To evaluate the importance of the Prognotic Nutritional Index(PNI) value for patient selection of active surveillance(AS) in prostate cancer.
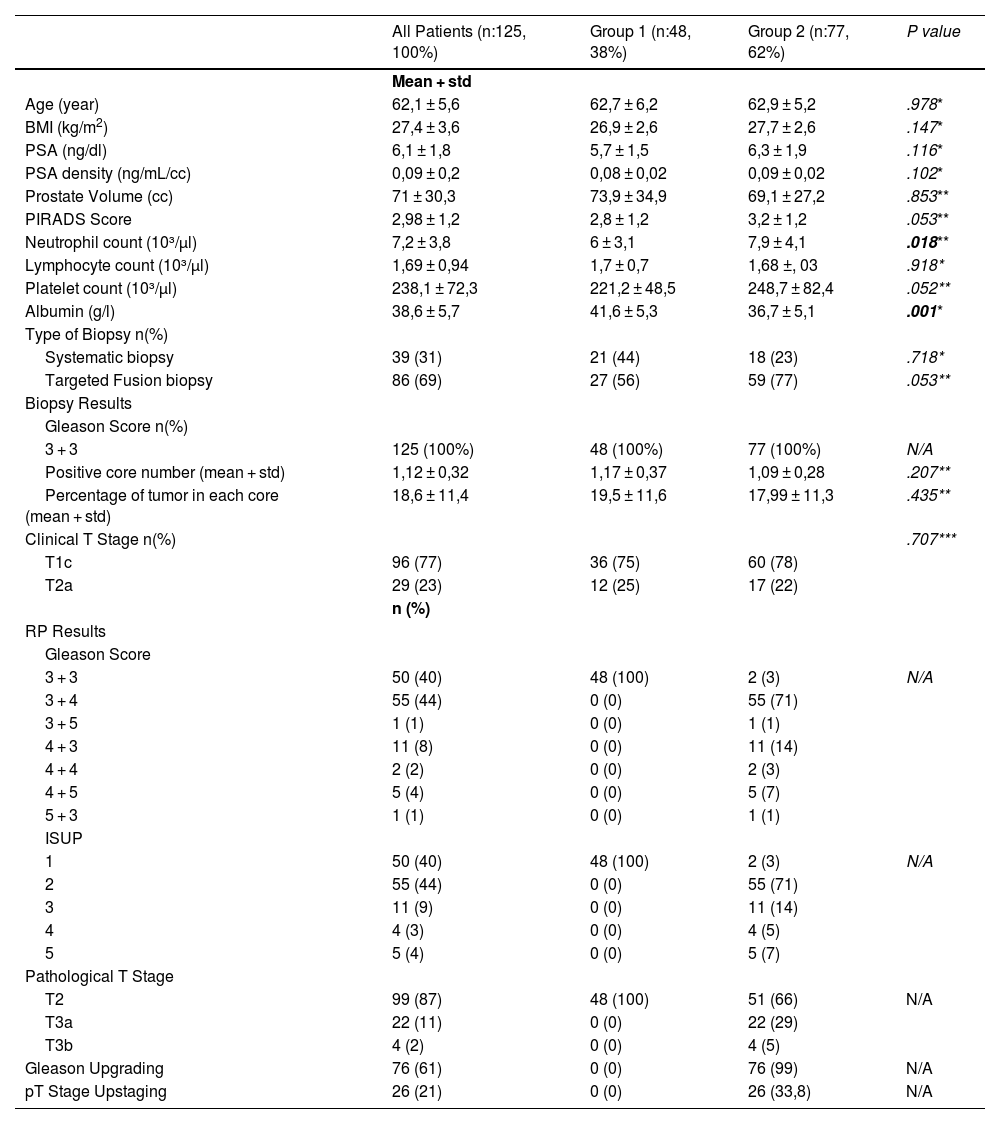
MethodsBetween September 2020 and June 2022, the data of 125-patients who underwent Robot-Assisted-Laparoscopic-Prostatectomy(RALP) were retrospectively analyzed. All patients were suitable for AS preoperatively. Using the pathological results of RALP, patients have been divided two groups. Patients who met the criteria for AS were defined as the first group, others were defined second. Demographic datas, PNI values and hematological parameters of the groups were compared.
