To understand the residents’ perceptions of the, COVID-19 driven, newly implemented online learning systems adopted among accredited urology residency programs nationwide, and their sustainability following the pandemic era.
Materials and methodsA survey was designed and dispersed to urology program coordinators and directors to distribute to their residents.
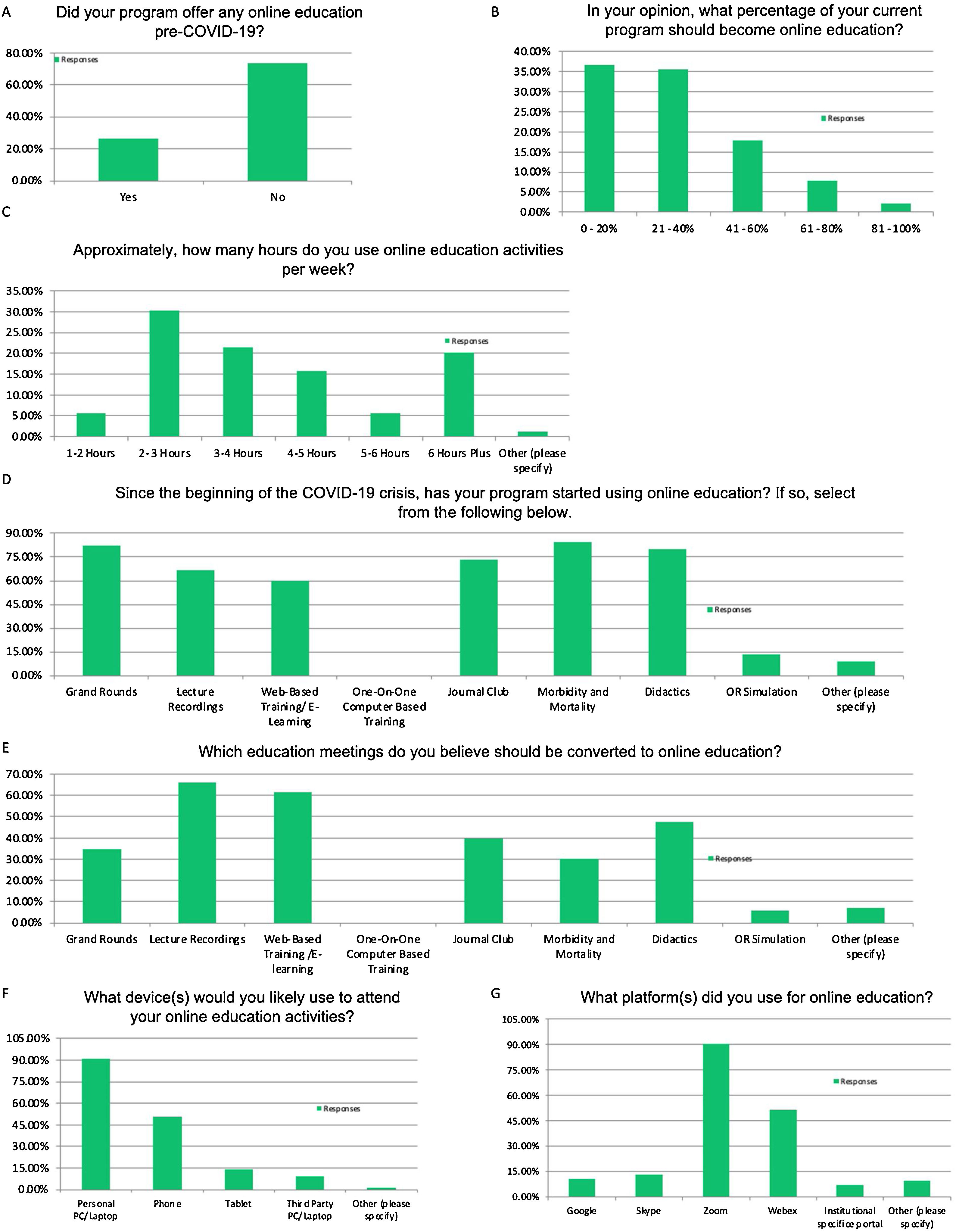
In the survey, Online education models was the all-encompassing term to describe any form of resident education that occurred online. Anonymous surveys were exported from Survey Monkey and data was analyzed for statistical significance.
