The first European Association of Urology (EAU) guidelines on incontinence were published in 2001. These guidelines were periodically updated in the past years.
ObjectiveThe aim of this paper is to present a summary of the 2009 update of the EAU guidelines on urinary incontinence (UI).
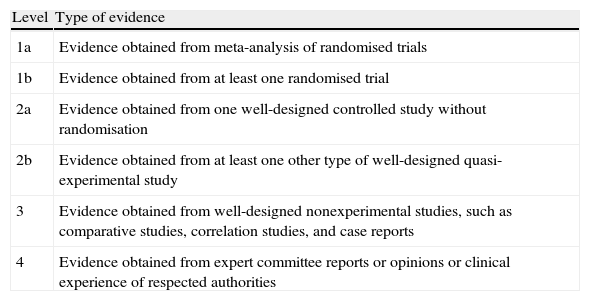
Evidence acquisitionThe EAU working panel was part of the 4th International Consultation on Incontinence (ICI) and, with permission of the ICI, extracted the relevant data. The methodology of the 4th ICI was a comprehensive literature review by international experts and consensus formation. In addition, level of evidence was rated according to a modified Oxford system and grades of recommendation were given accordingly.
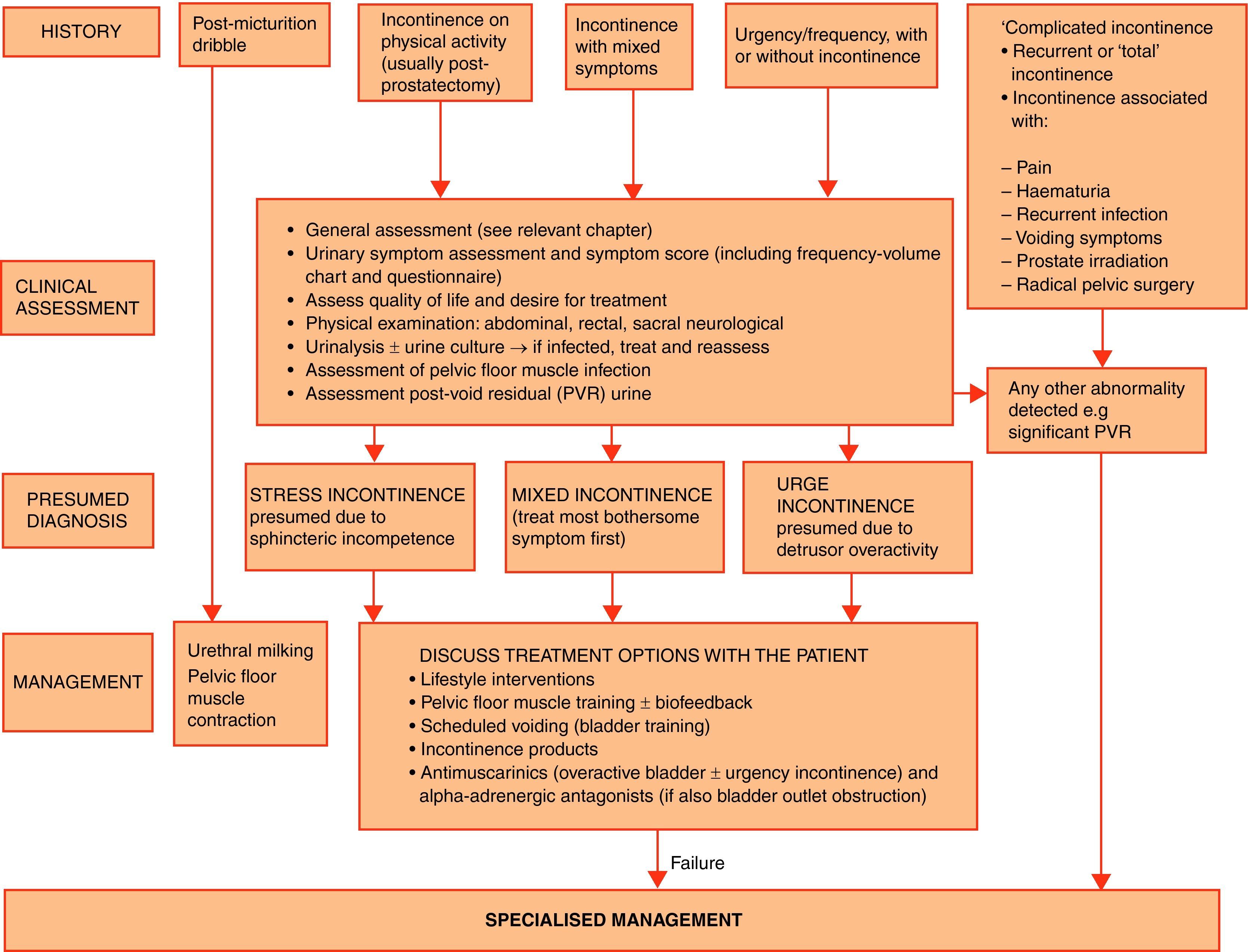
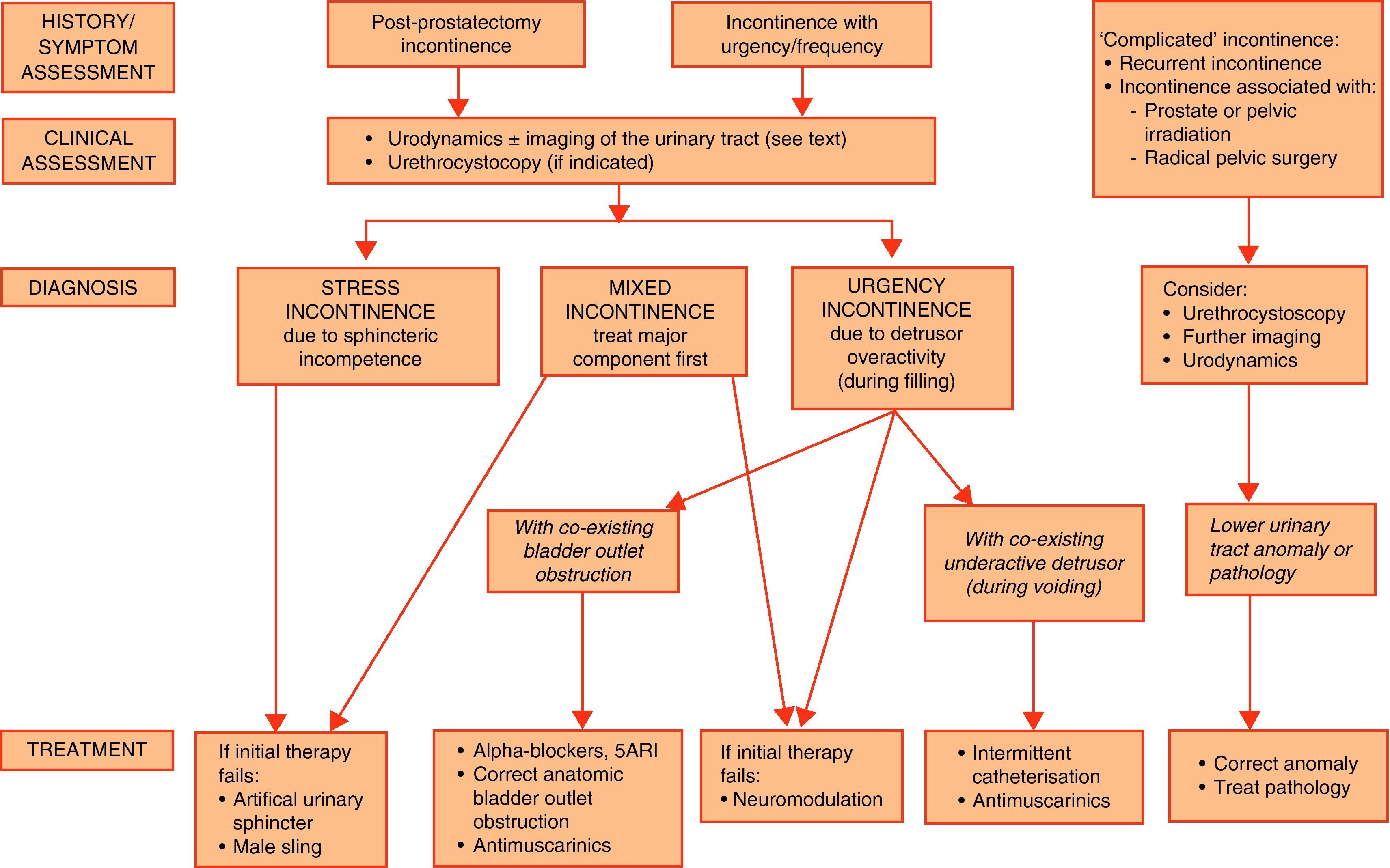
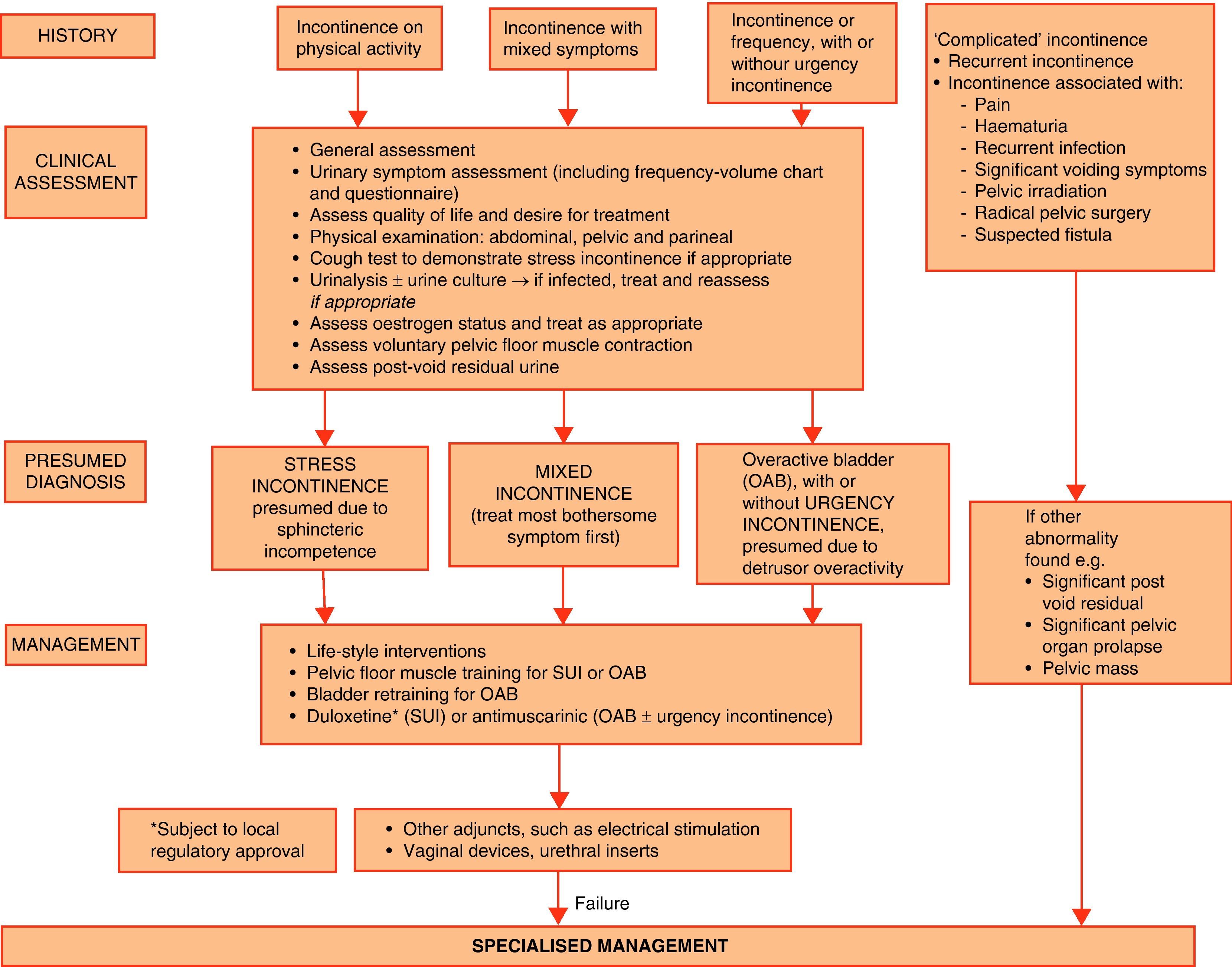
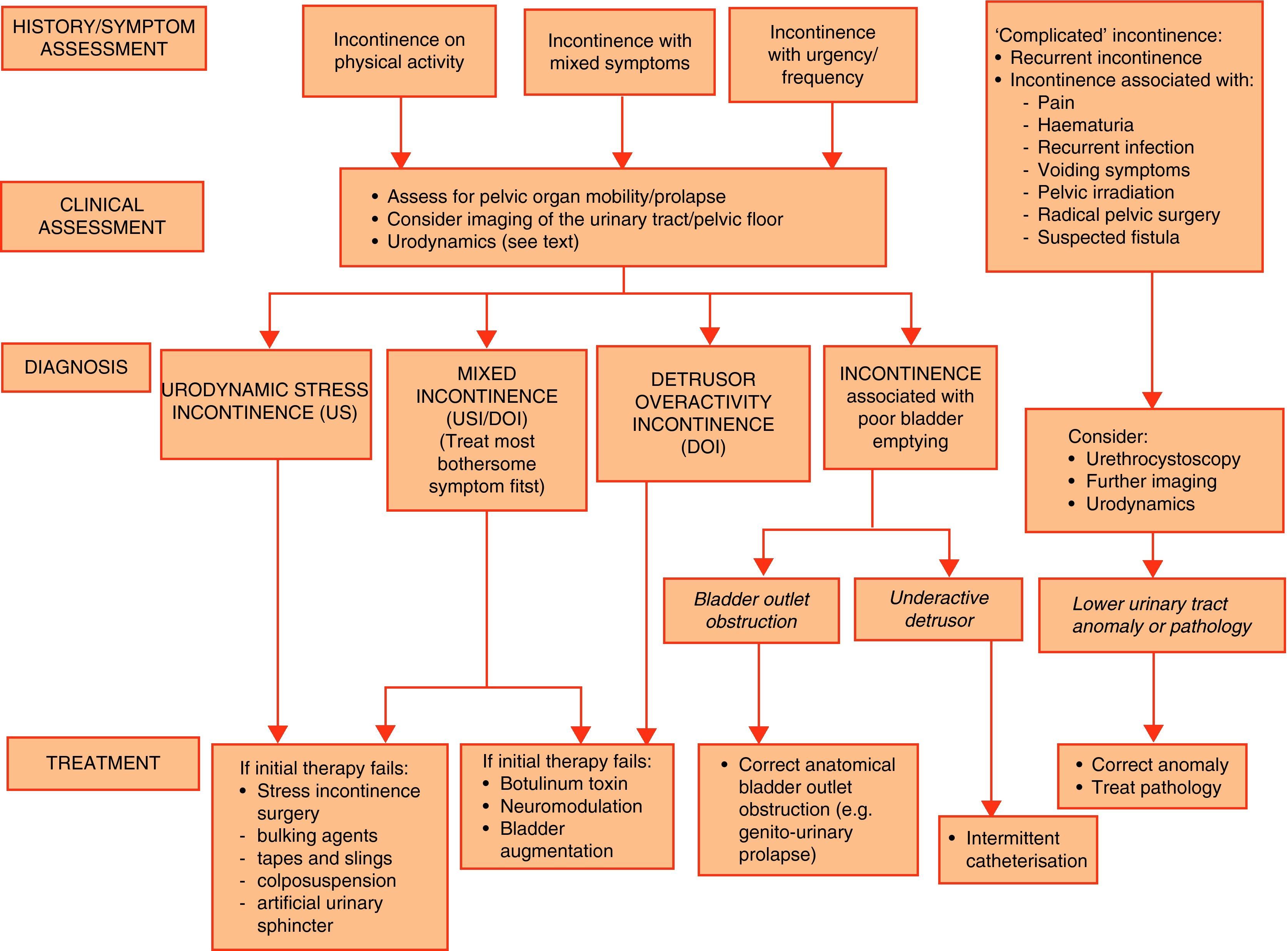
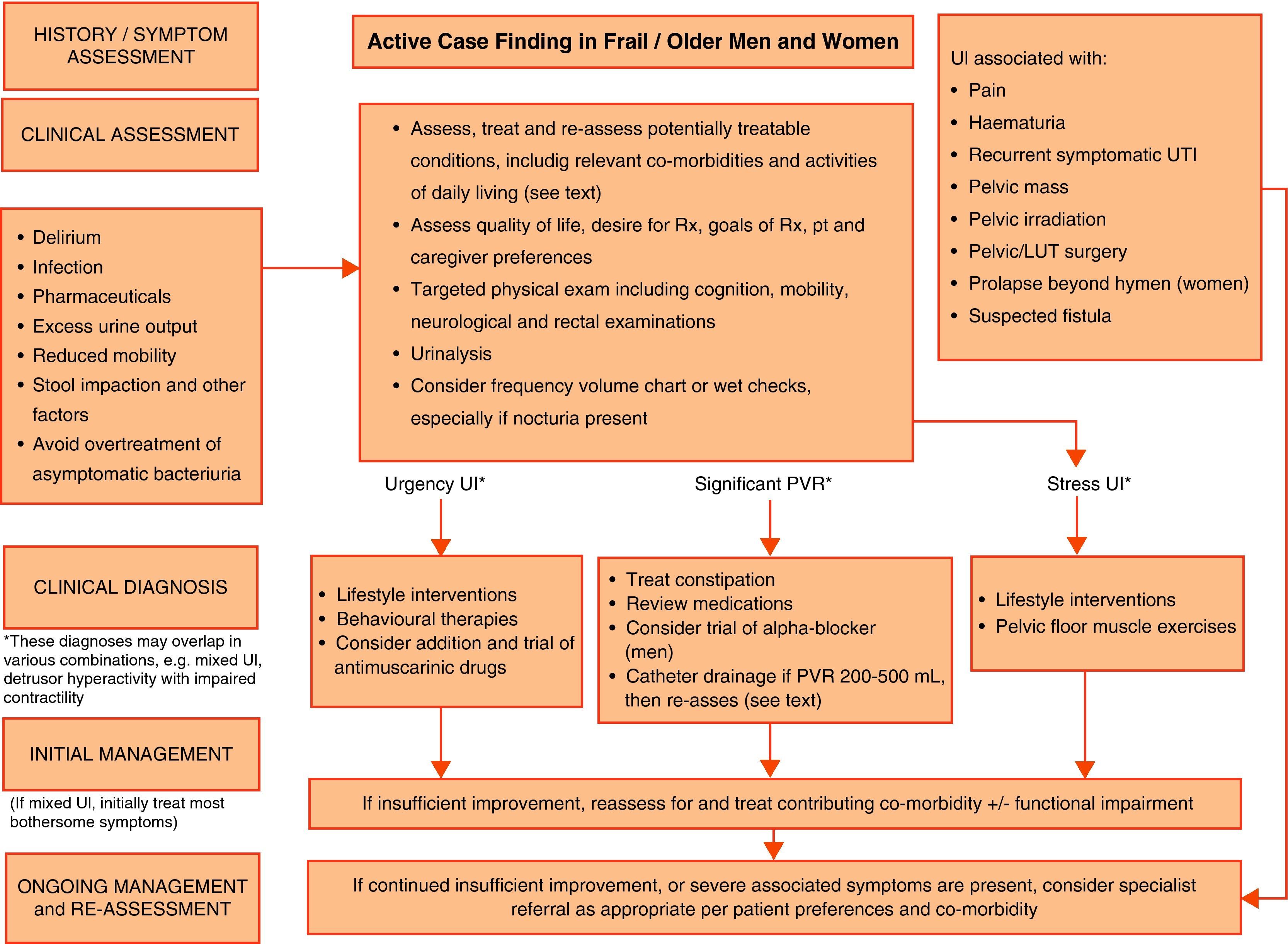
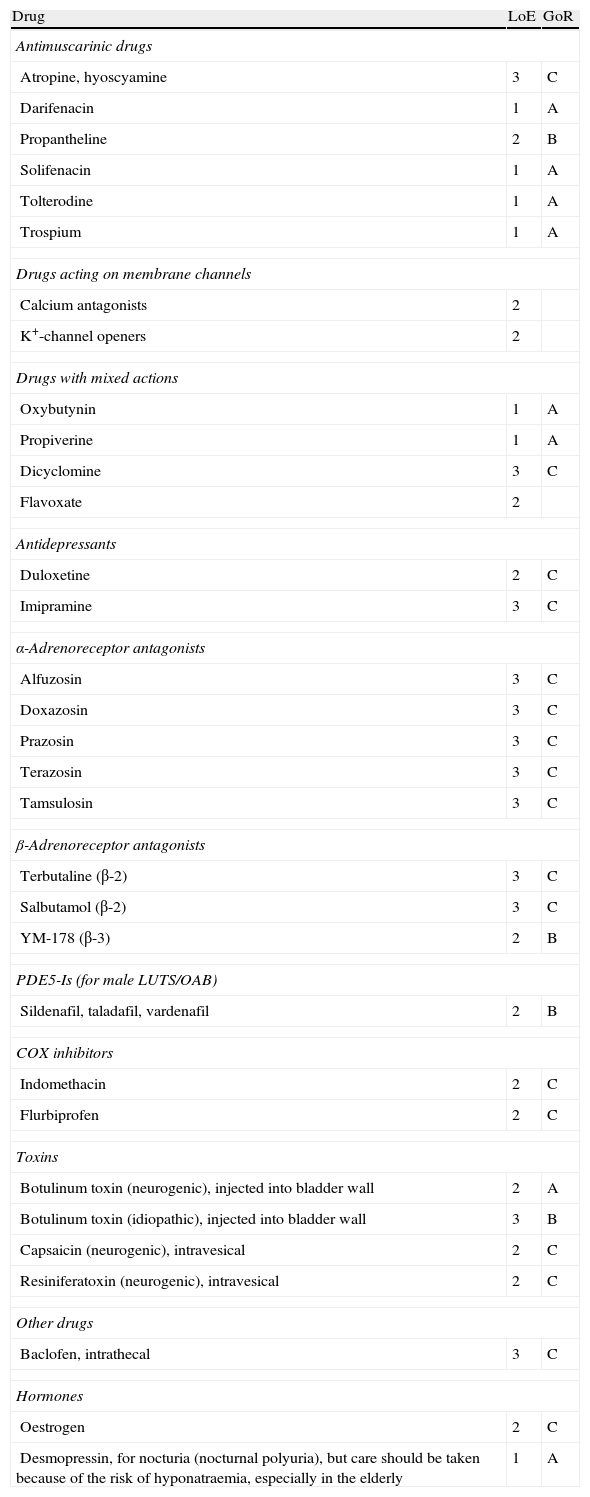
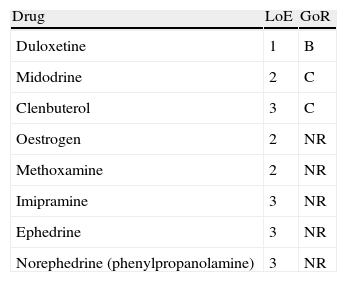
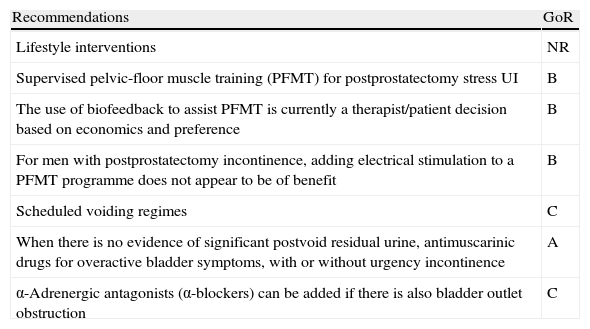
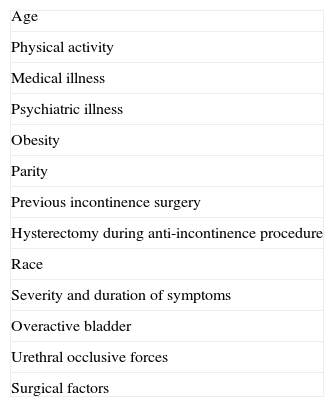
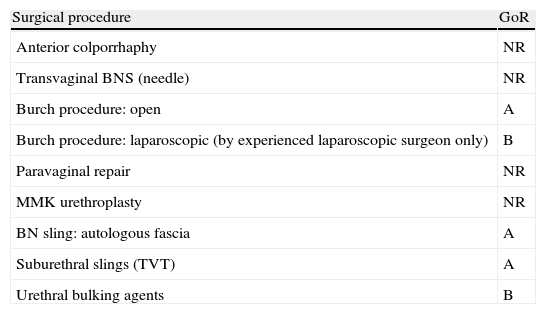
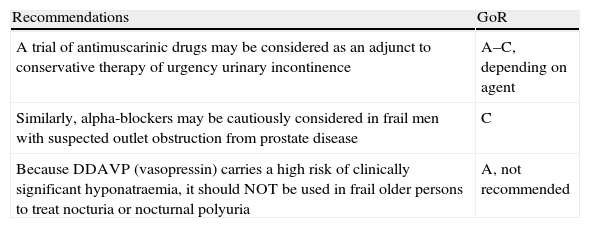
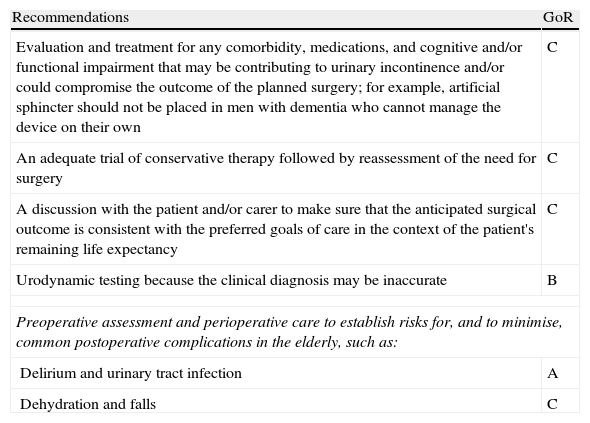
Evidence summaryA full version of the EAU guidelines on urinary incontinence is available as a printed document (extended and short form) and as a CD-ROM from the EAU office or online from the EAU Web