To investigate whether lymphovascular invasion (LVI) could be a factor in predicting recurrence and progression in patients with high and very high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) who received Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) treatment.
MethodsNinety-three patients with high and very high-risk NMIBC, diagnosed initially in our clinic, were treated with at least 1 year of BCG therapy, and they were followed up to assess recurrence and progression, comparing those with and without lymphovascular invasion (LVI) at the time of diagnosis.
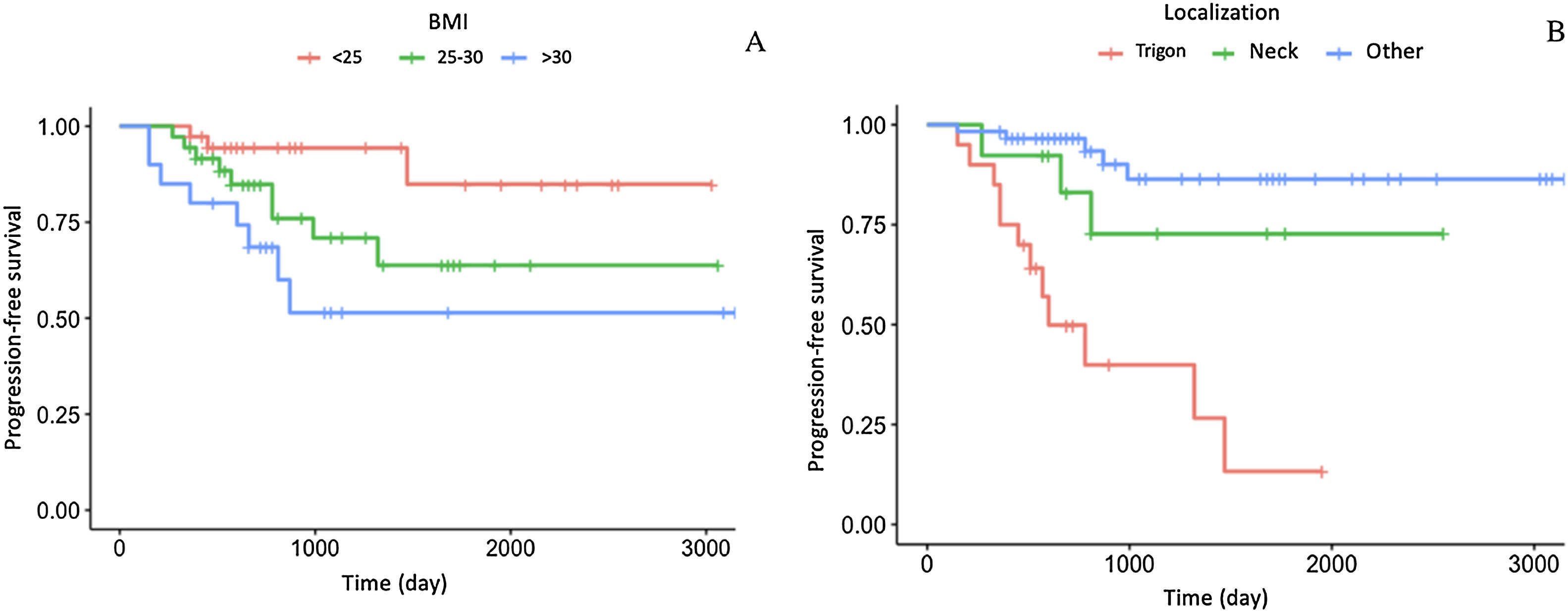
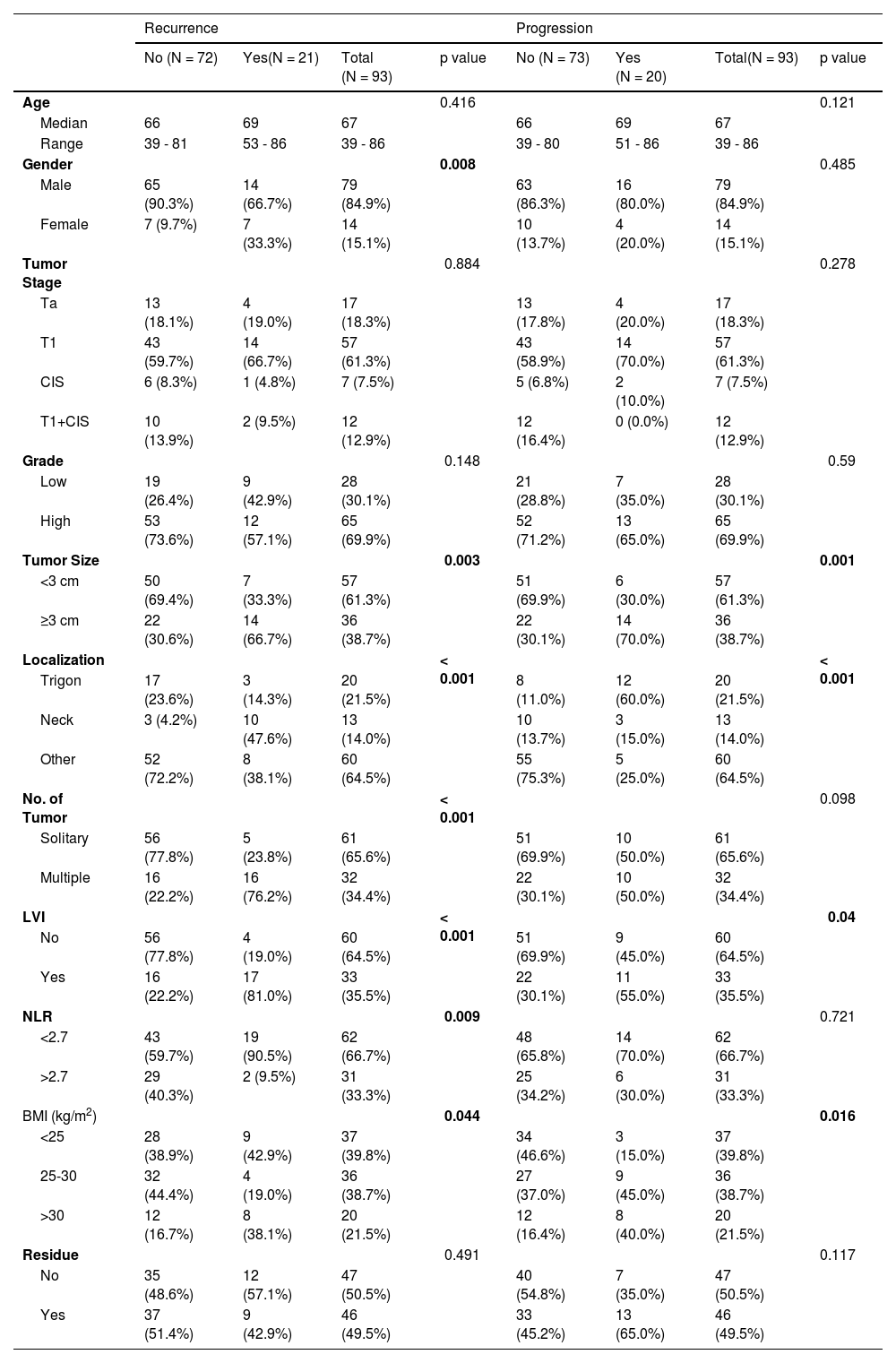
ResultsIn the entire cohort, LVI was present in 33 (35.5%) patients while absent in 60 (64.5%) patients. Among patients with LVI, 17 (51.5%) showed recurrence, and 11 (33.3%) showed progression. Statistically significant differences were observed in both recurrence and progression in patients with LVI compared to those without LVI (p < 0.001 and 0.04, respectively). Additionally, univariate and multivariate regression analysis revealed that the presence of LVI was an independent factor predicting recurrence (p = 0.001).
ConclusionIn our study, we demonstrated the importance of being cautious regarding recurrence and progression in patients with high and very high-risk NMIBC who also have LVI despite receiving standard treatment. We found that approximately one-third of these patients may experience recurrence within one year.