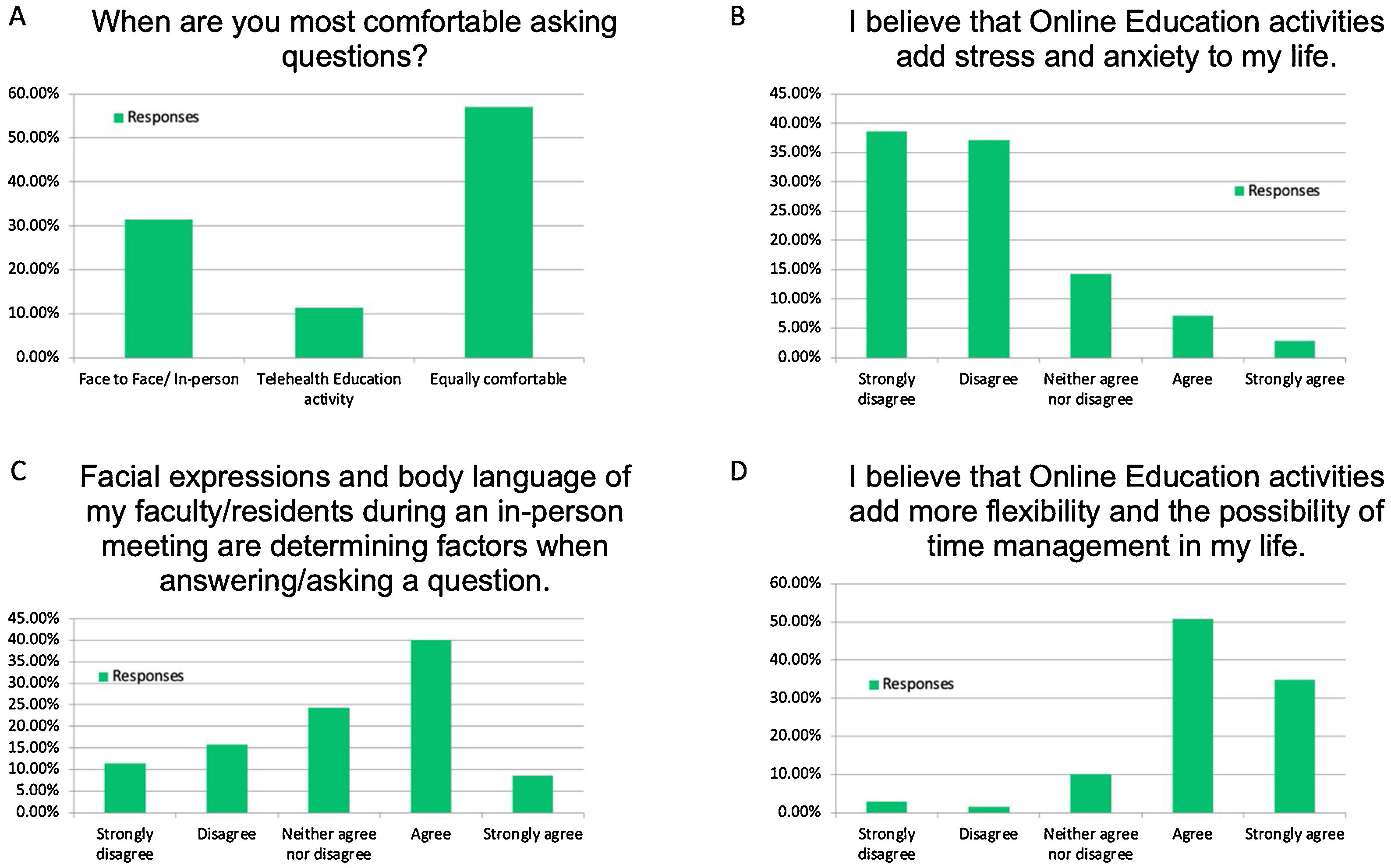
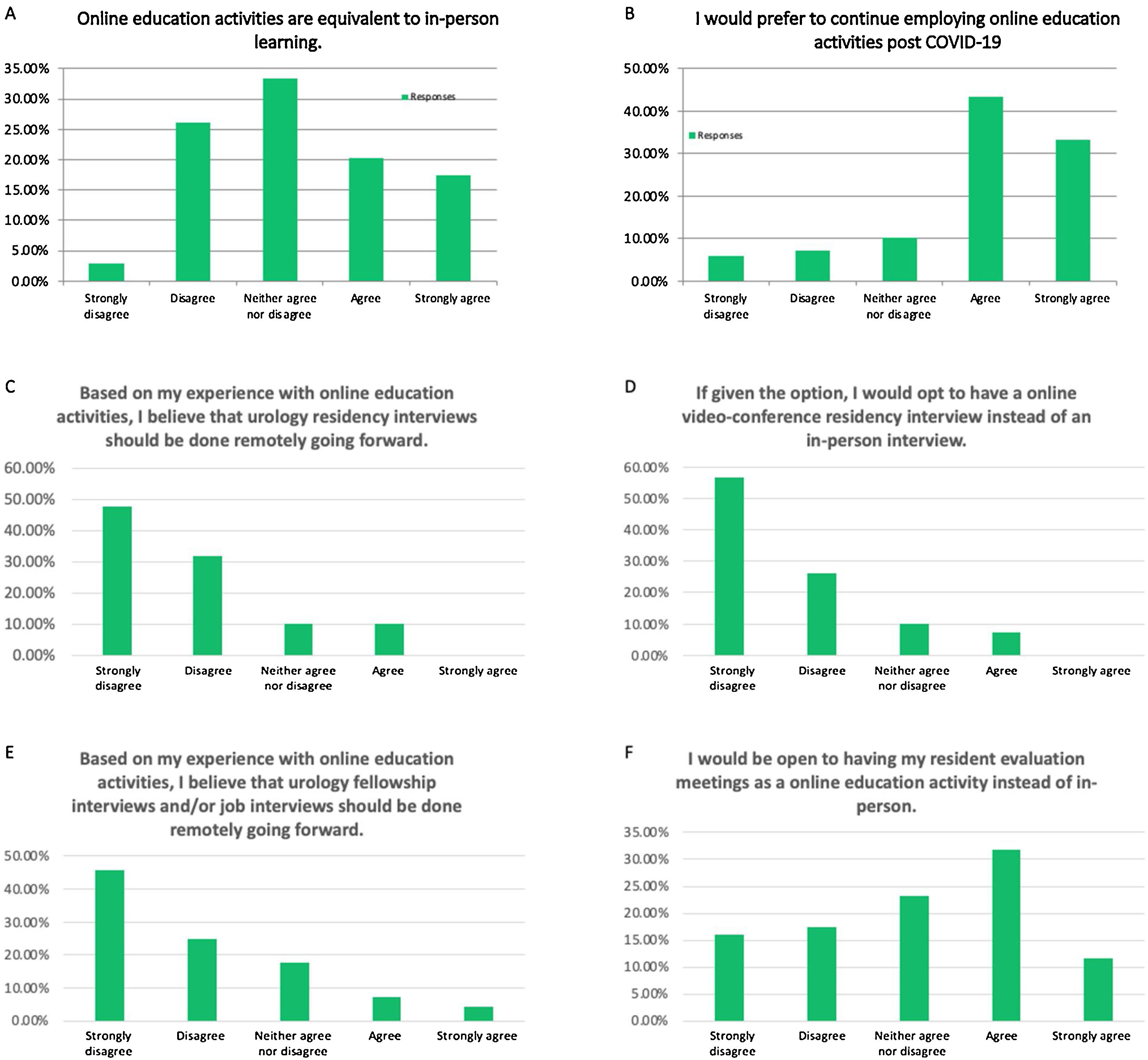
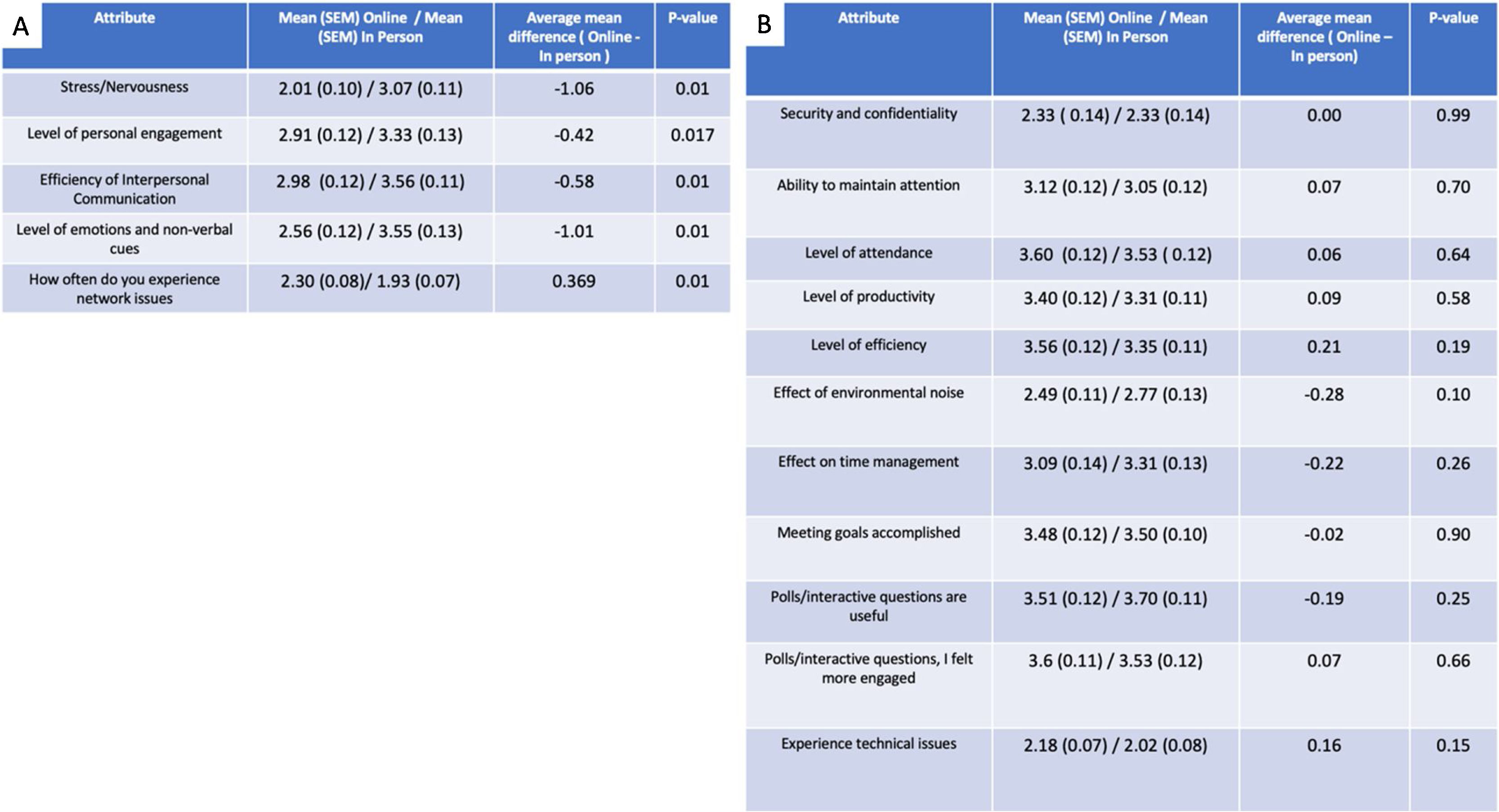
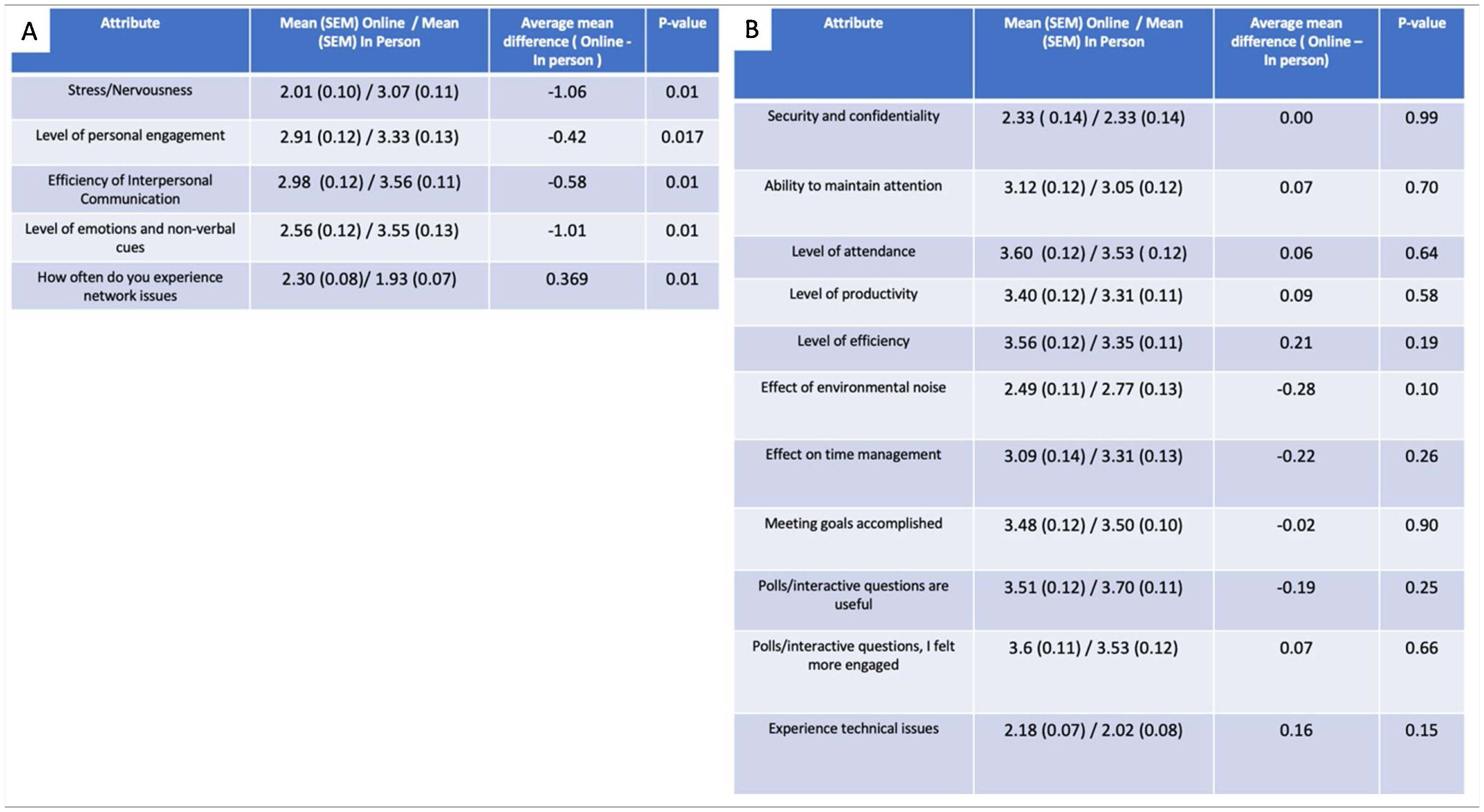
ResultsOver 70% of urology residents agreed or were neutral to the statement that Online education models were equivalent to in-person learning. Only 13% of residents stated that online learning should not be continued following the pandemic. Several different parameters were assessed, and only 5 of them showed statistical significance. Stress, personal engagement, interpersonal communication efficiency and non-verbal cues were all lower with online education