It has been described that thymoglobulin could increase the risk of infections and malignancies, in comparison to basiliximab. Leukopenia and thrombocytopenia are also more common within the first days after transplantation among thymoglobulin patients. Our objective was to analyze bleeding complications in this subset of patients.
Material and methodsBleeding complications were evaluated among 515 renal transplants carried out at our institution between 2012 and 2018. We compared patients treated with thymoglobulin (Group 1, N=91) with those treated with basiliximab (Group 2, N=424).
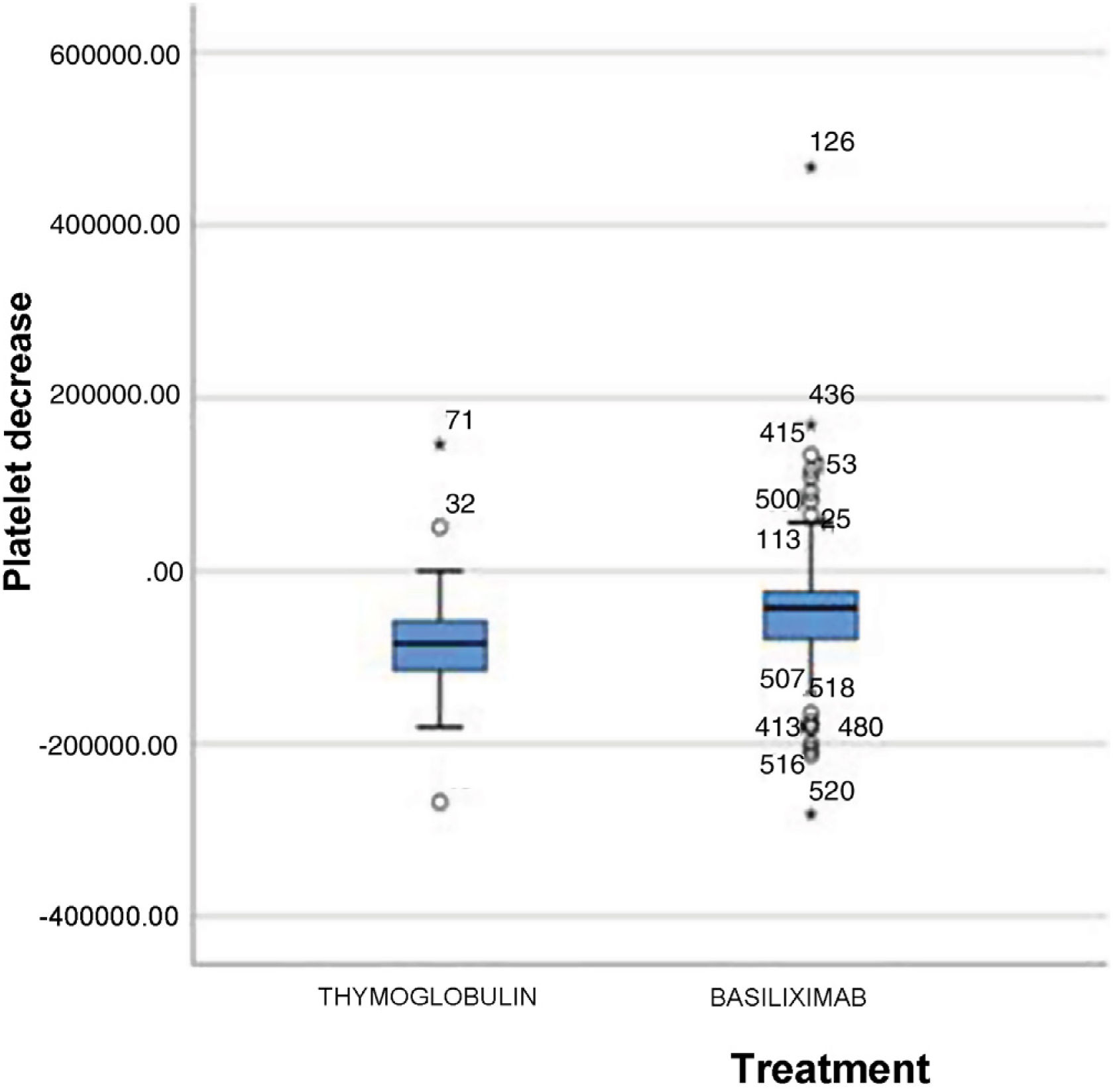
ResultsWe found differences in platelet decrease: 95,142.2 (55,339.6) in Group 1 and 52,364.3 (69,116.6) in Group 2 (P=0.001), number of patients with severe thrombocytopenia (<75,000/mm3) (20.8% vs. 3.7%, P=0.001), number of blood units transfused (3.25 (0.572) vs. 2.2 (0.191, P=0.028) and percentage of patients that required surgery due to bleeding (18.2% vs. 7.7%, P=0.046). In a multiple lineal regression multivariable analysis (dependent variable was number of blood units transfused), only age [OR 0.037, 95% CI (0.003–0.070)] and type of immunosuppression [OR 1.592, 95% CI (1.38–2.84)] showed statistical significance.
ConclusionsThe use of thymoglobulin in the perioperative transplantation period could increase bleeding complications. In our series, in the group of patients with thymoglobulin, severe thrombocytopenia was 6 times more frequent, and active bleeding that required surgery was also 2.5 times more frequent. One way to continue with the use of this immunosuppression agent, might be to adjust the dose instead of discontinuing it. The use of thymoglobulin should be a factor to consider in the postoperative period of these patients.
Se ha descrito que la timoglobulina podría aumentar el riesgo de infecciones y neoplasias, en comparación con basiliximab. La leucopenia y la trombocitopenia también son más frecuentes en los primeros días tras el trasplante en los pacientes tratados con timoglobulina.
Nuestro objetivo fue analizar las complicaciones hemorrágicas en este subconjunto de pacientes.
Material y métodosSe evaluaron las complicaciones hemorrágicas en 515 trasplantes renales realizados en nuestra institución entre 2012 y 2018. Se comparó a los pacientes tratados con timoglobulina (grupo 1, N=91) con los tratados con basiliximab (grupo 2, N=424).
ResultadosEncontramos diferencias en cuanto al descenso plaquetario: 95.142,2 (55.339,6) en el grupo 1 y 52.364,3 (69.116,6) en el grupo 2 (p=0,001), número de pacientes con trombocitopenia grave (<7.5000/mm3) (20,8% vs. 3,7%, p=0,001), número de concentrados de hematíes transfundidos (3,25 [0,572] vs. 2,2 [0,191], p=0,028) y porcentaje de pacientes que requirieron reintervención por sangrado (18,2% vs. 7,7%, p=0,046). En un análisis multivariable de regresión lineal múltiple (la variable dependiente fue el número de concentrado de hematíes transfundidos), solo la edad (OR 0,037, IC del 95%, 0,003–0,070) y el tipo de inmunosupresión (OR 1,592, IC del 95%, 1,38–2,84) tuvieron significación estadística.
ConclusionesEl uso de timoglobulina en el período perioperatorio del trasplante podría aumentar las complicaciones hemorrágicas. En nuestra serie, la trombocitopenia grave y el sangrado activo que requirió reintervención, fueron 6 y 2,5 veces más frecuente, respectivamente, enel grupo de pacientes con timoglobulina. En lugar de suspender el uso de este agente inmunosupresor, se podría ajustar la dosis para continuar con el tratamiento.