To examine the treatment outcomes of the prostate cancer (PCa) patients treated by radical prostatectomy (RP) who could be good candidates for active surveillance (AS) and test the confidence and reliability of the AS criteria for predicting advanced stage disease (RP Gleason score ≥7 or pathological stage T3).
MethodsBetween 2005 and 2012 the records of the 401 patients who underwent RP with a diagnosis of PCa were examined. Of these patients, 173 were found to be candidates of AS. The inclusion criteria were as follows; clinical stage T2a or less, PSA<10ng/ml, 2 or fewer cores involved with cancer, no single core with 50% or greater maximum involvement of cancer, and no Gleason grade greater than 3 in the specimen.
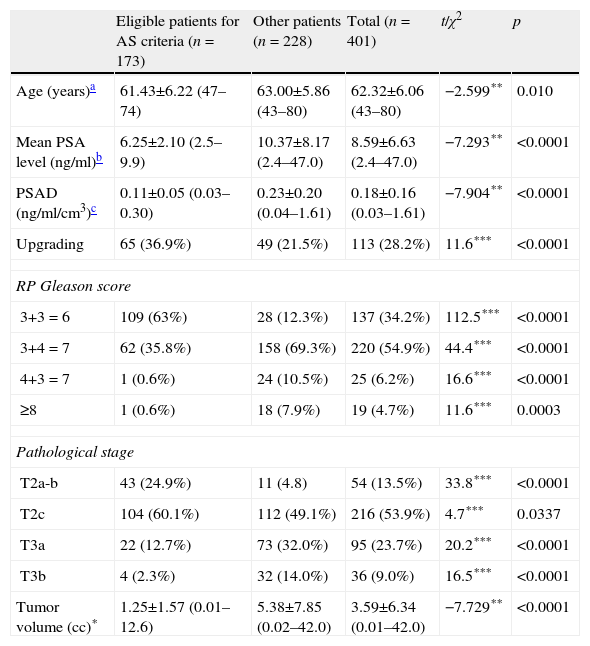
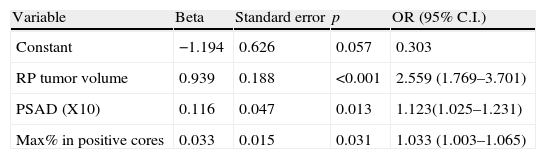
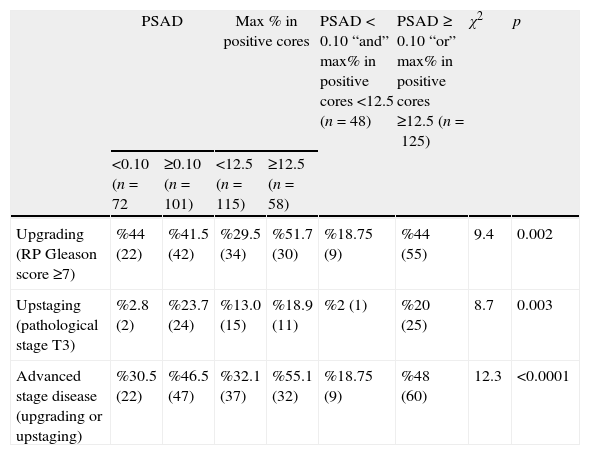
ResultsUnivariate analyses revealed that patients with advanced stage disease have higher prostate specific antigen density (PSAD), higher maximum percent (max%) in positive cores and higher RP tumor volumes. In multivariate analyses PSAD, max% in positive cores and RP tumor volumes were statistically significant determinants for advanced stage disease. ROC analyses revealed that the RP tumor volume is a good test on advanced stage disease.
ConclusionsDecreasing the cutoff values for PSAD and max% in positive cores should be considered for AS inclusion criteria. If we could calculate the tumor volume before RP, we can minimize the treatment failures (over or undertreatment) of PCa. Perhaps new biopsy protocols, tissue biomarkers, and molecular imaging technology may refine AS criteria.
Examinar los resultados del tratamiento en pacientes con cáncer de próstata (CP) tratados con prostatectomía radical (PR) que podrían ser buenos candidatos para vigilancia activa (VA) y evaluar la confianza y fiabilidad de los criterios de VA para predecir la enfermedad en estadios avanzados (puntuación de Gleason en PR≥7 o estadio patológico T3).
MétodosEntre 2005 y 2012 se examinaron los registros de 401 pacientes sometidos a PR con un diagnóstico de CP. De estos pacientes 173 resultaron ser candidatos para VA. Los criterios de inclusión fueron los siguientes: estadio clínico T2a o inferior, PSA<10ng/ml, 2 o menos núcleos afectados por cáncer, ningún núcleo con una afectación máxima por cáncer del 50% o más y ninguna puntuación de Gleason mayor de 3 en la muestra.
ResultadosLos análisis univariantes revelaron que los pacientes con un estadio más avanzado de la enfermedad tenían una densidad del antígeno prostático específico (PSAD) más elevada, un mayor porcentaje máximo (%máx) de núcleos positivos y un mayor volumen tumoral en PR. En los análisis multivariantes la PSAD, el %máx de núcleos positivos y el volumen tumoral en PR eran factores estadísticamente significativos de enfermedad en estadios avanzados. Los análisis ROC revelaron que el volumen tumoral en PR es un buen test de la enfermedad en estadio avanzado.
ConclusionesSe debería considerar reducir los valores umbral de PSAD y %máx en núcleos positivos como criterios de inclusión para VA. Si se pudiera calcular el volumen tumoral antes de la PR podríamos minimizar los fracasos del tratamiento (exceso o falta de tratamiento) de CP. Quizás los nuevos protocolos de biopsias, los biomarcadores de tejidos y la tecnología de imágenes moleculares puedan perfeccionar los criterios para VA.