide use of the MELD score, which prioritizes the most severely ill candidates for graft allocation, means that transplant coordinators are often faced with difficult decisions regarding the use of expanded-criteria donor grafts in sicker recipients. In an attempt to reduce the frequency of donor-recipient matches that might result in “futile” transplantation, Halldorson, et al.23 developed the D-MELD score, which employs two major predictors of post-liver transplantation outcomes: the clinical condition of the recipient at the time of transplantation, as estimated by the MELD score, and donor quality, expressed by age. The authors suggested that D-MELD scores above 1,600 would be indicative of a greater likelihood of poor outcomes after liver transplantation, particularly in high-risk cases (donor age ≥ 60 years and recipient MELD score ≥ 30). The score was validated in Italy, where a D-MELD of 1628 was identified as the cutoff point predictive of lower 3-year post-transplantation survival.25 The greatest advantage of the D-MELD score is its simplicity, which makes it readily applicable and obviates the need for complex computer-based calculation.
The present study is the first to describe the experience of a Brazilian transplant center with the D-MELD score as a predictor of post-transplantation survival with prolonged patient follow-up. As in the original study that developed the score,24 our analysis was restricted to patients with chronic liver disease who received deceased-donor grafts. The results presented herein demonstrated low accuracy of the D-MELD score as a predictor of post-transplantation mortality at the two time points of analysis (AUC < 0.7).
Some study limitations warrant mention. Singlecenter studies necessarily include a smaller number of cases compared with those using national registry data, such as the study by Halldorson, et al.,23 from which the score was derived. For example, two studies conducted in Europe26,27 evaluated the prognostic ability of D-MELD in 303 and 291 patients, respectively. However, and very importantly, in our cohort (n = 233) the median D-MELD score (650) was lower than that reported in previous studies,25,26 and the percentage of patients with D-MELD scores ≥ 1,600 (4.7%) was almost half of that reported by Halldorson, et al.23 and Vitale, et al.26 (8.1 and 8.0%, respectively). Furthermore, the large proportion of patients with HCC (58.4%) in this series may represent selection bias, as the MELD score does not take into account disease prognosis or severity. Therefore, our results should be considered within this context, with few patients in the higher risk category. In spite of that, the previously mentioned validation studies26,27 concluded that D-MELD was not a good predictor of survival after liver transplantation. Nevertheless, these differences do not appear to justify the absence of a correlation between D-MELD scores and post-transplantation mortality, as a scoring system must be universally applicable (as is the MELD score) if it is to be truly useful.28
The MELD score29 is used to stratify candidates for liver transplantation30 in several centers and has been postulated as a predictor of post-transplant survival. In our hospital, for example, we observed that the MELD score is a poor predictor of post-transplant mortality: the c-statistic value for 3-month patient mortality was 0.60.31 A recent systematic review (n = 53,691 patients) concluded that the MELD score actually has poor accuracy as a predictor of survival after transplantation.32 Other scores, using recipient and donor variables, have been developed aiming to estimate survival or outcomes after liver transplantation, such as the SOFT score33 and the BAR score.34 Although these scores are more complex than the D-MELD score for use in clinical practice, because they involve more variables, they appear to be more accurate. In both, the AUC value for 3-month survival after liver transplantation was 0.70, while for the D-MELD the AUC value was 0.60.33,34
In conclusion, D-MELD scores were unable to predict survival after liver transplantation in a cohort of patients from Southern Brazil. Other studies, with larger sample sizes and encompassing several geographic regions, should be conducted to assess the accuracy of the D-MELD score as a predictor of survival after liver transplantation. The greatest advantage of the D-MELD -its simplicity-may also be its greatest limitation.
Abbreviations- •
AUC: area under the curve.
- •
DCD: donation after cardiac death.
- •
DRI: donor risk index.
- •
HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma.
- •
HCV: hepatitis C virus.
- •
HR: hazard ratios.
- •
MELD: Model for End-stage Liver Disease.
- •
NTS: National Transplant System.
- •
ROC: receiver operating characteristic.
- •
SPSS: Statistical Package for the Social Sciences.
- •
UNOS: United Network for Organ Sharing.
This study should be attributed to Postgraduate Program in Medicine: Hepatology, Universidade Federal de Ciências da Saúde de Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil.
The study did not receive financial support or grants.
Author ContributionsCostabeber AM: data collection, data analysis/interpretation.
Lionço LC: data collection, data analysis/interpretation, article drafting.
Marroni C: critical revision of article.
Zanotelli ML: critical revision of article.
Cantisani G: critical revision of article.
Brandão A: concept/design, data analysis/interpretation, article drafting.
AcknowledgmentsThe authors would like to thank Dr. Mário Wagner for his assistance with the statistical analysis.
Costabeber AM, Lionço LC, Marroni C, Zanotelli ML, Cantisani G, Brandão A on behalf of the Liver Transplantation Group. D-MELD does not predict post-liver transplantation survival: a single-center experience from Brazil.