Evaluar si la invasión linfovascular (ILV) es un factor predictivo de recurrencia y progresión en pacientes con cáncer de vejiga no músculo invasor (CVNMI) de alto y muy alto riesgo tratados con bacilo de Calmette-Guérin (BCG).
MétodosSe incluyeron 93 pacientes con CVNMI de alto y muy alto riesgo diagnosticados en nuestra clínica, tratados con al menos 1 año de terapia con BCG. Se realizó un seguimiento para analizar la recurrencia y progresión de la enfermedad, comparando los pacientes con y ILV en el momento del diagnóstico.
ResultadosAl evaluar la ILV en toda la cohorte, se identificó que estaba presente en 33 (35,5%) pacientes, y ausente en 60 (64,5%) pacientes. Del grupo de pacientes con ILV, se observó recurrencia en 17 (51,5%) y progresión en 11 (33,3%). Se encontraron diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre los pacientes con ILV y aquellos sin ILV (p < 0,001 y 0,04, respectivamente) en la recurrencia y progresión. El análisis de regresión univariante y multivariante confirmó que la presencia de ILV es un factor predictivo independiente de recurrencia (p = 0,001).
ConclusionesNuestros hallazgos resaltan la importancia de vigilar de cerca a los pacientes con CVNMI de alto y muy alto riesgo que presentan ILV, incluso tras recibir tratamiento estándar con BCG. Aproximadamente un tercio de estos pacientes pueden experimentar recurrencia en el primer año de seguimiento.