To estimate the prevalence, age distribution, impact on quality of life and type of urinary incontinence (UI) in women over 30 years in Mallorca (Spain).
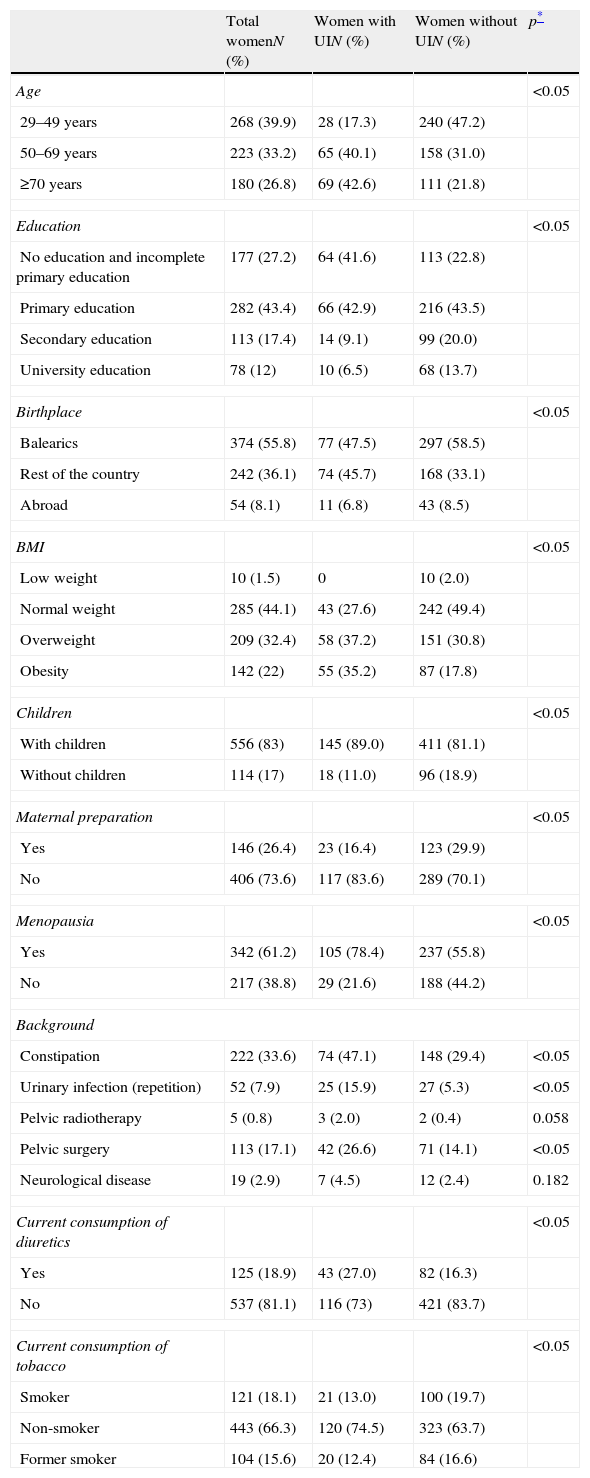
Material and methodsCross-sectional descriptive study on a randomized sample of 673 women in the health district affiliated to Son Llàtzer Hospital and the 14 Community Health Centres on its area of influence. Following an invitation to participate in the study, women were interviewed twice by their Community Nurse, through the phone and face-to-face. Every interview comprised the completion of the Spanish versions of the ICIQ-SF and EuroQol-5D questionnaires. Prevalence, type and severity (ICIQ-SF) of UI, previous health history and quality of life of women suffering from and free from UI were all estimated.
