To determine the urodynamic efficacy and factors that influence the urodynamic results of treatment of neurogenic detrusor hyperactivity with intradetrusor injection of botulinum toxin type A (BTX-A) in patients with spinal cord injury (SCI).
Material and methodsA retrospective study was conducted with a cohort of 70 patients composed of 40 men and 30 women with stable SCI (mean age, 39±13.3 years) who underwent an intradetrusor injection of 300 IUs of BTX-A. A urodynamic study was conducted prior to the injection and 6±4.3 months after the treatment. New urodynamic studies were subsequently performed up to an interval of 16±12.2 months.
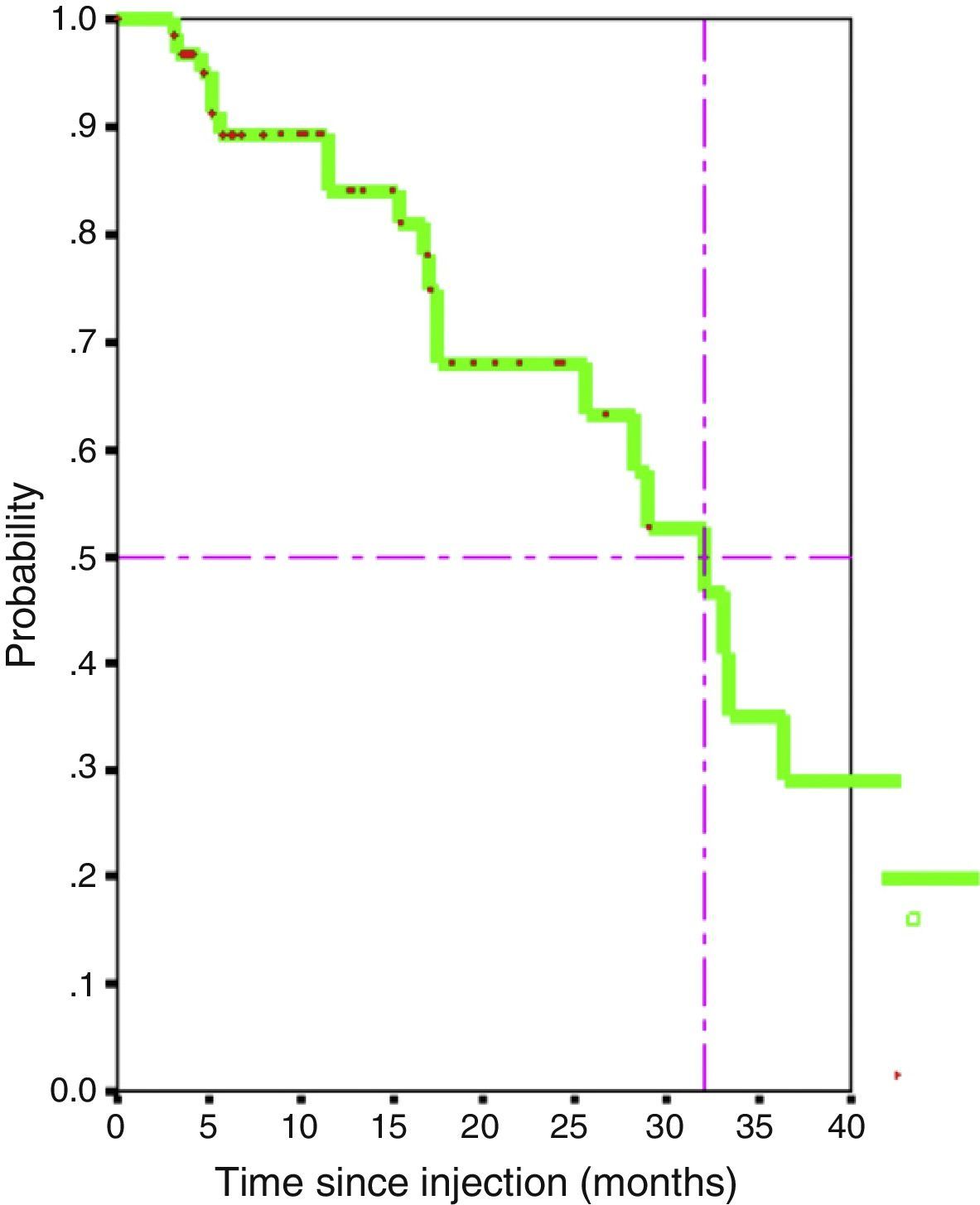
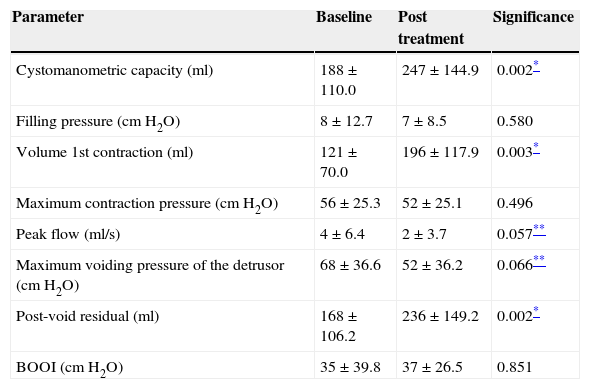
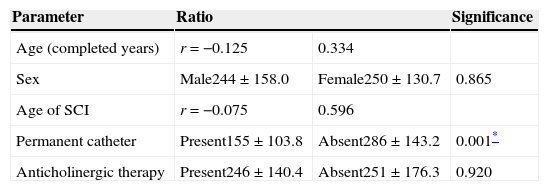
ResultsThe BTX-A significantly increased (p<.05) the cystomanometric bladder capacity, the bladder volume of the first involuntary contraction of the detrusor and the postvoid residue. We observed a decrease that tended toward statistical significance (p<.1) of the maximum detrusor pressure and the maximum urine flow. Neither the bladder accommodation nor the urethral resistance index (bladder outlet obstruction index) varied significantly. The increase in vesical capacity was maintained in 50% of the sample for more than 32 months. Age, sex, anticholinergic treatment and lesion age showed no influence in terms of the increase in bladder capacity. The indwelling urinary catheter (IUC) was the only statistically significant negative factor.
ConclusionsThe urodynamic effect of BTX-A is maintained for a considerable time interval. The IUC negatively influences the result of the treatment.
