To demonstrate the existence of relation between metabolic syndrome and erectile dysfunction (ED) and to analyze the hormone profile of these patients regarding a healthy population group.
Material and methodsA case–control study was designed with 65 men divided into 2 groups according to presence or non-presence of ED. Group A was made up of 37 men with ED and group B for 28 healthy men without ED. Ages ranged from 40 to 65 years. The presence of metabolic syndrome according to the ATP III definition, performance of physical exercise, smoking habit, body mass index (BMI) and complete hormone profile including testosterone (total, free and bioavailable) was studied.
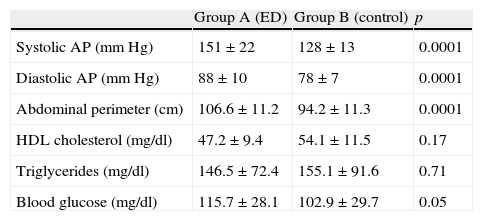
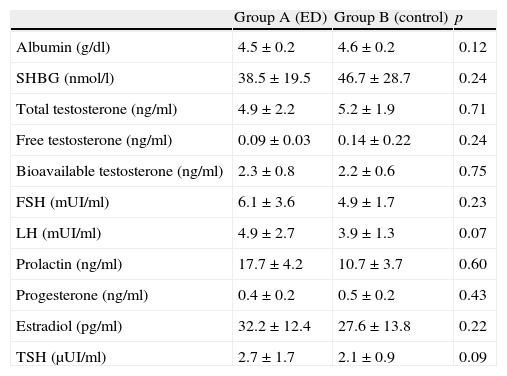
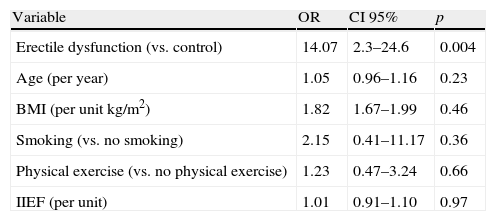
ResultsGreater presence of metabolic syndrome was detected among men of group A (72.9%) vs. those of group B (17.8%) (p=0.0001). Among the parameters that make up the metabolic syndrome, there are differences between both groups in systolic and diastolic blood pressure, fast blood sugar and abdominal circumference, all these differences being significant. After performing multivariate analysis between the metabolic syndrome and ED adjusted for age, BMI, International Index for Erectile Function (IIEF), physical exercise and smoking habit, we have observed an independent significant relation between the metabolic syndrome and ED. We have not found differences between both groups in any hormone parameter.
ConclusionA relationship is found between metabolic syndrome and ED. Thus, it seems recommendable to perform the metabolic profile and cardiovascular risk study in these patients.
Demostrar la existencia de relación entre síndrome metabólico y disfunción eréctil y analizar el perfil hormonal de estos pacientes con respecto a un grupo de población sana.
Material y métodosSe ha diseñado un estudio de casos y controles con 65 hombres divididos en dos grupos según la presencia o no de disfunción eréctil. El grupo A está formado por 37 hombres con disfunción eréctil y el grupo B por 28 hombres sanos sin disfunción eréctil. La edad estuvo comprendida entre 40 y 65 años. Se estudió la presencia de síndrome metabólico según la definición ATP III, la realización de ejercicio físico, tabaquismo, índice de masa corporal (IMC) y perfil hormonal completo incluyendo testosterona total, libre y biodisponible.
ResultadosSe ha detectado mayor presencia de síndrome metabólico entre los hombres del grupo A (72,9%) con respecto a los del grupo B (17,8%) (p=0,0001). Entre los parámetros que conforman el síndrome metabólico existen diferencias entre ambos grupos en los niveles de presión arterial sistólica y diastólica, la glucemia en ayunas y el perímetro abdominal, siendo todas ellas significativas. Tras realizar análisis multivariante entre síndrome metabólico y disfunción eréctil ajustado por edad, IMC, IIEF, ejercicio físico y tabaquismo hemos observado relación significativa independiente entre síndrome metabólico y disfunción eréctil. No hemos encontrado diferencias entre ambos grupos en ningún parámetro hormonal.
ConclusiónExiste relación entre síndrome metabólico y disfunción eréctil, por lo que parece recomendable llevar a cabo el estudio de perfil metabólico y riesgo cardiovascular en estos pacientes.