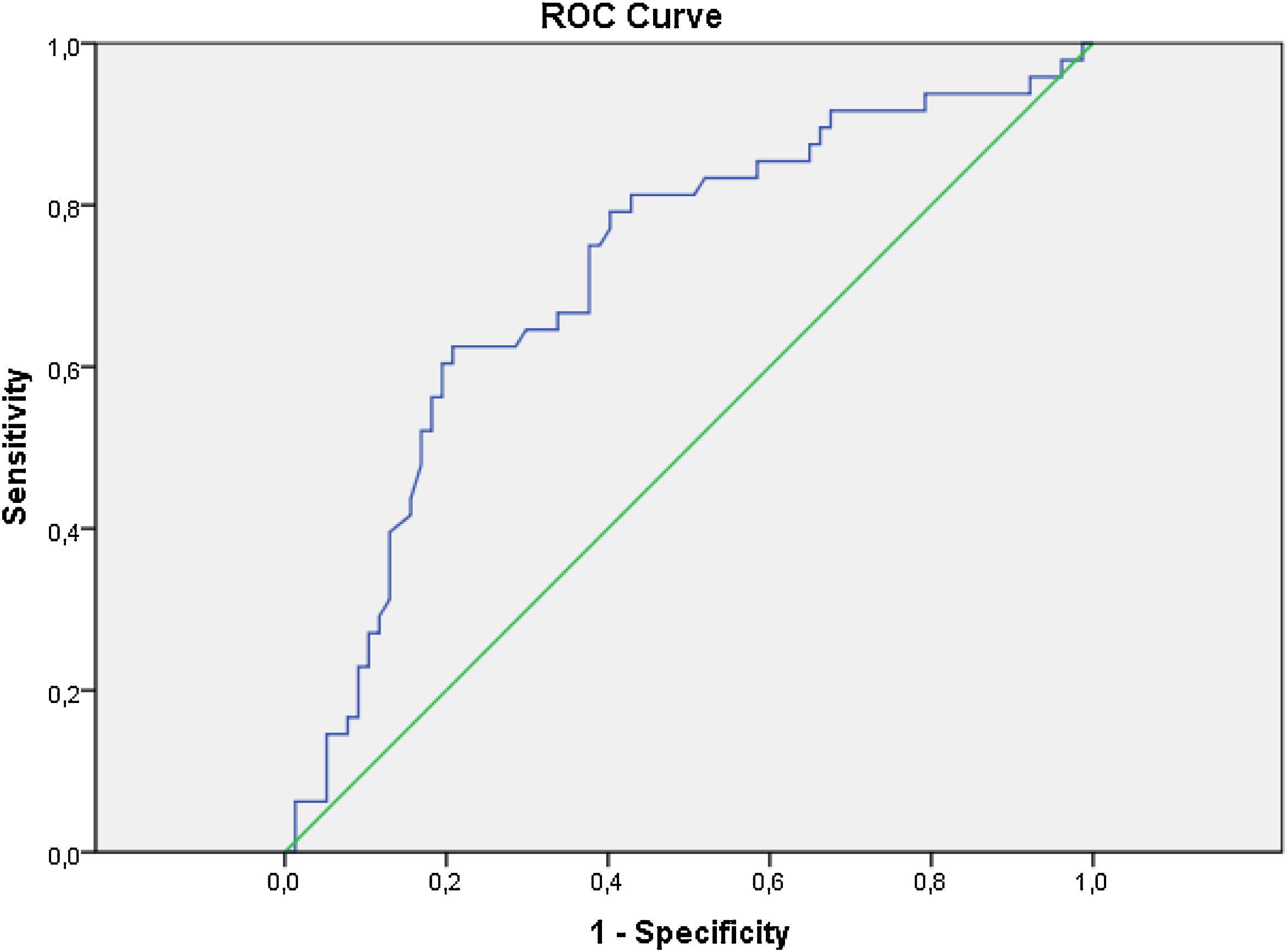
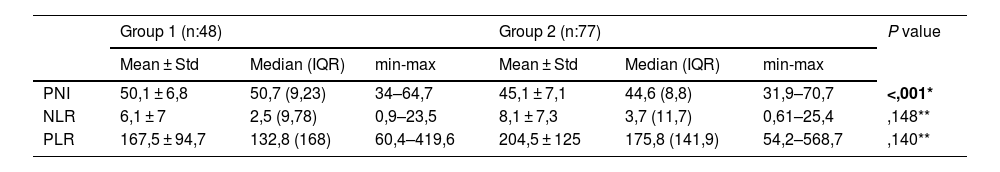
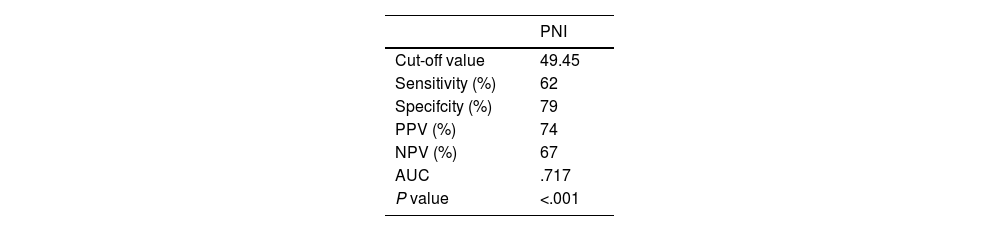
Results38% (n:48) patients were found suitable for the group1, and 62%(n:77) were found suitable for the group 2. Upgrading and upstaging were found at 76 patients (61%) and 26(21%), respectively. There is no significant difference between groups on age, BMI, PSA, PSA-density, prostate volume, and PIRADS. PNI value was found higher at first group. The value of 49.45 was calculated by ROC analysis as the ideal PNI cut-off value for predicting upgrading and upstaging of prostate cancer (P < ,001). According to the both univariate and multivariate regression analysis, PNI was found a predictor for exclusion from AS (P < ,001).
ConclusionUpgrading and upstaging are detected at a higher rate in patients with low PNI values. The use of PNI value in the selection of patients to AS will increase the success rate of ideal patient selection.
Determinar el valor del Índice Nutricional Pronóstico (INP) en la selección de pacientes para vigilancia activa (VA) en cáncer de próstata (CaP).
MétodosEntre septiembre de 2020 y junio de 2022, se analizaron retrospectivamente los datos de 125 pacientes que se sometieron a prostatectomía laparoscópica asistida por robot (PLAR). Todos los pacientes eran candidatos aptos