site (http://www.uroweb.org/guidelines/online-guidelines/). The extent and invasiveness of assessment of UI depend on severity and/or complexity of symptoms and clinical signs and are different for men, women, frail older persons, children, and patients with neuropathy. At the level of initial management, basic diagnostic tests are applied to exclude an underlying disease or condition such as urinary tract infection. Treatment is mostly conservative (lifestyle interventions, physiotherapy, physical therapy, pharmacotherapy) and is of an empirical nature. At the level of specialised management (when primary therapy failed, diagnosis is unclear, or symptoms and/or signs are complex/severe), more elaborate assessment is generally required, including imaging, endoscopy, and urodynamics. Treatment options include invasive interventions and surgery.
ConclusionsTreatment options for UI are rapidly expanding. These EAU guidelines provide ratings of the evidence (guided by evidence-based medicine) and graded recommendations for the appropriate assessment and according treatment options and put them into clinical perspective.
Las primeras directrices sobre incontinencia de la European Association of Urology (EAU) se publicaron en 2001. Dichas directrices se han actualizado con regularidad en los últimos años.
ObjetivoEl objetivo de este artículo es ofrecer un resumen de la actualización de las directrices sobre incontinencia urinaria (IU) de la EAU realizada en 2009.
Recogida de evidenciasEl comité de trabajo de la EAU formó parte de la IV Consulta Internacional sobre Incontinencia (ICI) y, con permiso de la ICI, llevó a cabo la extracción de la información de relevancia. La metodología de la IV ICI consistió en una amplia revisión de la literatura por parte de expertos internacionales y en la creación de un nivel de consenso. Asimismo, el nivel de evidencia se calificó de acuerdo con un sistema Oxford modificado y los grados de recomendación se atribuyeron en consonancia.
Resumen de evidenciasEstá disponible una versión completa de las directrices de la EAU sobre incontinencia urinaria en formato impreso (ampliada y en formato reducido), así