Penile prosthesis (PP) implantation is an effective option for erectile dysfunction. Although initially PP surgery was carried out in an inpatient setting, there is a growing trend to implant PP as a major ambulatory surgery (MAS). This study aimed to perform a systematic review of the literature to identify available evidence of the implantation of PP under MAS setting and go carry out a comparison between MAS and inpatient procedures.
Material and methodsPubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library and MEDES electronic databases and non-indexed supplements for scientific congresses were searched to identify articles related to the surgical implantation of PP in MAS up to February 2021. Key search terms included penile prosthesis, erectile dysfunction, ambulatory surgery, ambulatory care, and surgery.
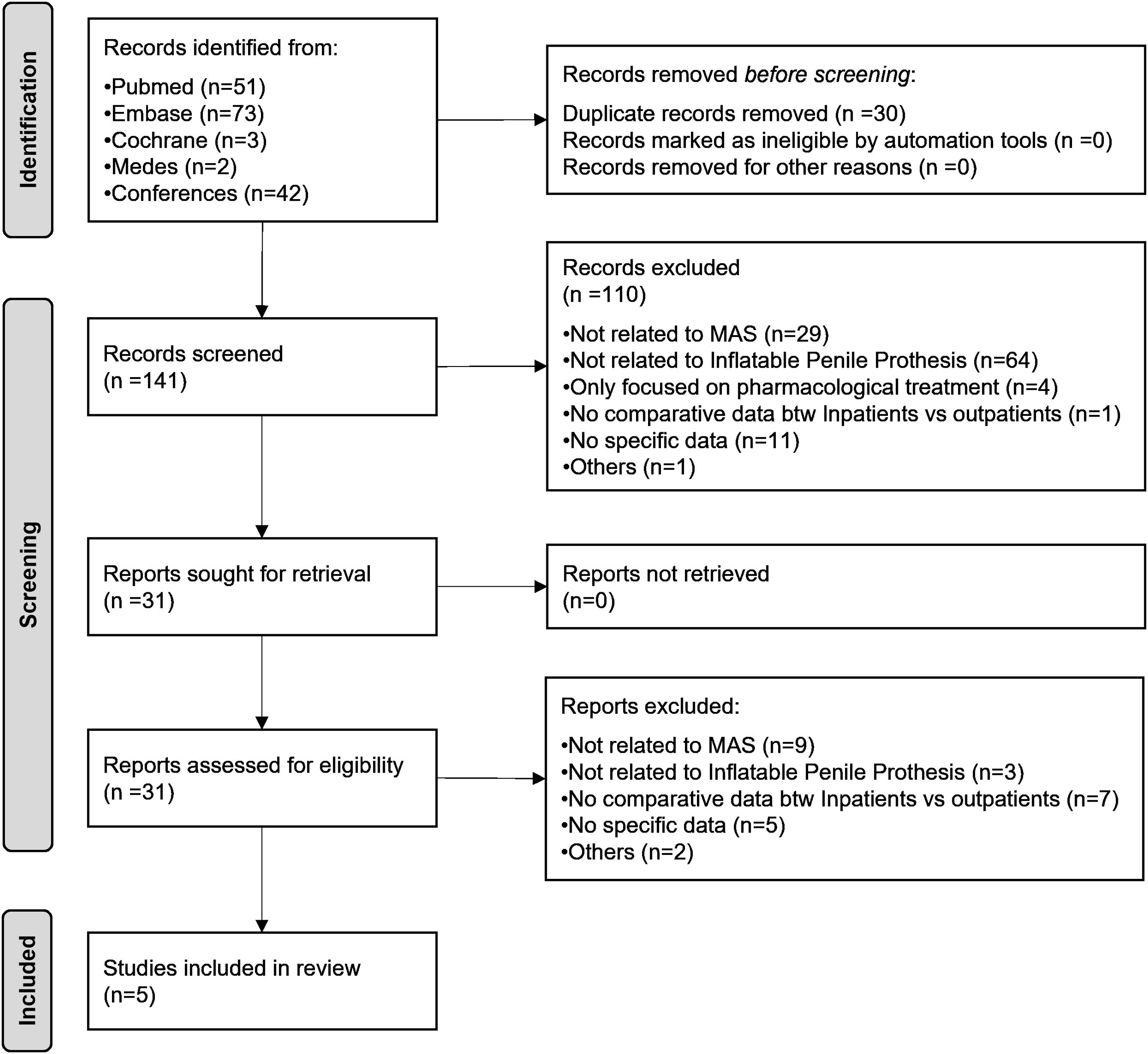
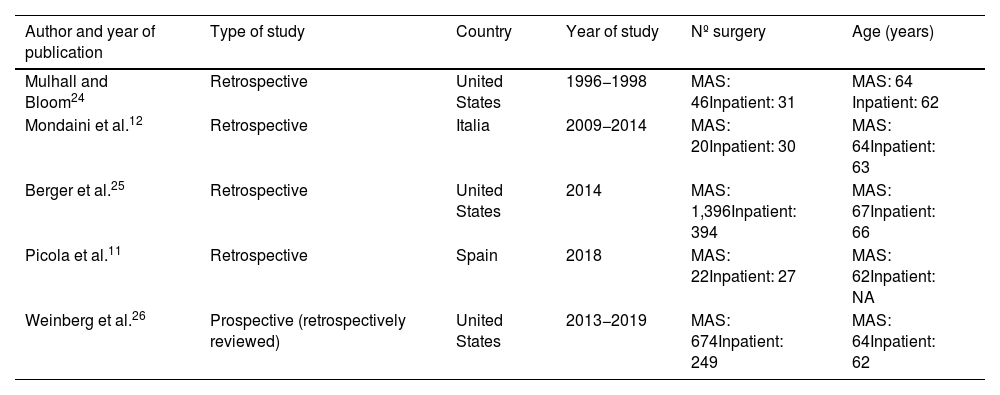
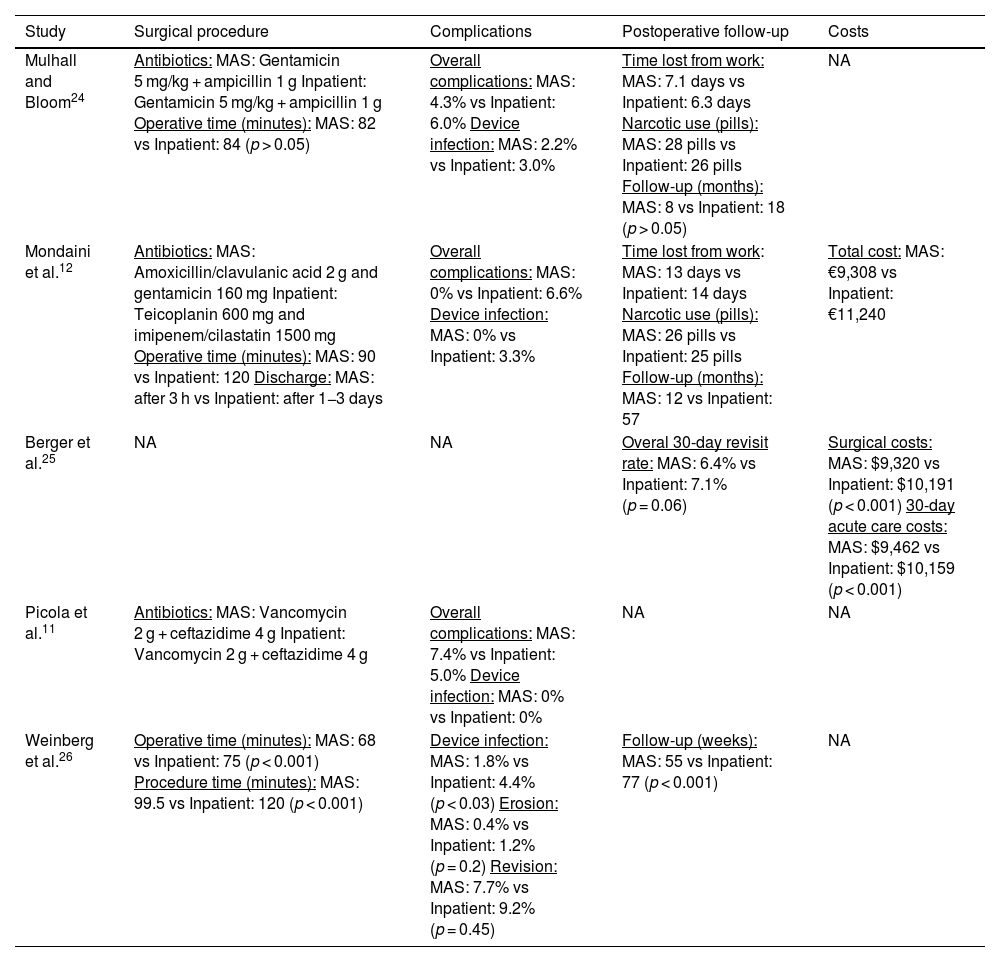
ResultsAmong 171 publications retrieved (51 PubMed, 73 EMBASE, 3 Cochrane, 2 using MEDES and 42 manual searching), 5 studies were finally selected. There were no significant differences between MAS or inpatient setting in terms of the type of device, surgical approach, or location of reservoir. Complication