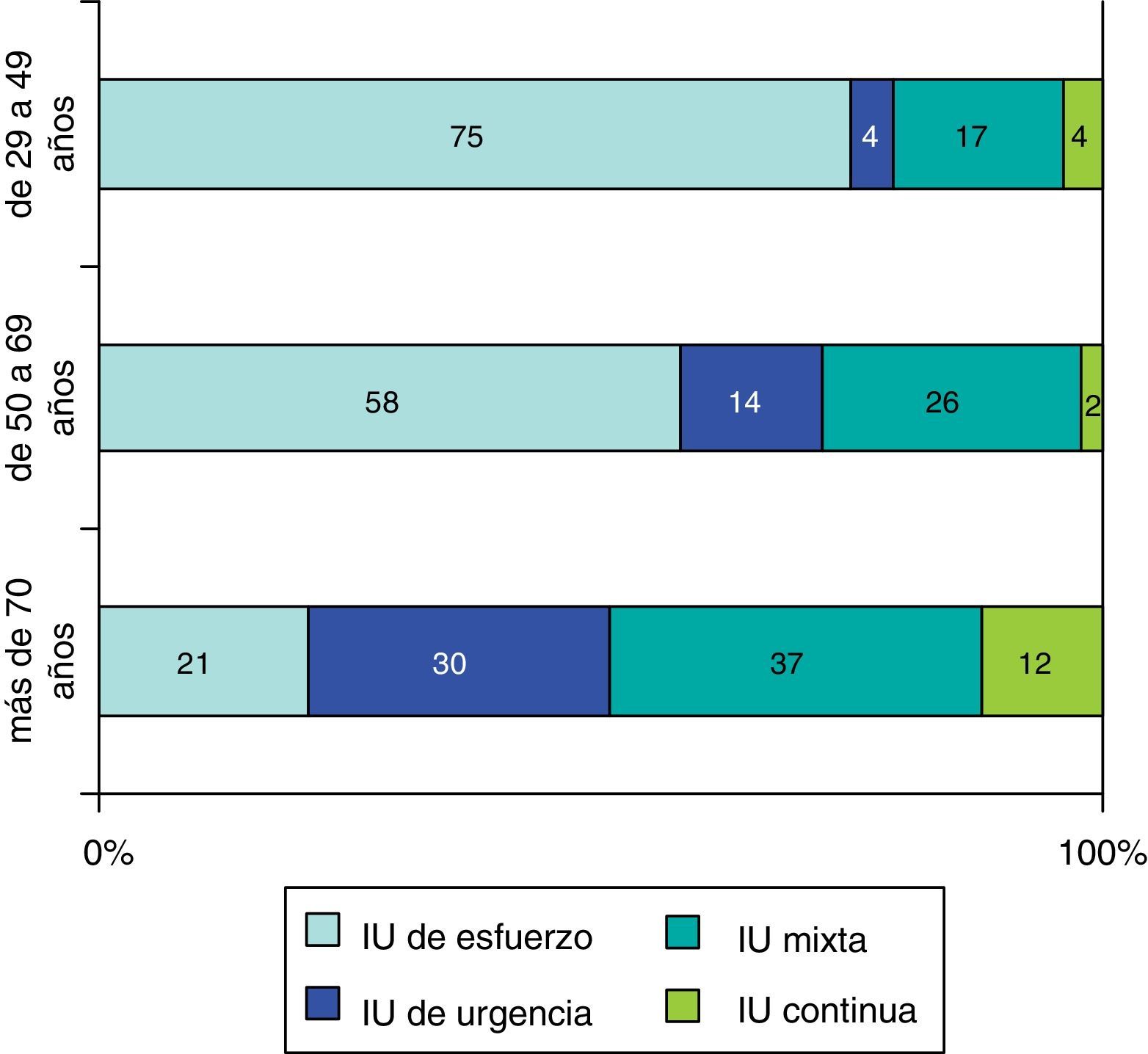
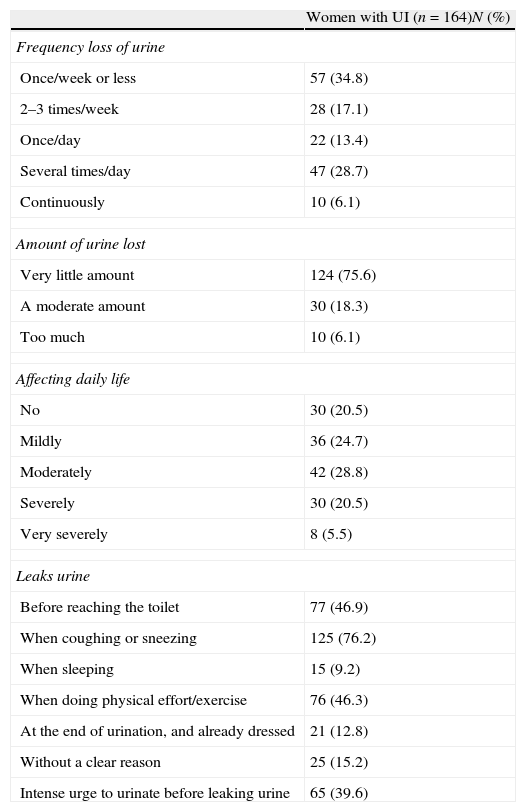
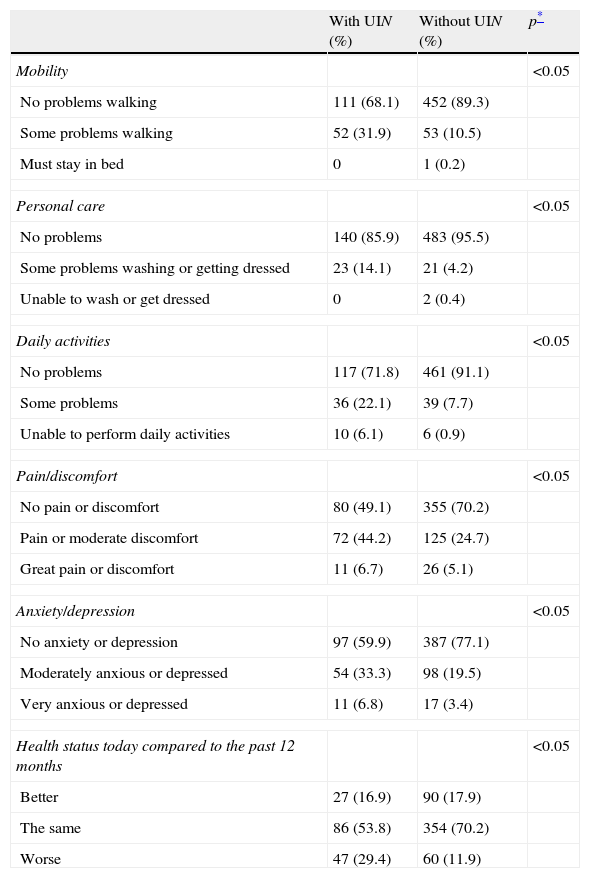
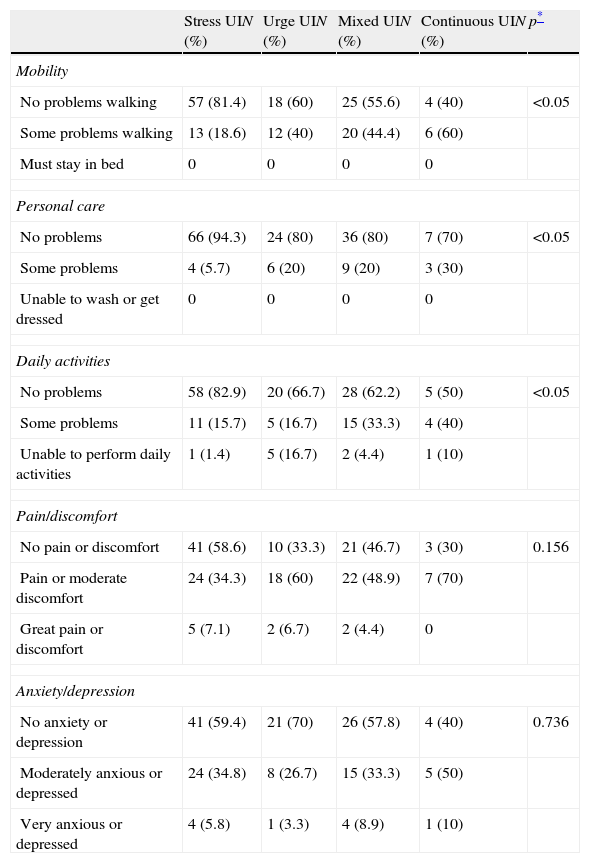
Results24% (CI 95%=20.9–27.5%) of women suffered from UI and prevalence increased significantly with age. Most frequently identified type of UI was stress incontinence (45%) followed by mixed incontinence (29%), urge incontinence (19.4%) and continuous incontinence (6.5%). For women suffering from UI, ICIQ-SF mean total score was 9.2, 25.2% of these suffering from moderate to severe UI. Women suffering from mixed or continuous UI scored highest at ICIQ-SF. Women suffering from UI showed worse quality of life in every dimension of EuroQol-5D. Quality of life was especially poor for women suffering from mixed or continuous UI.
ConclusionsOne in four women suffers from UI. UI prevalence increases with age. Half of identified women suffered from stress UI. A fourth of identified incontinences were described as moderate to severe. Women suffering from UI showed worse quality of life.
Estimar la prevalencia poblacional de incontinencia urinaria (IU) en mujeres mayores de 30 años de Mallorca, su distribución por edad y tipo de incontinencia y su repercusión en la calidad de vida.