models. The only attribute that was scored higher by residents was network connectivity issues.
ConclusionsAn overwhelming majority of urology residents in the United States believe Online education models should continue to be adopted once the pandemic is over.
Comprender la percepción de los residentes respecto a los sistemas de aprendizaje en línea, los cuales, impulsados por la pandemia del COVID-19, han sido recientemente implementados a nivel nacional en los programas de residencia urológica acreditados. Adicionalmente, nos proponemos analizar su sostenibilidad tras la era de la pandemia.
Material y métodosSe diseñó una encuesta para, a través de los coordinadores y directores de programas de urología, difundir a los residentes de urología.
En la encuesta, los modelos de educación en línea englobaron cualquier forma de educación recibida por los residentes que se diera en línea. Las encuestas anónimas se exportaron de Survey Monkey y se analizaron los datos para determinar la significación estadística.
ResultadosMás del 70% de los residentes de urología estuvieron de acuerdo, o mostraron una actitud neutral, ante la afirmación de que los modelos de educación en línea eran equivalentes al aprendizaje presencial. Sólo el 13% de los residentes afirmó que el aprendizaje en línea no debería continuar tras la pandemia. Se evaluaron diversos parámetros, y sólo 5 de ellos mostraron significación estadística. El estrés, el compromiso personal, la eficacia de la comunicación interpersonal y las señales no verbales fueron más bajos para los modelos de educación en línea. El único aspecto al que los residentes dieron mayor puntuación fue el de los problemas de conectividad a una red.
ConclusionesLa gran mayoría de los residentes de urología en Estados Unidos cree que los modelos de educación en línea deben mantenerse una vez terminada la pandemia.