como en formato de CD-ROM, pudiendo solicitarse a la oficina de la EAU o en línea en la dirección (http://www.uroweb.org/guidelines/online-guidelines/). La amplitud e invasividad de la evaluación de la IU depende de la gravedad y/o complejidad de los síntomas y signos clínicos, y es diferente para varones, mujeres, personas mayores de salud delicada, niños y pacientes con neuropatías. En el nivel de tratamiento inicial se aplican pruebas básicas de diagnóstico para descartar enfermedades o problemas subyacentes, tales como infecciones del tracto urinario. El tratamiento suele ser conservador (intervenciones en los hábitos de vida, fisioterapia, terapia física, farmacoterapia) y es de naturaleza empírica. En el nivel de tratamiento especializado (cuando haya fracasado la terapia inicial, ante un diagnóstico incierto o si los síntomas y señales son complejos o graves) suele ser necesaria una evaluación más elaborada, incluyendo técnica de imagen, endoscopia y urodinámica. Entre las opciones de tratamiento se incluyen intervenciones invasivas y la cirugía.
ConclusionesLas opciones de tratamiento de la IU están creciendo en número con rapidez, y estas guías de la EAU proporcionan una gradación de las evidencias (orientada por la medicina basada en la evidencia), así como una escala de recomendaciones para que la valoración sea la adecuada y las opciones de tratamiento estén en consonancia, aplicándose así una perspectiva clínica.