Material y métodosEstudio descriptivo transversal, poblacional, en muestra aleatoria de 673 mujeres de la población adscrita al Hospital Son Llàtzer y a los 14 centros de salud de su sector de influencia. Tras invitación a participar en el estudio, fueron entrevistadas telefónicamente y en consulta por sus enfermeras de atención primaria, cumplimentando un cuestionario con las versiones españolas del ICIQ-SF y EuroQol-5D. Se estimó la prevalencia, los tipos de IU y su severidad (ICIQ-SF de 0 a 21 puntos), los antecedentes y la calidad de vida de mujeres con y sin incontinencia.
ResultadosUn 24% (IC 95%=20,9–27,5%) sufría incontinencia, y la prevalencia aumentaba de manera significativa con la edad. El tipo de IU más frecuente fue de esfuerzo (45%), seguido de mixta (29%), de urgencia (19,4%) y continua (6,5%). En las mujeres incontinentes la puntuación total media del ICIQ-SF fue de 9,2; un 25,2% correspondía a IU moderada-severa. La mayor puntuación del ICIQ-SF fue en la IU mixta y continua. Las mujeres incontinentes presentaron peor calidad de vida en todas las dimensiones del EuroQol-5D, observando una mayor afectación en aquellas mujeres con IU mixta y continua.
ConclusionesUna de cada 4 mujeres sufre IU y tienen peor calidad de vida. La prevalencia aumenta con la edad, la mitad es de esfuerzo y una cuarta parte moderada-grave.