Determinar la eficacia urodinámica y los factores que influyen en los resultados urodinámicos del tratamiento de la hiperactividad neurógena del detrusor con inyección intradetrusoriana de toxina botulínica tipo A (TXB-A) en pacientes con lesión medular (LM).
Material y métodosSe realizó un estudio retrospectivo en una cohorte de 70 pacientes formada por 40 varones y 30 mujeres con LM estable de 39±13,3 años de edad (media±desviación típica), sometidos a inyección intradetrusoriana de 300UI de TXB-A. Se realizó un estudio urodinámico previo y otro a los 6±4,3 meses del tratamiento. Posteriormente se realizaron nuevos estudios urodinámicos hasta un intervalo de 16±12,2 meses.
ResultadosLa TXB-A aumentó significativamene (p<0,05) la capacidad vesical cistomanométrica, el volumen vesical de la primera contracción involuntaria del detrusor y el residuo posmiccional. Se observó una disminución con tendencia hacia la significación estadística (p<0,1) de la presión máxima miccional del detrusor y el flujo miccional máximo. No varió significativamente la acomodación vesical ni el índice de resistencia uretral (BOOI). El aumento de la capacidad vesical se mantuvo en el 50% de la muestra más de 32 meses. La edad, el sexo, el tratamiento anticolinérgico y la antigüedad de la lesión no mostraron influencia respecto del aumento de la capacidad vesical. La sonda a permanencia (SVP) fue el único factor negativo estadísticamente significativo.
ConclusionesEl efecto urodinámico de la TXB-A se mantiene durante un considerable intervalo de tiempo. La SVP influye negativamente en el resultado del tratamiento.