Despite the growing trend in the development of orthotopic neobladders, the procedure cannot be performed in many cases, thereby retaining the validity of other techniques. We propose a comparative analysis between patients with radical cystectomy for bladder neoplasm and reconstruction using the ileal conduit (IC) or ureterosigmoidostomy (USG).
Patients and methodObservational retrospective study on 255 patients with radical cystectomy between 1985 and 2009, selecting group assignments by the use of IC and USG. Analysis of the demographic and preoperative characteristics, perioperative complications, pathology and medium to long-term complications. Comparison of groups using T-Student, U-Mann–Whitney and chi square tests, with p<0.05 indicating statistical significance. Preparation of survival tables according to Kaplan–Meier, establishing comparisons using the log-rank test.
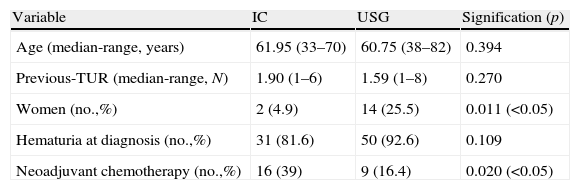
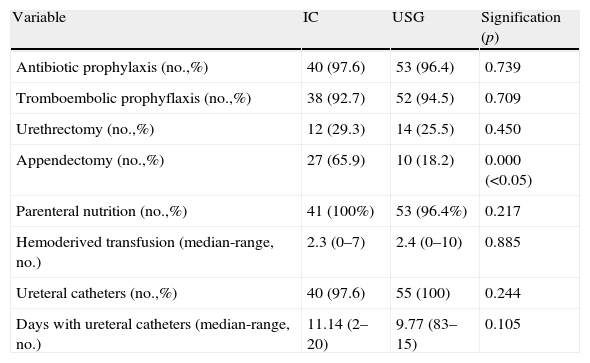
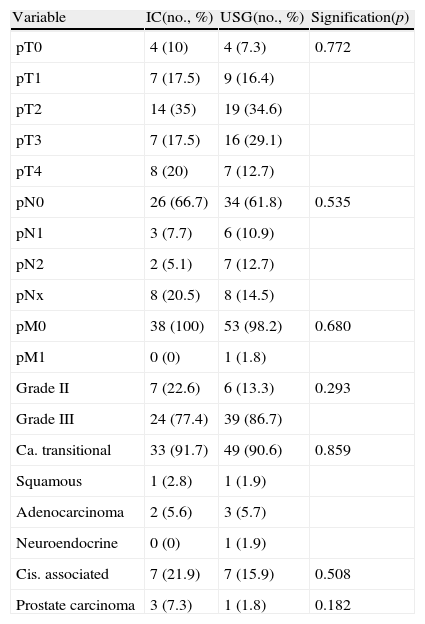
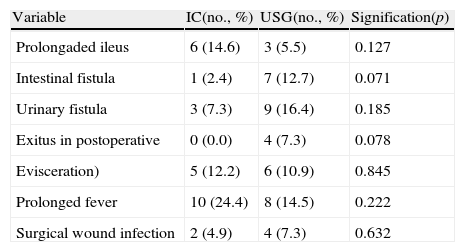
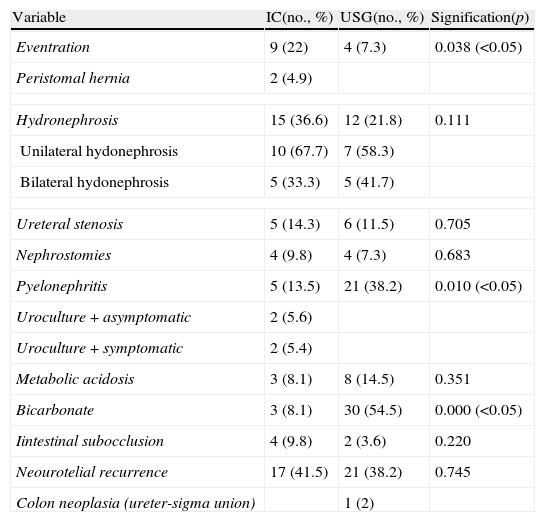
ResultsThere were 41 cases of IC and 55 cases of USG, with a mean patient age of approximately 61 years. USGs were performed on a greater number of females than ICs. There were no differences in the need for transfusion, with similar results as other series. There was a greater trend toward the appearance of intestinal fistulae and greater morbidity and mortality in the postoperative period in USG, although it was not significant. There was a greater long-term presence of eventrations in IC, and of pyelonephritis and the need for taking alkalinizing agents in USG. The appearance of peristomal hernias in IC was less than in previous series. With a mean follow-up greater than 50 months, the overall survival was 40% at 5 years, with no differences according to urinary diversion.
ConclusionsIC and USG are two applicable urinary diversions in the event that orthotopic neobladder surgery cannot be performed. They have a similar long-term complication and survival profile in our series, although with a higher morbidity in postoperative complications for USG.
Pese a la tendencia creciente a la elaboración de neovejigas ortotópicas, en muchos casos no es posible su realización, manteniendo su vigencia otras técnicas. Planteamos un análisis comparativo entre pacientes con cistectomía radical por neoplasia vesical y reconstrucción mediante conducto ileal (CI) o ureterosigmoidostomía (USG).
Pacientes y métodoEstudio retrospectivo observacional sobre 255 pacientes con cistectomía radical entre 1985 y 2009, seleccionando las derivaciones mediante CI o USG. Análisis de características demográficas y prequirúrgicas, complicaciones periquirúrgicas, anatomía patológica y complicaciones a medio y largo plazo. Comparación entre grupos mediante «t» de Student, U Mann-Whitney y chi cuadrado, considerando significación estadística si p<0,05. Elaboración de tablas de supervivencia según Kaplan-Meier, estableciendo comparaciones mediante el test log rank.
ResultadosCuarenta y un CI y 55 USG, con edad media aproximada de 61 años. USG realizada en un mayor número de mujeres que el CI. Sin diferencias en la necesidad de transfusión, con resultados similares a otras series. Mayor tendencia hacia la aparición de fístulas intestinales y mayor morbimortalidad en el postoperatorio en la USG, aunque no significativa. A largo plazo, mayor presencia de eventraciones en CI y pielonefritis, y necesidad de toma de alcalinizantes en USG. Aparición de hernias periestomales en CI menor que en series previas. Con seguimiento medio superior a 50 meses, supervivencia global del 40% a 5 años, sin diferencias según derivación urinaria.
ConclusionesCI y USG son 2 derivaciones urinarias aplicables en caso de no poder realizar neovejiga ortotópica, con un perfil de complicaciones y supervivencia a largo plazo similares en nuestra serie, aunque con una mayor morbilidad en las complicaciones postoperatorias de la USG.