para VA antes de la operación. Con base en los resultados patológicos obtenidos en la PLAR, los pacientes fueron asignados a dos grupos. Los pacientes que cumplían con los criterios para VA se asignaron al grupo 1 y los demás se asignaron al grupo 2. Se compararon datos demográficos, valores de INP y parámetros hematológicos de los grupos.
ResultadosEl 38% (n:48) de los pacientes cumplió los criterios del grupo 1 y el 62% (n:77) cumplió los criterios del grupo 2. Se encontró un incremento de grado y estadio (upgrade y upstage) en 76 (61%) y 26 (21%) pacientes, respectivamente. No hay diferencias significativas entre los grupos en cuanto a edad, IMC, PSA, densidad de PSA, volumen prostático y PI-RADS. El primer grupo obtuvo un valor de INP más alto. El valor de 49,45 se calculó mediante análisis ROC como el valor de corte ideal de INP para predecir la reclasificación a un grado y estadio más alto del cáncer de próstata (P < ,001). De acuerdo con el análisis de regresión tanto univariante como multivariante, se encontró que el INP era un predictor de exclusión de la VA (P < ,001).
ConclusiónLos incrementos de grado y estadio se detectan con mayor frecuencia en pacientes con valores bajos de INP. El uso del valor INP en la selección de pacientes para VA aumentará la tasa de éxito en la selección de los candidatos óptimos.