rates observed in both groups were similar. Implantation of PP in MAS was less expensive than inpatient surgery and was associated with acceptable patient satisfaction rates and adequate pain control.
ConclusionsStudies demonstrated that outpatient PP surgery can achieve similar outcomes in terms of safety and satisfaction to implantation of PP in the inpatient setting, while it could reduce costs and improve the efficiency. This research could support decision makers to extend PP surgery into the ambulatory setting.
La implantación de prótesis de pene (PP) es una alternativa eficaz para la disfunción eréctil. Aunque inicialmente la cirugía de PP se realizaba en régimen hospitalario, existe una tendencia creciente a realizar el implante de PP en un modelo de cirugía mayor ambulatoria (CMA). El objetivo de este estudio es realizar una revisión sistemática de la literatura para identificar la evidencia disponible sobre la implantación de PP en el marco de la CMA en comparación con el procedimiento realizado en régimen hospitalario.
Material y métodosSe realizo una búsqueda en las bases de datos electrónicas PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library y MEDES y en los suplementos no indexados de los congresos científicos para identificar artículos relacionados con la implantación quirúrgica de PP en CMA hasta febrero de 2021. Los términos de búsqueda incluyeron prótesis de pene, disfunción eréctil, cirugía ambulatoria, atención ambulatoria y cirugía.
ResultadosEntre las 171 publicaciones obtenidas (51 en PubMed, 73 en EMBASE, 3 en Cochrane, 2 mediante MEDES y 42 mediante búsqueda manual), se seleccionaron finalmente 5 estudios. No hubo diferencias significativas entre la CMA y el régimen hospitalario en términos del tipo de dispositivo, el abordaje quirúrgico o la ubicación del reservorio. Las tasas de complicaciones observadas en ambos grupos fueron similares. La implantación de PP en régimen de CMA supuso un menor coste que la cirugía en régimen hospitalario y se asoció con tasas aceptables de satisfacción de los pacientes y un adecuado control del dolor.
ConclusionesLos estudios demostraron que la implantación de PP en régimen de CMA puede lograr resultados similares en términos de seguridad y satisfacción a la implantación de PP en el régimen hospitalario, pudiendo también reducir los costes y mejorar la eficiencia. Esta investigación podría ayudar a los responsables de la toma de decisiones a extender la cirugía de PP al régimen ambulatorio.